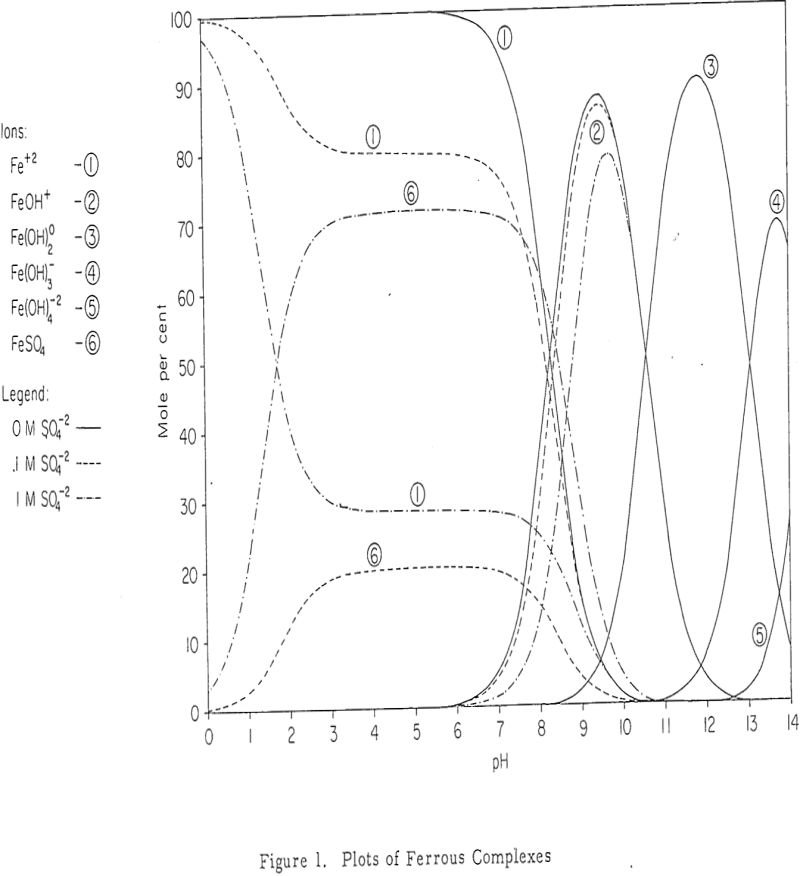
How does Cyanide Depress Pyrite – Mechanisms
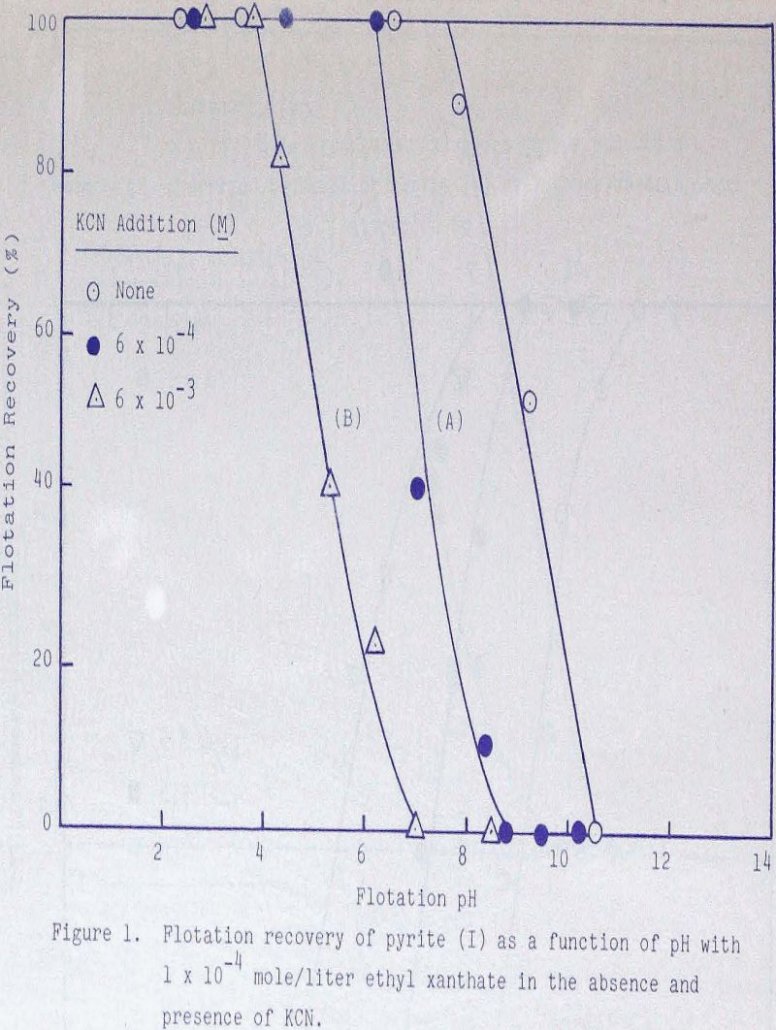
Oxidation potentials have been measured in the presence of various concentrations of cyanide, ferrocyanide, and ferricyanide and ethyl xanthate at various values of pH and related to flotation response. Eh-pH diagrams are constructed and show that the formation of surface ferric ferrocyanide is probably responsible for depression when cyanide is added. Experimental Materials and Techniques […]
Laser Alignment Underground
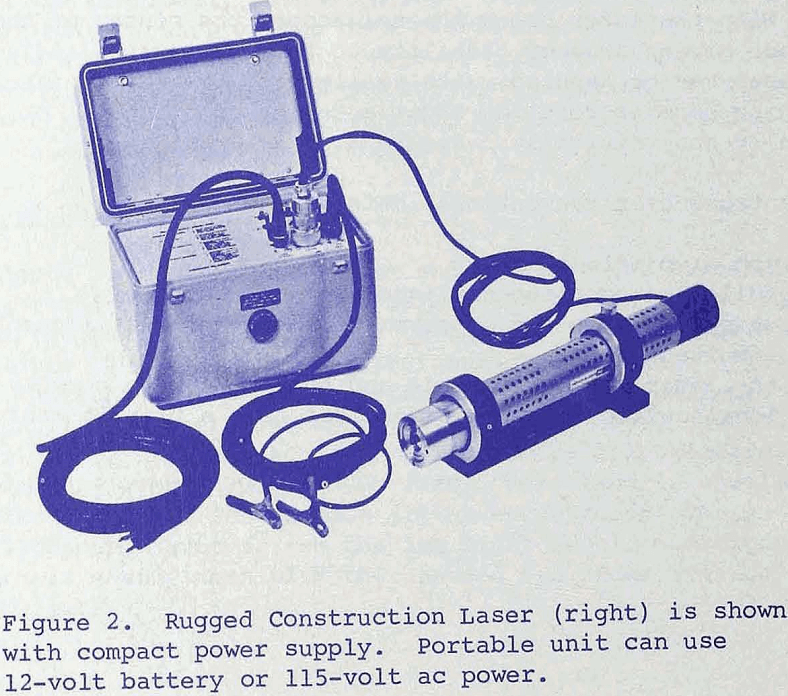
Accurate and economic control of line and grade on long tunnels, large structures, excavations and waterways, has been a problem to surveyors and engineers for decades. The conventional method of surveying, incorporating a level, transit, and a number of surveying technicians, has proven, in the past, to be a very expensive and time-consuming operation. Operation […]
