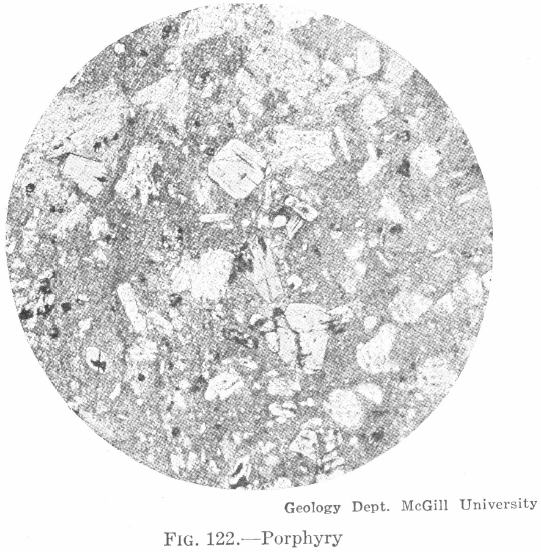
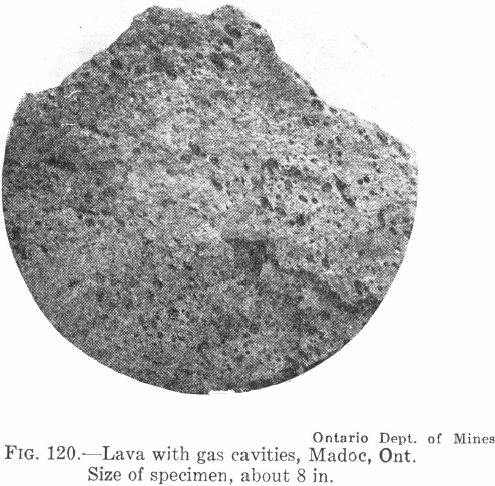
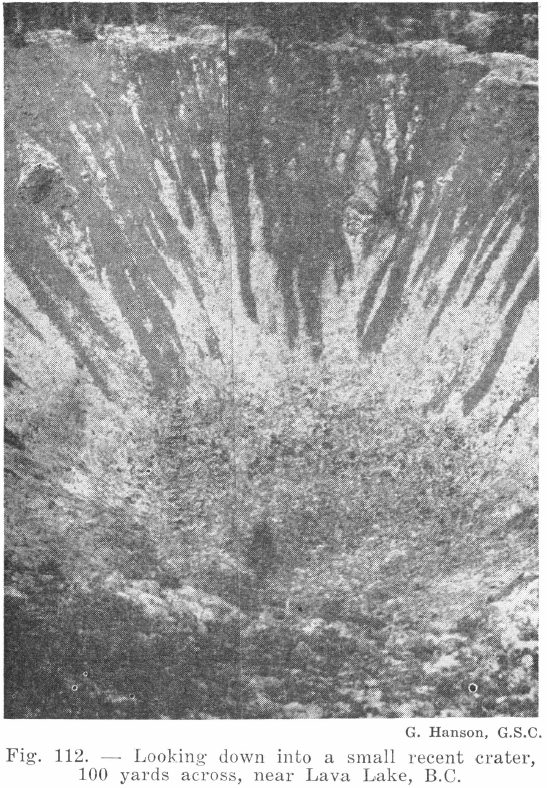
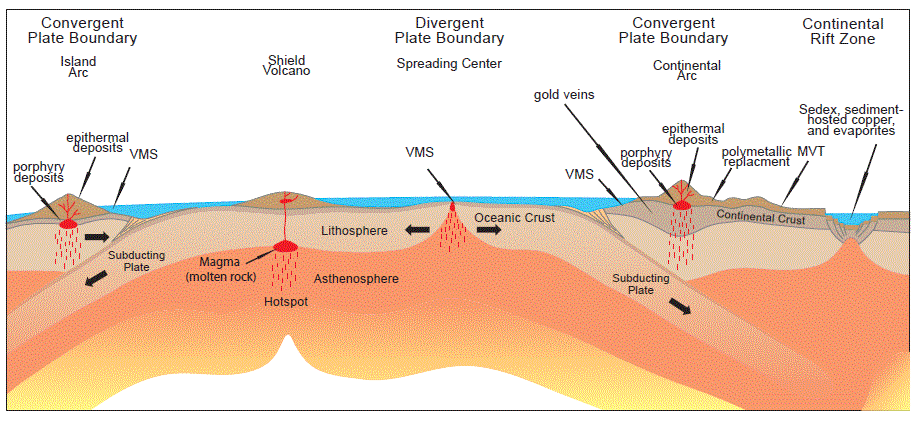
What is a Mineral Deposit by Definition
An ore is defined as a mineral or rock from which some valuable constituent, usually a metal, can be profitably extracted. Thus hematite and magnetite are ores of iron; galena is an ore of lead; zinc blende is an ore of zinc. With the ore-mineral is more or less material of no value, called gangue; … Read more