Recovery of Iron Ores Containing Titanium Manganese Chromium and Alkali Metal Sulfates
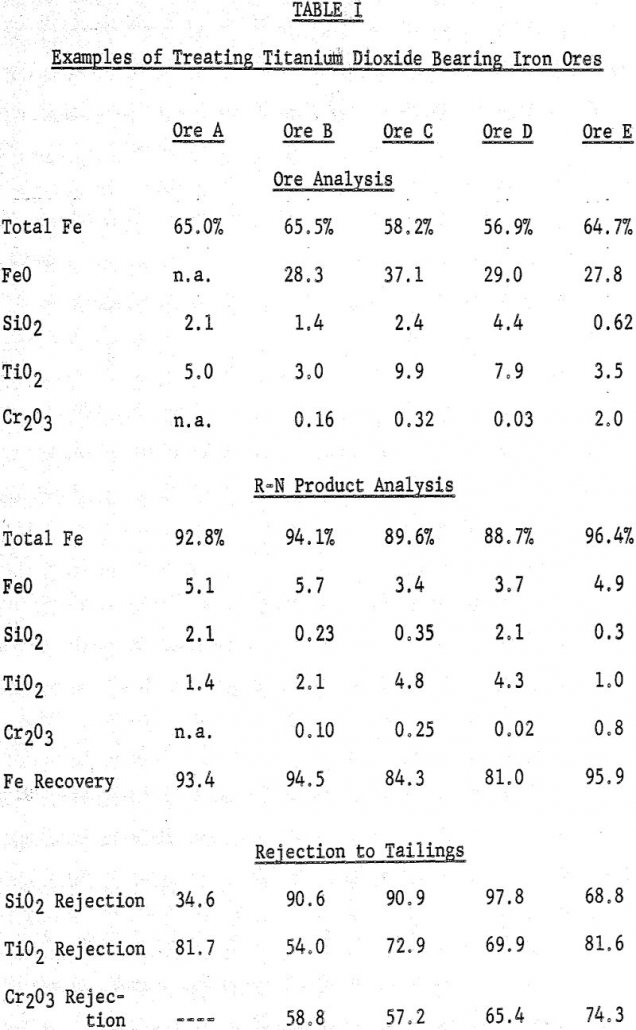
Most iron ores treated by the R-N direct reduction process yield metallic iron products considerably lower in titanium, manganese, and chromium oxides and alkaline metal sulfates/sulfides than were contained in the original ores. These metallic iron products are suitable as feed stock for the open hearth and electric steel-making furnaces. The elements which are rejected […]
Gravity Drainage Theory
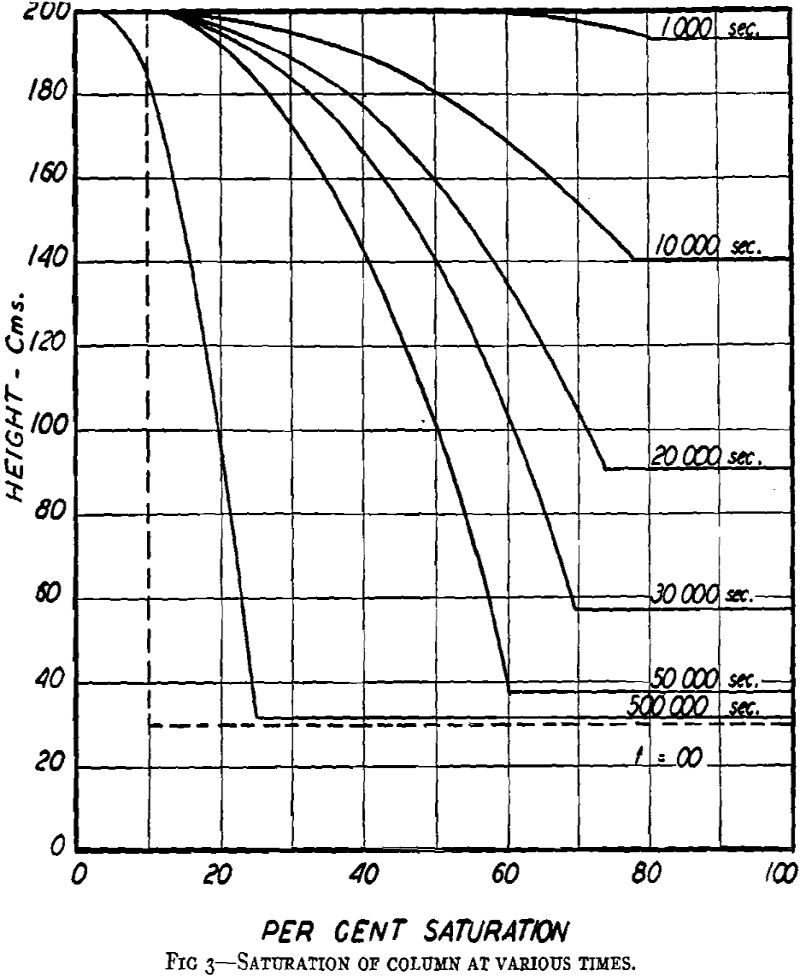
This paper presents a theory for estimating the rate of gravity drainage of a liquid out of a sand column. Account is taken of the variation in permeability to the liquid as the saturation in the upper part of the sand becomes less than 100 pct. Differential Equations of Capillary Flow The flow of liquids […]