Flotation Cell Hydrodynamics
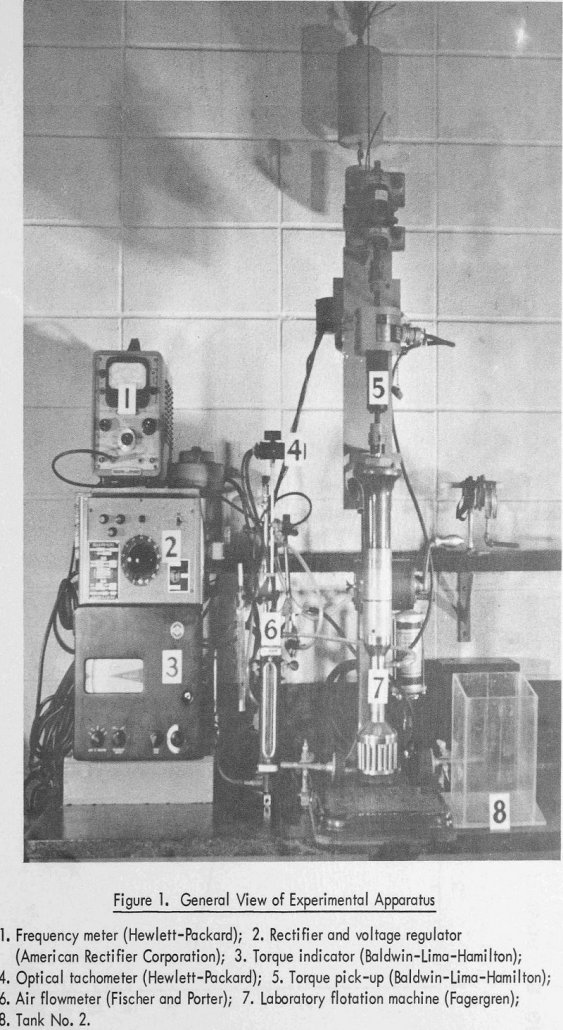
A fully-instrumented driving mechanism has been constructed to study the power, aerating and solid suspension characteristics of several laboratory flotation machines. Machines operating over normal flotation speed ranges give constant power numbers in liquid systems indicating that they operate under fully baffled turbulent flow conditions. Owing to lack of geometrical scaling, power numbers for different […]
Hydrochloric Acid Leaching of Iron from Aluminous Clays

Pennsylvania has ample reserves of high-alumina clays which are potential sources of alumina, but many of these clays contain large amounts of iron, which makes them unsuitable for treatment by acid processes. Of all the clay minerals tested, only