Gold Alloy Granulation
The gold to be parted must be approximately free from base metals, particularly from those which are not soluble in nitric acid, such as tin, arsenic, antimony. If these were present they would form insoluble oxides, which would remain with the gold, so that further refining operations would be necessary: they would, moreover, cause a […]
PARTING: Separate Gold and Silver by Melting
Parting is the separation of silver from gold and a process during which the base metals are separated from both, but, as the presence of a high percentage of these base metals is injurious to the successful conduct of the processes which are chiefly in use, a preliminary refining by one of the methods already […]
How to Make a Gold Bar by Casting Gold Bullion Ingot

The operation of refining by one of the methods described above is necessary before gold can be exactly valued. When base metals other than copper are present, segregation occurs and the solidified metal is not uniform in composition. The result is that the exact value of the bullion cannot be determined, and the buyer must […]
Gold Refining Methods
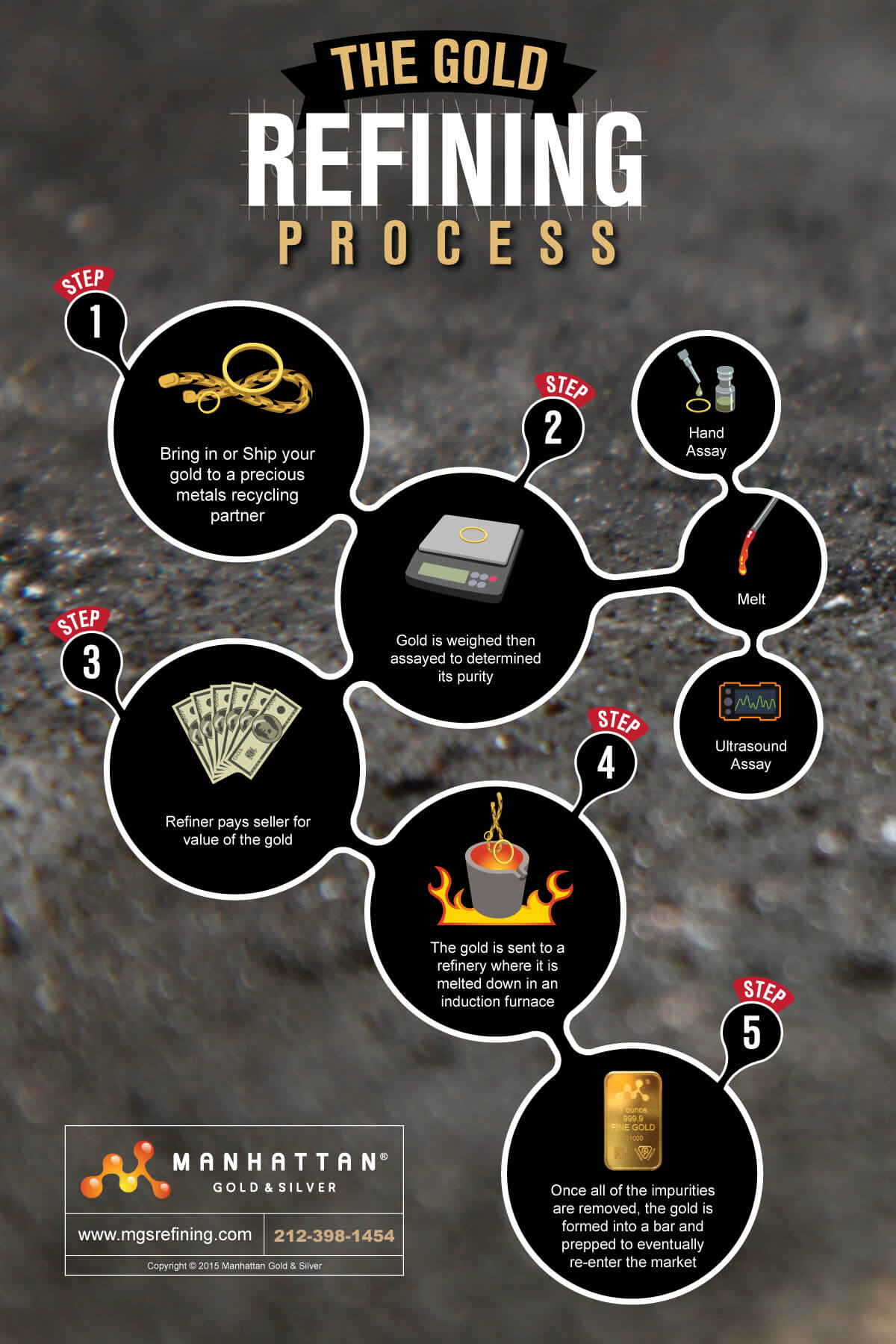
The processes used for Gold Refining are as follows: Volatilisation. Oxidation (a) by air blowing or roasting. (b) by “ bessemerising” (c) by nitre. (d) by metallic oxides. (e) by cupellation. Chlorination. Sulphurisation. The use of iron or carbon. The method to be used depends partly on the composition of the bullion, and partly on […]
Gold Melting Furnaces: Key Features and Applications
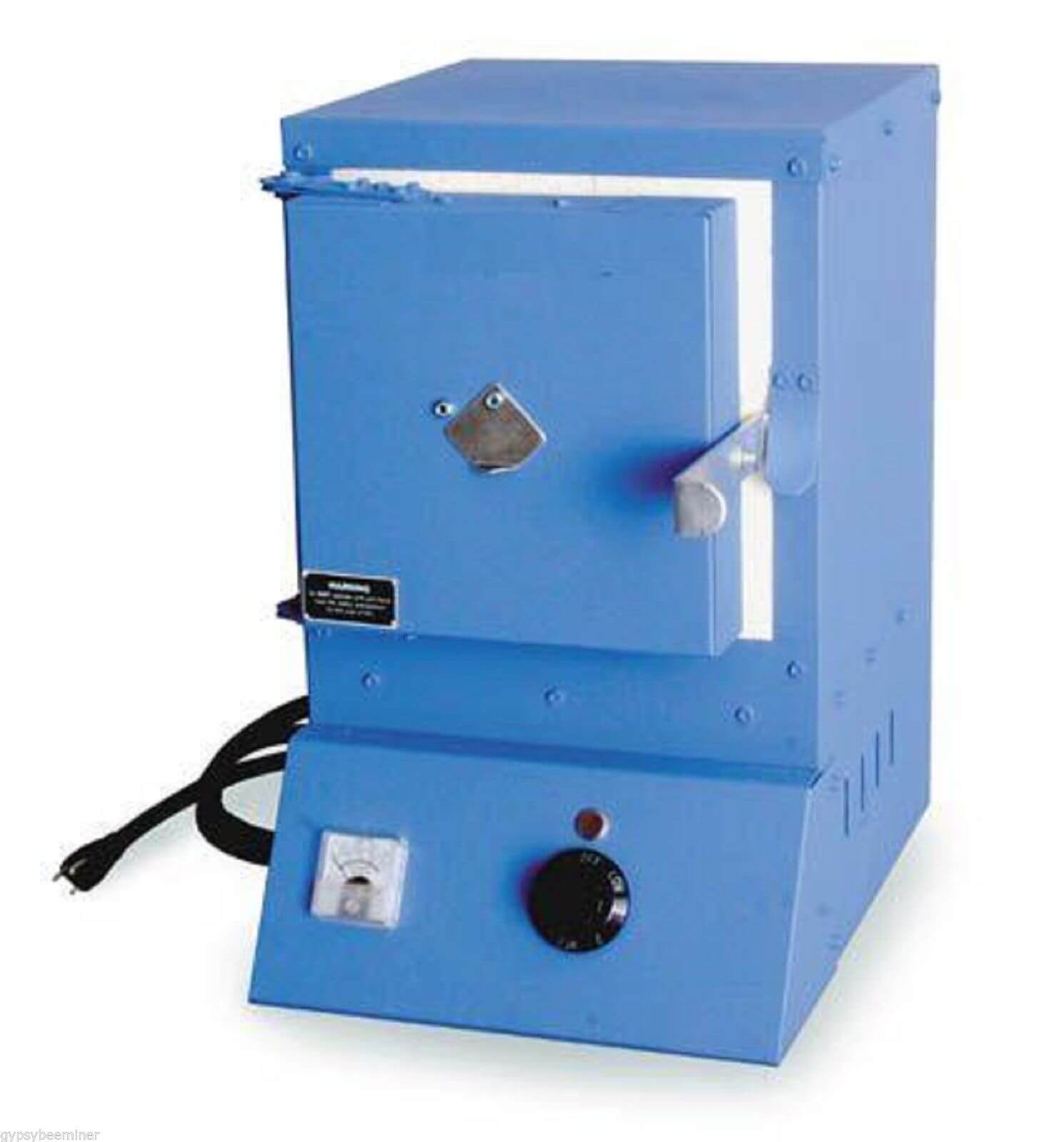