Sinking Large Diameter Mine Shafts by Rotary Drilling
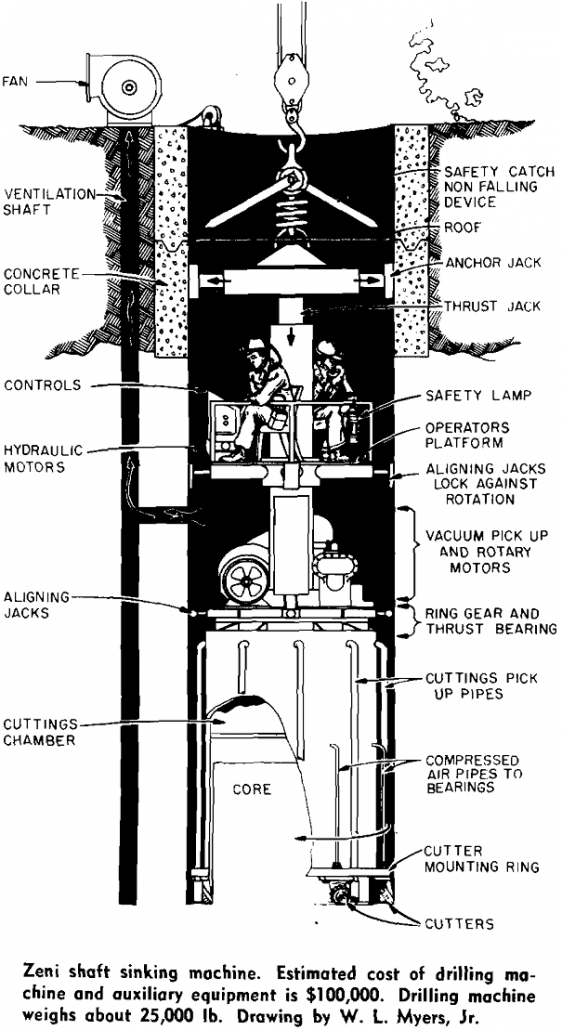
A 6-ft diam core drilling machine has successfully completed seven mine shafts in Virginia and West Virginia to depths as great as 465 ft. There is no practical depth limitation to this new system—a potential method in formations not easily penetrated with other large-scale drilling programs—and higher penetration rates and larger diameters are possible in […]
Underground Conveyor

The Inland Steel Company operates five underground iron mines in the Lake Superior District. The two largest of these, from the standpoint of productive capacity, are the Sherwood Mine in Iron River and the Bristol Mine in Crystal Falls, both on the Menominee Range of Michigan. It is at these two mines that we have […]