gibbsite exhibits high acid solubility. Kaolinite, diaspore, and boehmite, which are the major alumina-bearing minerals in […]
Heap Leaching Economics
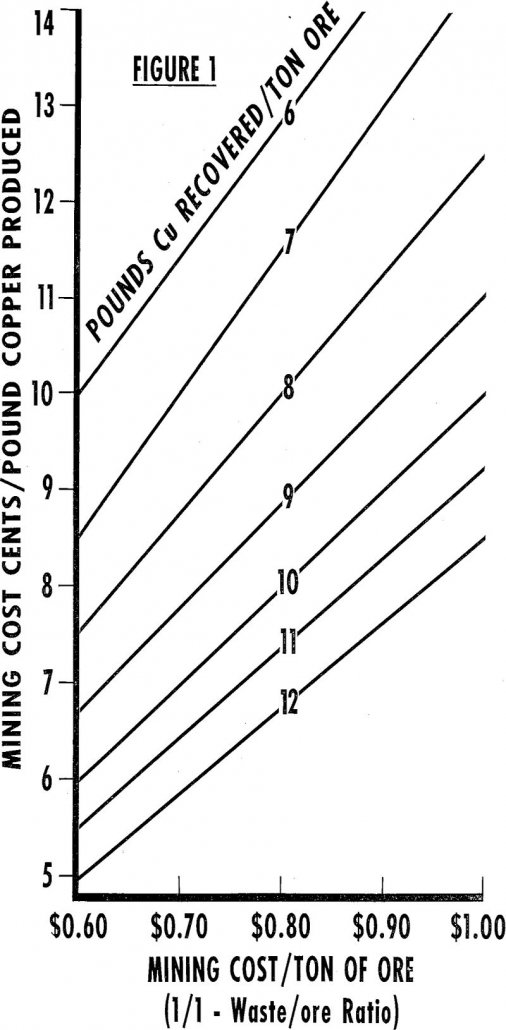
Expanded markets for copper in the past few years and a consequent search for new ore bodies have revitalized the widely known but seldom applied method of producing copper called heap leaching. This term should be differentiated from dump leaching in that the latter is applied to dumps of mixed oxide and sulfide ores (although […]
Fly Ash as a Portland Cement Raw Material
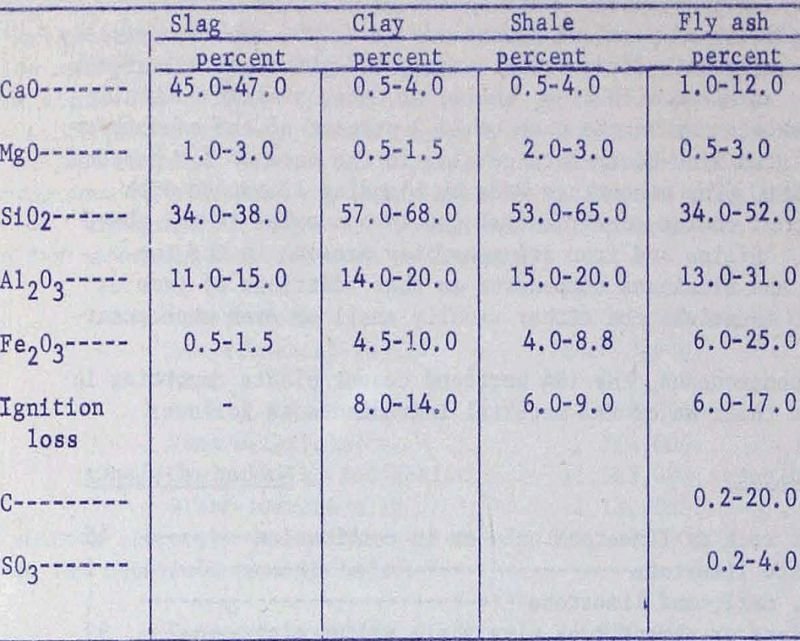
In 1966, approximately 125 million tons of raw materials, exclusive of fuel, air, water, and power were consumed to produce almost 74 million tons of portland cement in the United States that is about 3,400 pounds of raw material per ton of finished cement produced. To present the figure in another way, a single plant […]
