Flotation Uranium bearing Copper ore
Uraninite and masuyite are the major uranium minerals, essentially fine grained, in the ores studied. Over 40% of the uranium is distributed in the -8µm fractions compared with copper, which is concentrated mainly in the +8-20µm range. Uranium is concentrated mainly in the copper ore zones, with only marginal levels in the gold-only ores. Poor liberation […]
Froth Factor for Pump Sizing
The ‘froth factor’ is a measure of the air contained in the froth. It is quantified by filling a measuring cylinder or bucket, of known volume, with froth and measuring the froth column. After air dissipation the remaining water and solids volume is measured. The ratio of the original volume of froth to the remaining […]
MIBC Frother Pump
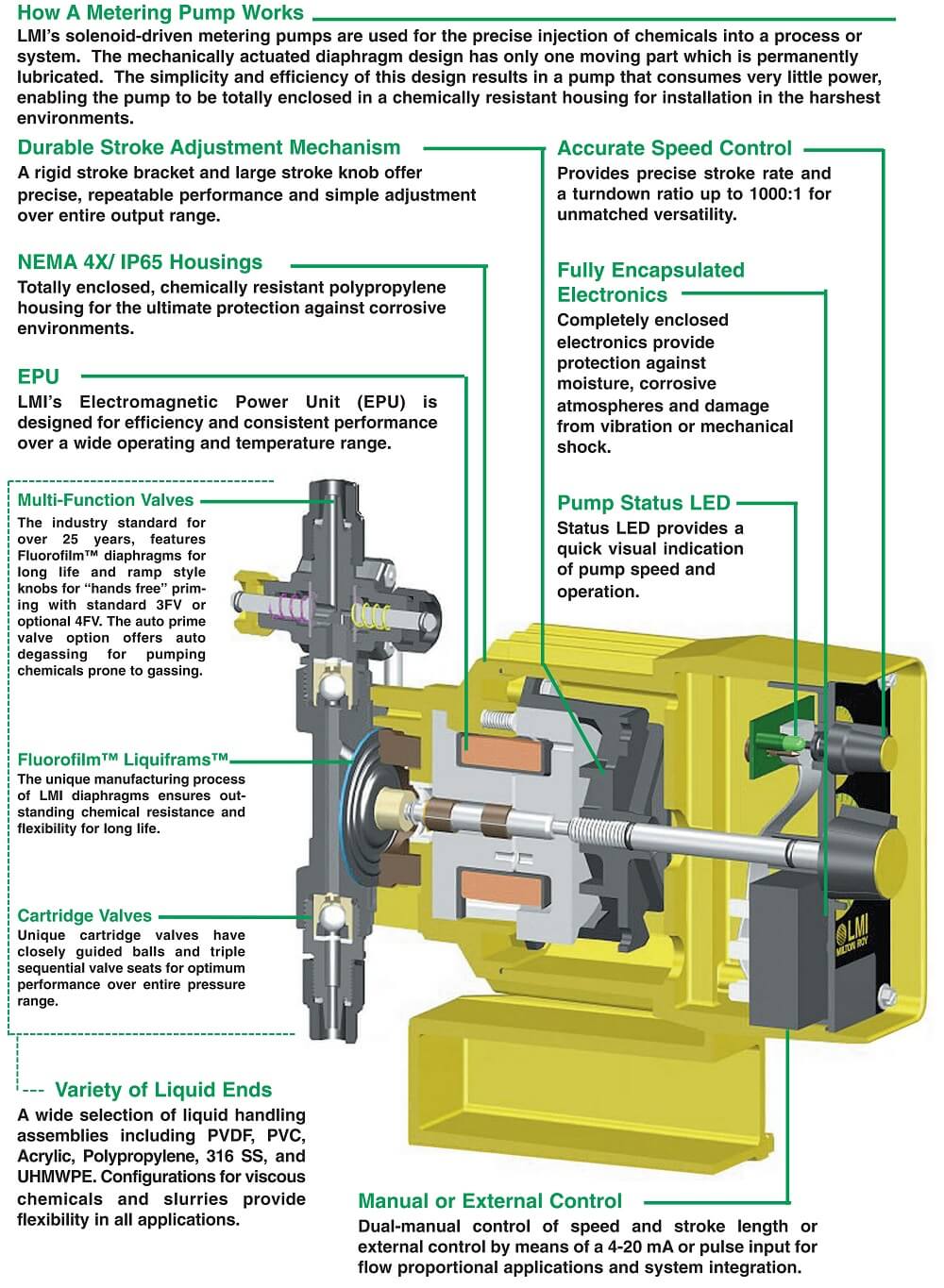
I once had to conduct an MIBC frother test to confirm if it could give me better flotation results than the glycol frother my client was using. The technical/metallurgical problem we had in the plant was best described in the video below as well as a poor concentrate grade. My “challenge” was that since MIBC […]
Aerating or Oxygenating Cyanide Solutions