Single Stage VS Two Stage Grinding
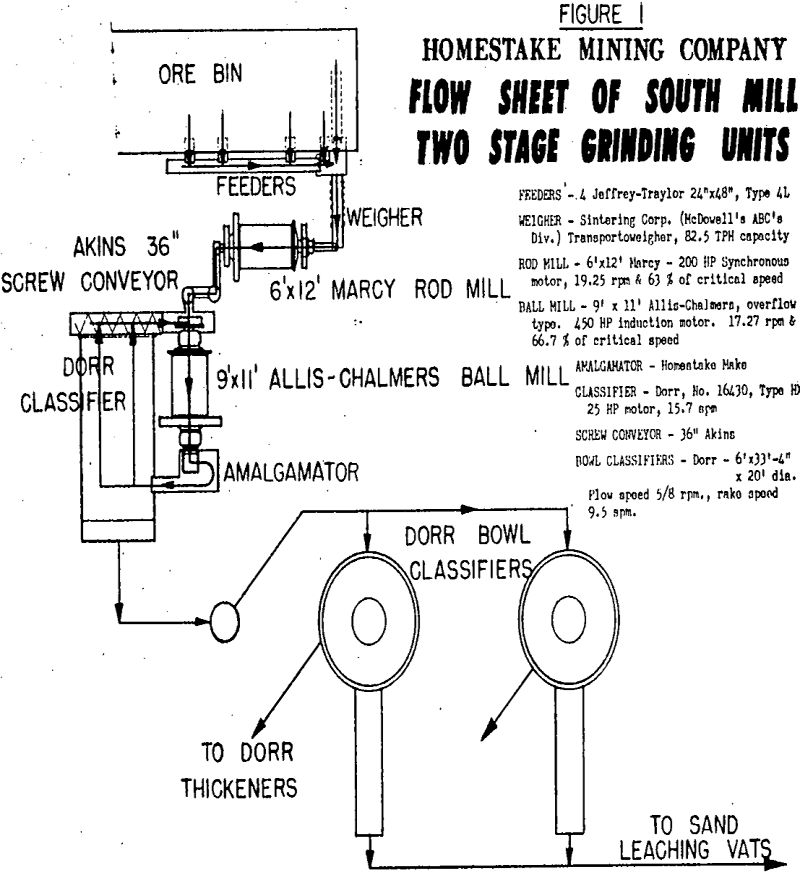
Homestake crushing and grinding-practice was completely revised during the period of 1951-1953. During the conversion, both crushing, plants at the head frames, the Ross and the Yates, were rebuilt. The flowsheet changes at each plant involved replacing the two 8K gyratories with a single thirty inch gyratory for primary crushing to four inch. The gyratory […]
Semi-Automatic Hoist
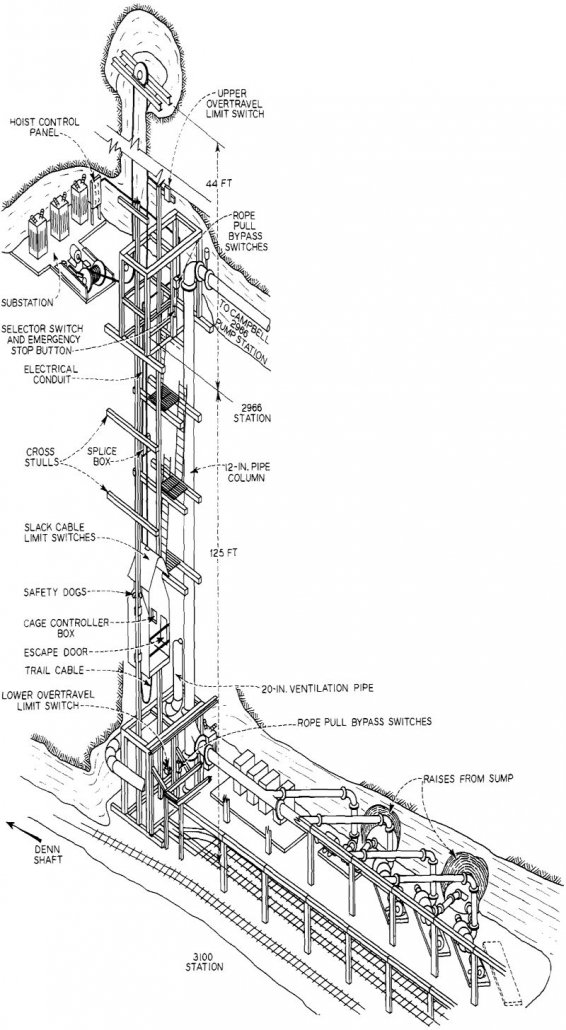
A Semi-Automatic hoist has been installed at the 2966 station of the Copper Queen mine, since neither the bulk of supplies handled nor the number of men engaged in developing the 3100 level justifies the constant attendance of two cagers and two hoist operators. The connecting service shaft between the 2966 and 3100 levels is […]
