Pulp and Slurry Thickening Test and Calculations

The slime pulp or slurry on leaving the sand classifier with its proper admixture of lime is first led to some form of thickening device if, as is usually the case, the ratio of liquid to solid is too large for economic handling in the cyanide treatment. The form of thickener almost universally used in […]
Leaching Fine Gold
Many definitions of the word “slime” have been attempted to Leaching Fine Gold but the one that best expresses its meaning from a practical point of view is that given by Park that it is that part of the pulverized ore that is not percolable on a commercial scale without the use of pressure. The […]
Method to Measure Lime Content in Cyanide Leach Solution
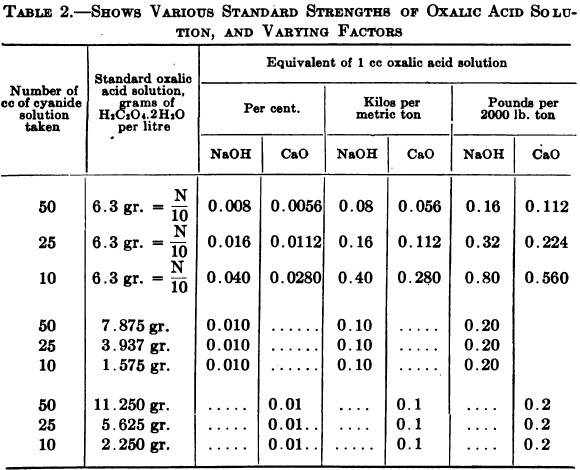
This term is usually defined as “the alkaline hydrates and half the monocarbonates” whose action is to protect the cyanide from decomposition, by acids developed in the ore and by atmospheric carbon dioxide. Either oxalic acid or a mineral acid may be used as a standard solution. Objections have been raised to the use of […]
Assay Method of Zinc in Cyanide Leach Solution

To ascertain the presence of zinc add a few drops of sodium sulphide solution to 50 cc of the solution to be tested (which should be strongly alkaline), and heat to boiling point. If zinc is present it will come down as a flocculent white precipitate. It sometimes happens that a cyanide solution will contain […]
Measure Copper Content of Cyanide Leach Solution
To assay for copper contained in a cyanide solution, the first essential step of the method is to completely decompose all the cyanogen compounds. For this purpose Clennell recommends evaporating 100 cc of the solution to be tested with 5 cc of nitric and 10 cc of sulphuric acid until dense white fumes are freely […]
Thiocyanide Thiocyanate Sulphocyanate Assay Determination

The method usually given for detection of Sulphocyanate (Thiocyanide, Thiocyanate) is to acidify and add a ferric salt, a blood-red color indicating the presence of KCNS. Silver and copper, however, interfere, and if present in sufficient amount may entirely prevent the formation of the characteristic color, so they must be removed before any determination can […]
Cyanate Determination Method
Clennell gives among other cyanate assay methods the following based on the fact that when KCNO is treated with an acid it does not decompose into HCN but reacts in the sense of the equation, KCNO + 2HCl + H2O = KCl + NH4Cl + CO2 By determining the amount of ammonium compound formed a measure […]
Determination of Ammonia and Ammonium Salts
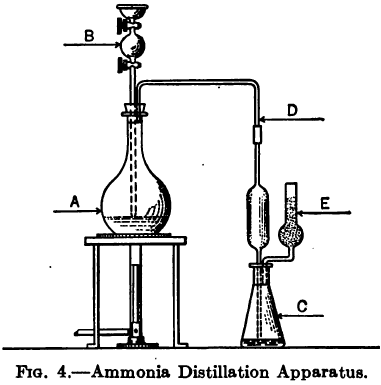
The following method is given by Clennell to determine the Ammonia and Ammonium Salts content by assaying cyanide leach solutions. “Add excess of AgNO3, i.e., sufficient to precipitate all cyanogen compounds, then a little NaCl to remove excess of AgNO3, filter, wash, evaporate filtrate on a water bath to a moderate bulk, distil with caustic soda or sodium […]
Volhard’s Silver Determination & Argentometry
Volhard’s method is a type of Argentometric titration of silver content determination. The Volhard Method requires: a decinormal ammonium or potassium sulphocyanate solution, a decinormal silver nitrate solution, ferric indicator. A decinormal silver nitrate solution contains 16.988 grams of AgNO3 per litre, or 10.788 grams of Ag. It may be made up by direct weighing of the pure […]
Determination of Acetates
Julian and Smart state that cyanide solutions undergoing decomposition form not only formates but acetates. Clennell states that he has never found acetates present in a working cyanide solution unless lead acetate was being used, but on the assumption that acetates may perhaps be formed in certain circumstances he suggests the following equation. 4KCN + 5H2O […]
