The below Cement Rock Beneficiation Process flowsheet represents a simplified flow diagram of a cement plant in which beneficiation of raw materials is employed. Using a crude feed of limestone and/or clay, the flowsheet produces raw clay by multi-stage cycloning, and “Sub-A” Flotation upgrades the impure limestone. Turbine-type Agitators are used for storage and homogenous mixing of the raw mill feed and kiln feed slurries. SRL Rubber Lined Pumps provide long operating periods of minimum maintenance and parts cost. Below we discuss the subject of cement rock beneficiation using flotation. In the above flowsheet fatty acid reagents are employed to float the calcium carbonate as a froth product; however, in some instances cationic flotation of the silica as a froth product is economically advantageous. Various modifications to this basic flowsheet are already in use. The best method is dependent upon the feed characteristics and comprehensive test work coupled with the specifications demanded.
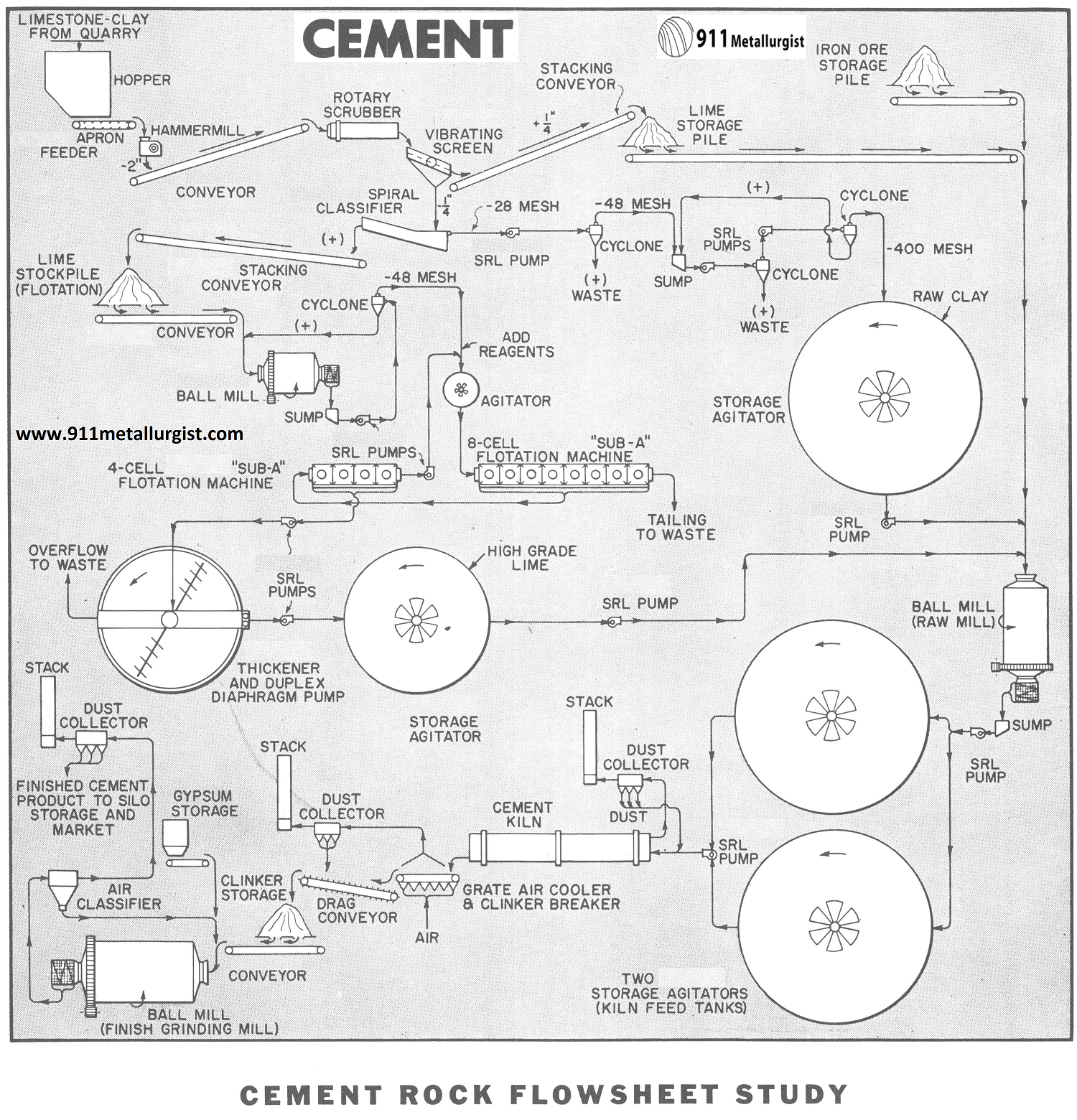
Cement Rock Beneficiation Process
Market Specifications
Flotation concentration, generally of high-lime carbonate cement rock, is used to remove calcite to produce a balance for various classes of portland cement.