Diatomite – Diatomaceous earth
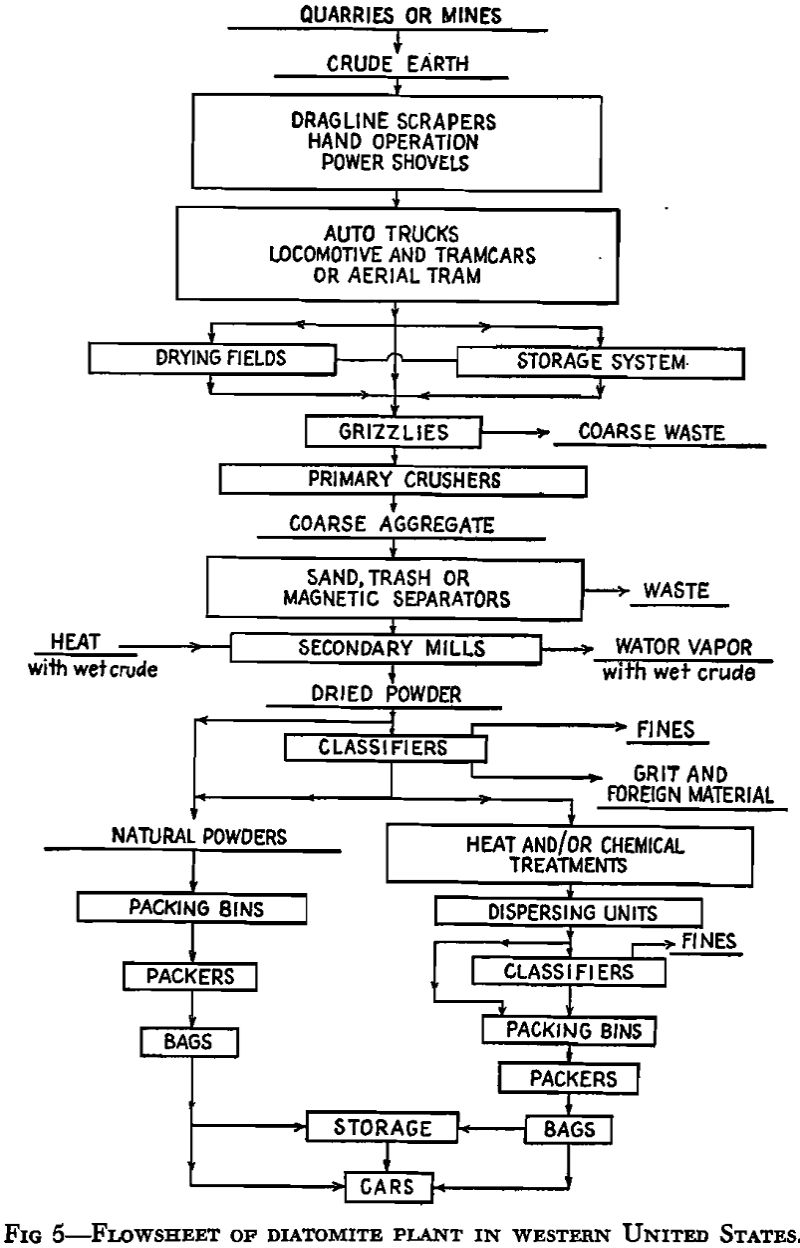
Diatomite is a hydrous or opaline form of silica, commonly known as diatomaceous earth, diatomaceous silica or kieselguhr. The term “infusorial earth” has lost its original meaning and today is incorrect in view of the distinctions between diatoms and infusoria. Various locality and variety names are obsolete but some retain local significance. Moler and Celite […]
Using Cyclone as a Thickener

With the exception of pneumatic processes and a few special bencficiation methods of comparatively limited application, all mechanical coal-cleaning and mineral-dressing processes involve the admixture of solid particles with a liquid, generally water. Upon completion of the beneficiation process the solids must be reclaimed from the water. With coarse particles separation of solids from water […]