A process for aerating or oxygenating cyanide solutions was announced by T. K. Prentice in the Jour. C.M. and M.S.S.A., February, 1934 (see Fig. 56). It immediately attracted attention, and the article was reprinted in part by United States and Australian technical journals. The process received practical plant trials at the Nourse mine on the […]
Effect of Impurities on Cyanide Leach Solution
That cyanide solutions in works practice do not remain pure in a chemical sense is to be expected, having in view their contact during treatment with the many contaminants found in gold or silver ore amenable to cyanidation. Impurities cause a chemical cyanide loss and at times detrimentally affect the extraction of the valuable metals […]
Effect of Altitude & Pressure on Gold Leaching Kinetics

Altitude-pressure and Standard Saturation Curves: Chart A (Fig. 55) is used to determine barometric pressure at various altitudes; Chart B is used to determine standard saturation values for various temperatures and pressures. In Chart A, altitudes, in feet, are plotted on the horizontal axis and pressures, in millimeters, on the vertical axis. To find the pressure […]
Cyanide Solution Control Parameters
In both cyanidation and flotation practice it is necessary to keep a close check on the working solutions, since the concentration of various soluble salts derived from, the ore or supplied as a protective measure to the system is usually critical. Alkalinity Because of the need in most instances for maintaining a definite protective lime […]
Sampling Pregnant Solution

The press-tails solution going to storage discharges into a spill box (A in drawing), thence passing through a bottom pipe into the barren-solution storage tank. The solution will stand in the spill box at a level depending on the volume of flow, i.e., the volume precipitated. On the side of box A is a smaller […]
Superpanner
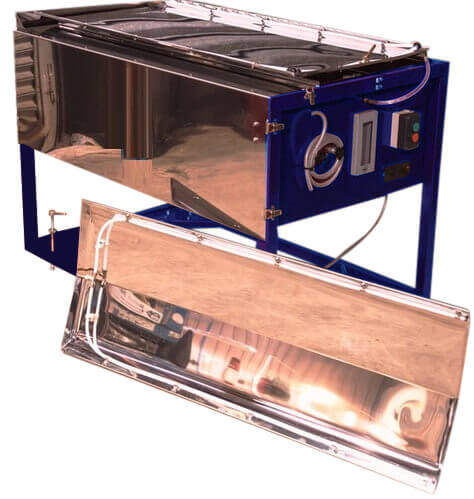
The superpanner is another device worked out by Professor Haultain for the accurate panning of small samples (see Fig. 59). This is a mechanized sichertrog or gold-panning horn. The pan is trough-shaped, about 30 in. long by 10 in. wide. The radius of curvature of the bottom diminishes from the lower end to the upper end. […]
Infrasizer

Because of the extremely fine grinding necessary to liberate the gold values, closer control than that obtained by screens was found to be necessary, and Professor Haultain’s “Infrasizer” was successfully adopted as a plant-control and research device. A brief description of the instrument is found in “Fine Grinding Investigations at Lake Shore Mines” {Trans. 42, […]