A.S.T.M. standards recognize five types of portland cement.
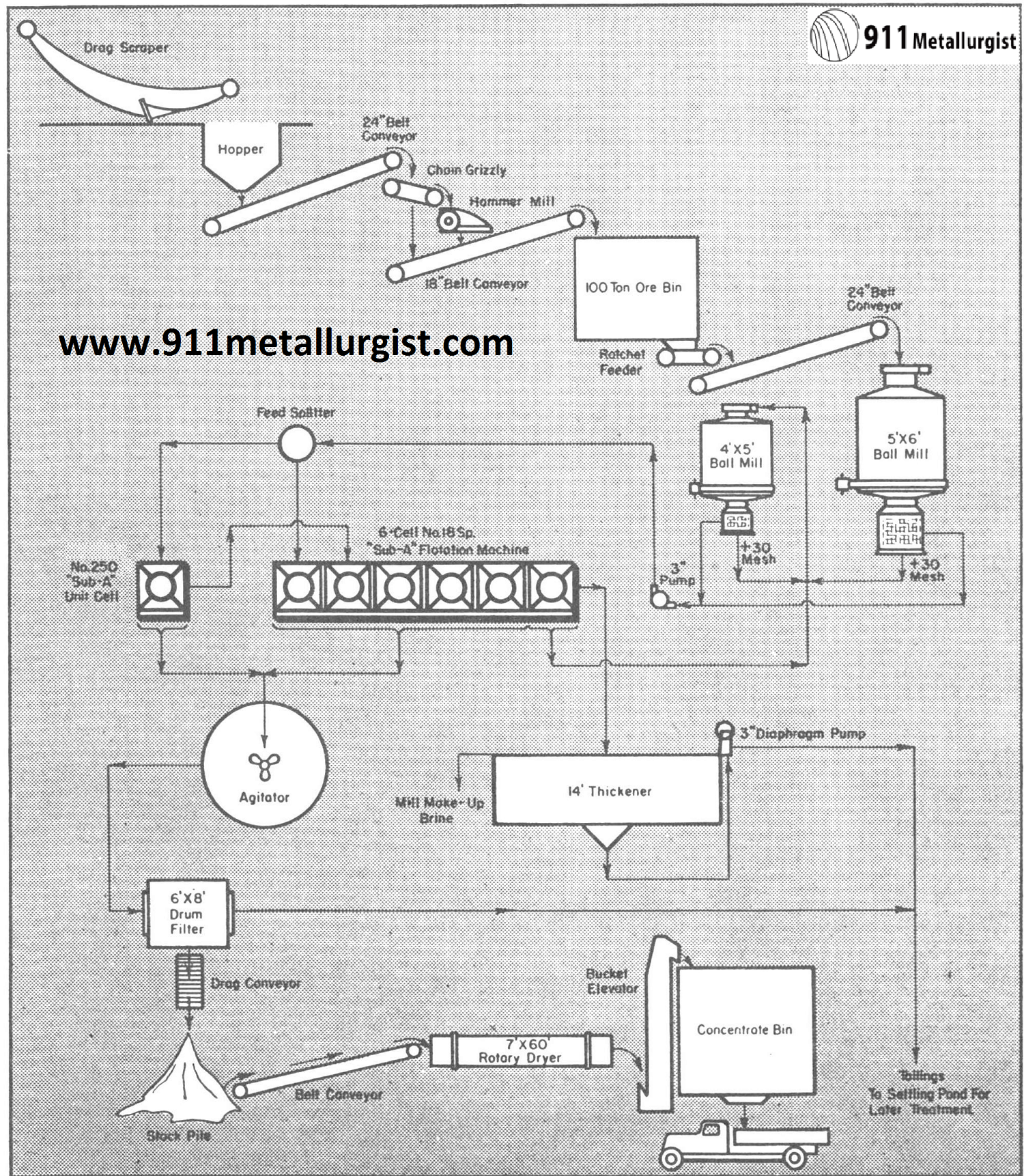
Flow-sheet of a potash flotation plant in Utah. Since installation of this pilot plant, capacity has been increased to over 1,000 tons per day. Potassium chloride is floated from sodium chloride.
