- To participate in the 911Metallurgist Forums, be sure to JOIN & LOGIN
- Use Add New Topic to ask a New Question/Discussion about Hydrometallurgy.
- OR Select a Topic that Interests you.
- Use Add Reply = to Reply/Participate in a Topic/Discussion (most frequent).
Using Add Reply allows you to Attach Images or PDF files and provide a more complete input. - Use Add Comment = to comment on someone else’s Reply in an already active Topic/Discussion.
Please join and login to participate and leave a comment.

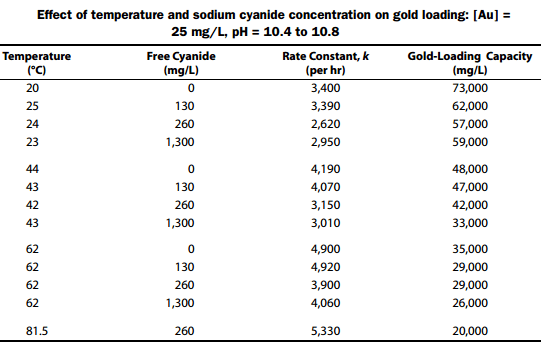
kindly asking what are the factors affecting activated carbon adsorptivity?
does cyanide strength affect carbon adsorption and if so, what concentration?