Stone Crushing
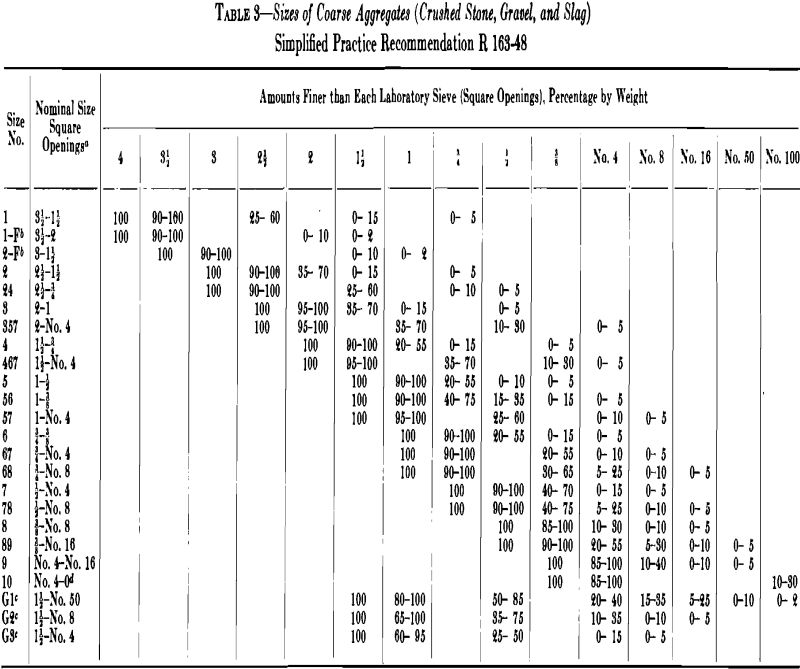
The use of stone as a building material in relatively large blocks is recorded in ancient historical records but only within the past 200 years has broken stone in small sizes begun to have extensive use, principally in highway-construction. Tresaguet, in 1764, describing his method for highway construction in France, required the top surface to […]
Clay
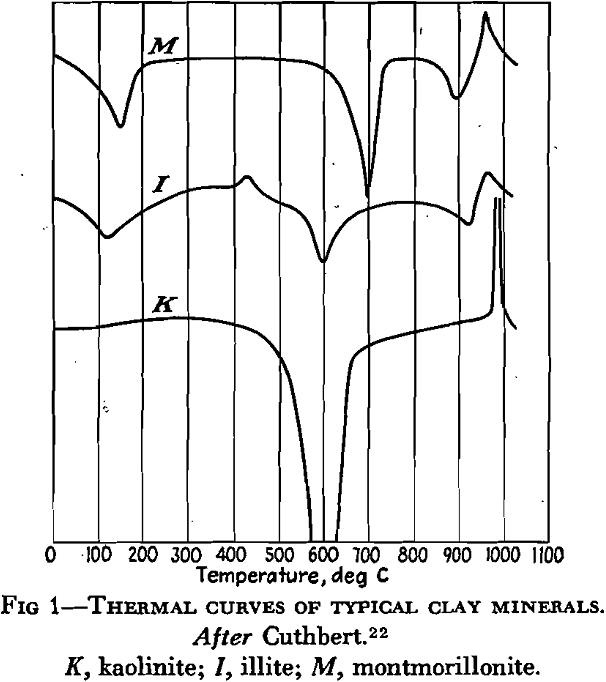
The term “clay” is applied usually to certain earthy rocks whose most prominent property is that of plasticity when wet. This permits them to be molded into almost any shape, which they retain when dry. Furthermore, they harden under fire. Clays contain hydrous aluminum silicates—the clay minerals—in appreciable amounts, but aside from this a number […]