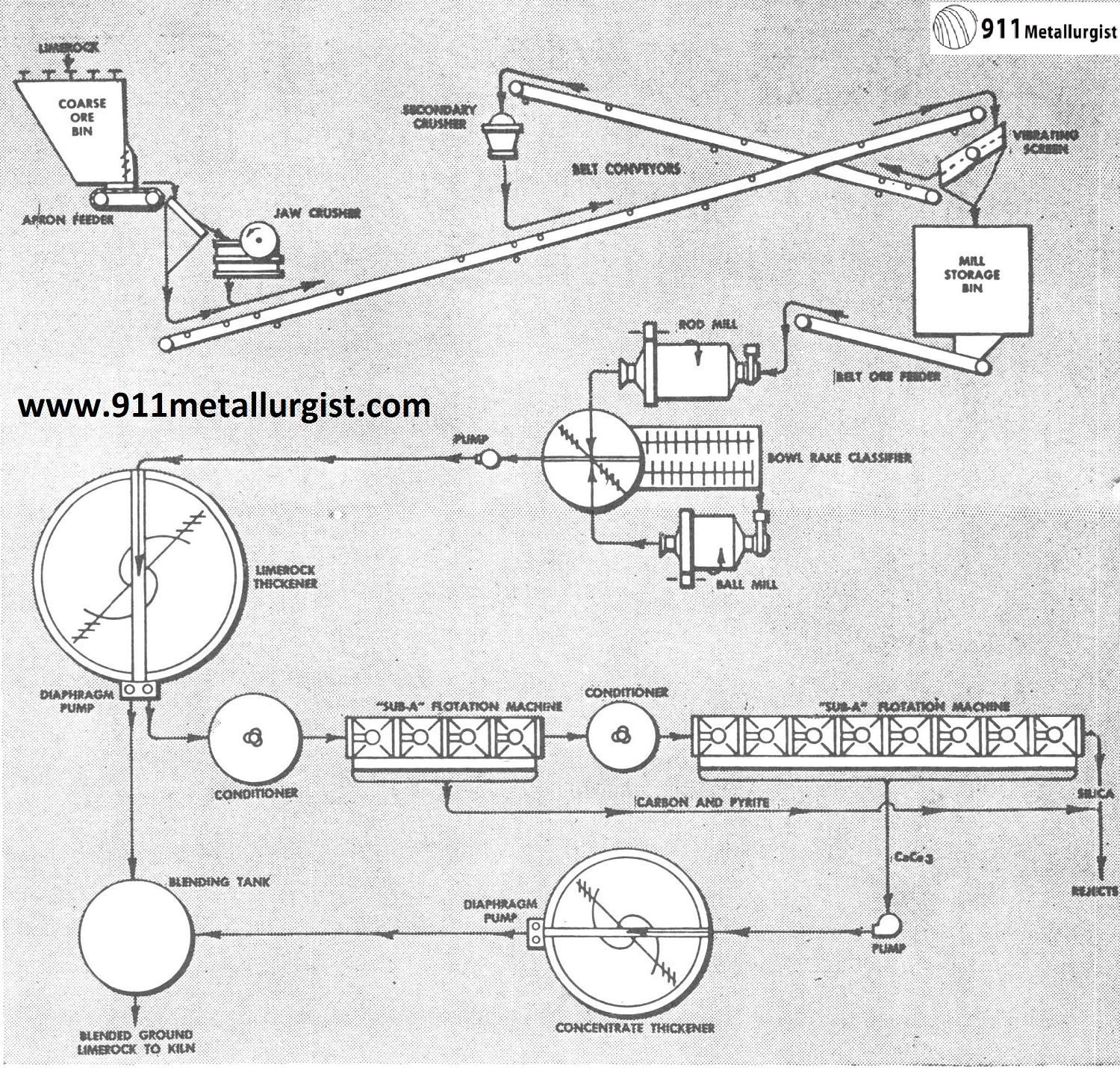
The application of flotation concentration as an aid in securing a proper balance of the various ingredients in cement manufacture is relatively new and has solved the problem in many localities where the proper amounts of the various materials needed are not available in the immediate vicinity. Impurities such as carbonaceous matter and pyrite are removed by flotation; then the calcite is floated from the silica and magnesium silicates. Blending of the calcite flotation concentrate with ground lime-rock then gives the proper chemical balance for the feed to the kiln.
Production Problems
The application of flotation concentration as an aid in securing a proper balance of the various ingredients in cement manufacture is relatively new and has solved the problem in many localities where the proper amounts of the various materials needed are not available in the immediate vicinity. Impurities such as carbonaceous matter and pyrite are removed by flotation; then the calcite is floated from the silica and magnesium silicates. Blending of the calcite flotation concentrate with ground lime-rock then gives the proper chemical balance for the feed to the kiln.
Cement lime-rock flow-sheet, showing part of mill tonnage processed through flotation to remove impurities. The high- grade calcium carbonate flotation froth is thickened and blended back with the ground lime-rock, thus giving uniform chemical composition of feed to cement kiln.