Emulsion Flotation
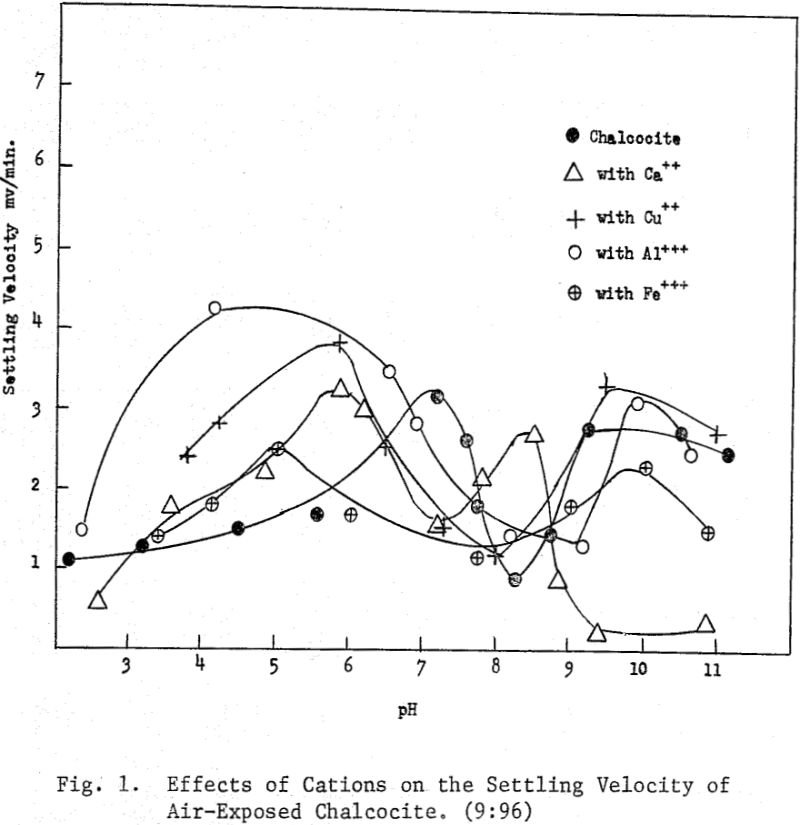
Because of the extensive surface area of oil droplets in emulsions, emulsion flotation offers possibilities for the recovery of finely divided mineral particles. Surfactants must stabilize the emulsion and possess an affinity for the desired minerals. Other important factors are the nature of the emulsion ingredients, the relative volumes of the continuous and discontinuous phases, […]
Removal of Iron from Aluminum Sulfate Solutions
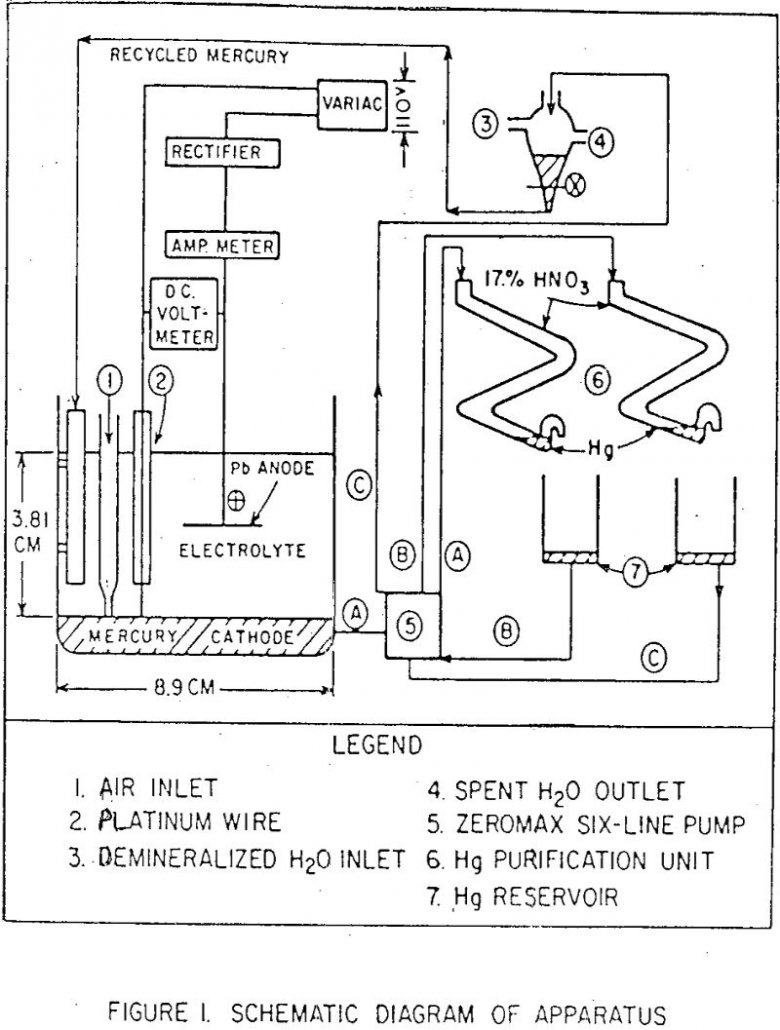
A study on the sulfuric acid extraction of alumina from some Pennsylvania ferruginous clays indicated that the published electrolytic method seems to be more efficient than the known chemical methods for removing iron from the leach liquor. The main disadvantages of the chemical methods are the consumption of excessive amounts of reagents and/or the precipitation […]