The furnace used for melting gold bullion is of simple construction. It may be round or square, with walls consisting of an outer layer of ordinary brick and an inner layer, at least 4 inches thick, of the best firebrick. There is often a complete outer casing of iron, which is useful in keeping the […]
Sample Salting in Geology
There are two kinds of sample salting: intentional and innocent. Intentional salting can be defined as the surreptitious addition of valuable material to a sample with intent to deceive. Innocent salting, which can have the same end effect, can be accidental or the result of carelessness or improper working procedures. Although intentional salting is seldom […]
How pH Affects Cyanide Decomposition & Use Alkalinity to Preserve Cyanide
Since acidity of the ore causes decomposition of the cyanide, an obvious method of reducing the loss is to add alkali in some form. Before doing this, the free sulphuric acid and soluble salts may be removed by leaching with water, and then a solution of caustic soda or lime is run on to the […]
Potassium Cyanide Chemistry on Minerals & Metals

The ordinary gangue of most ores (silica and silicates of the alkalies and alkaline earths) exercises no direct influence on the cyanide solution. The carbonates of the alkaline earths are also probably without influence. The decomposing effects of sulphides of the heavy metals vary with the physical state of the sulphides. Metallurgists found that dilute cyanide […]
Potassium Cyanide Leaching with Gold and Mercury
These methods are described here for convenience, as being more intelligible after the chemistry of the process has been discussed. The necessity of the presence of oxygen has already been dwelt on above. It has, however, been frequently pointed out that in the interior of a mass of ore undergoing treatment the conditions are not […]
Oxidised Pyrite Leaching by Potassium Cyanide

When the pyrites occur in tailings which have been subjected to the action of the weather for some time before treatment, compounds are formed which are more prejudicial to the solution than the sulphides. Sulphide of iron, FeS2, is oxidised by air and water, ferrous sulphate and free sulphuric acid being formed, thus: FeS2 + […]