Reagent Combinations
Carbonaceous matter and pyrite are floated from the ground lime-rock with xanthate and a frother such as pine oil or one of the higher alcohols. Calcite is floated with a fatty acid such as oleic or with Tall oil. Sodium silicate is used to depress the silica and silicates.
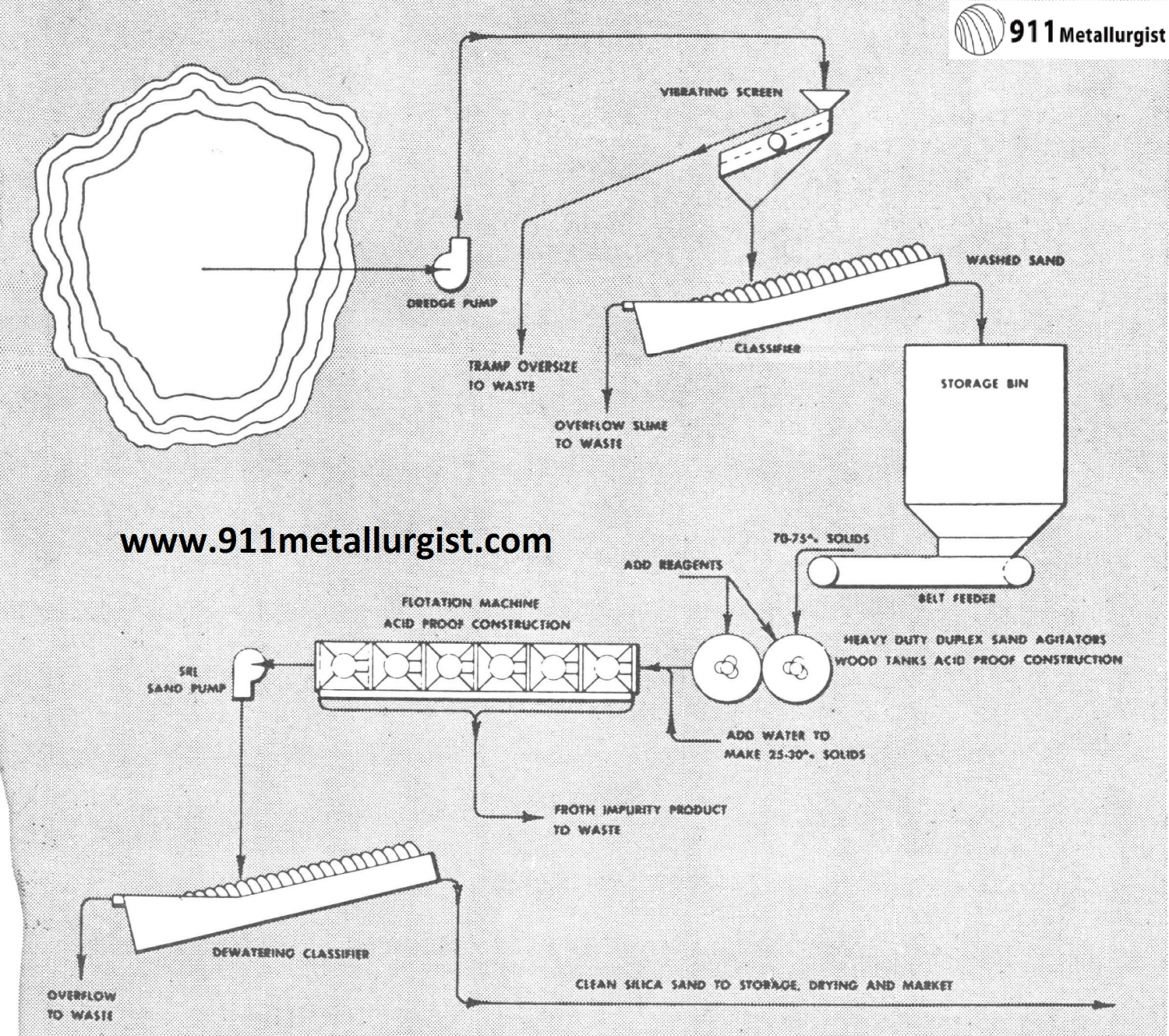
Flow-sheet of a typical silica sand flotation plant. Flotation removes iron oxide and other impurities. Glass-sand specifications usually call for less than 0.030 per cent Fe2O3. De-sliming and high-density agitation are essential for maximum removal of iron oxides by flotation.
Source:
This article is a reproduction of an excerpt of “In the Public Domain” documents held in 911Metallurgy Corp’s private library.