Dump Leaching
The dump leaching of low-grade copper ores, as an integral part of the open-pit mining operations in the Southwest, has been practiced for the last fifty years and is increasing in importance as one of the major sources of copper. The recent acceleration in dump leaching can be attributed to the greater tonnages of low-grade […]
Bin Design and Construction
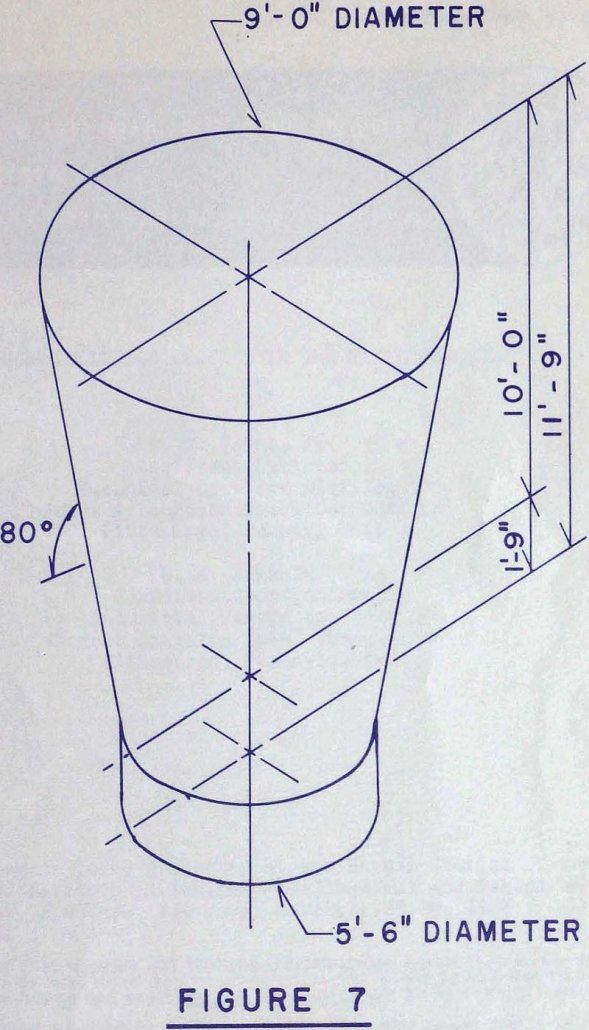
For many years, the Machinery Division of Dravo Corporation has been designing and constructing bins and bunkers as part of overall plant facilities. We have designed bins to handle a variety of materials including coal, coke, iron ores and concentrates, sintered and pelletized ores, calcined and raw limestone, bentonite, alloys for BOF shops, and even […]
