Gross-Count Method of Microscopic Quantification
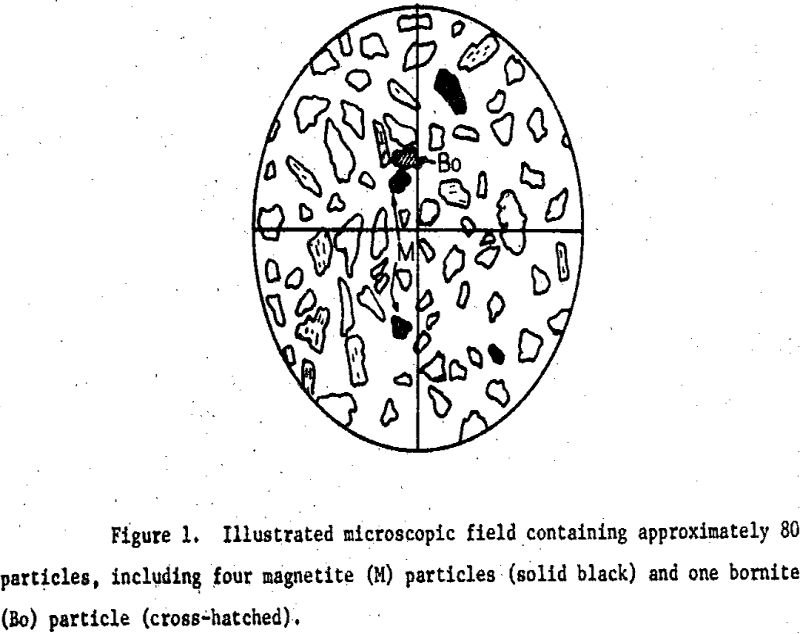
Microscopic evaluation of trace quantities of metalliferous phases in flotation products requires counting large numbers of particles. Particle counts of many thousands may be required for precision, but not “obtained practically by conventional microscopic techniques. A less tedious microscopic method for evaluating trace sulfides in mill tailings was developed for the O’okiep Mining Company in […]
How much Gold in Sea Water
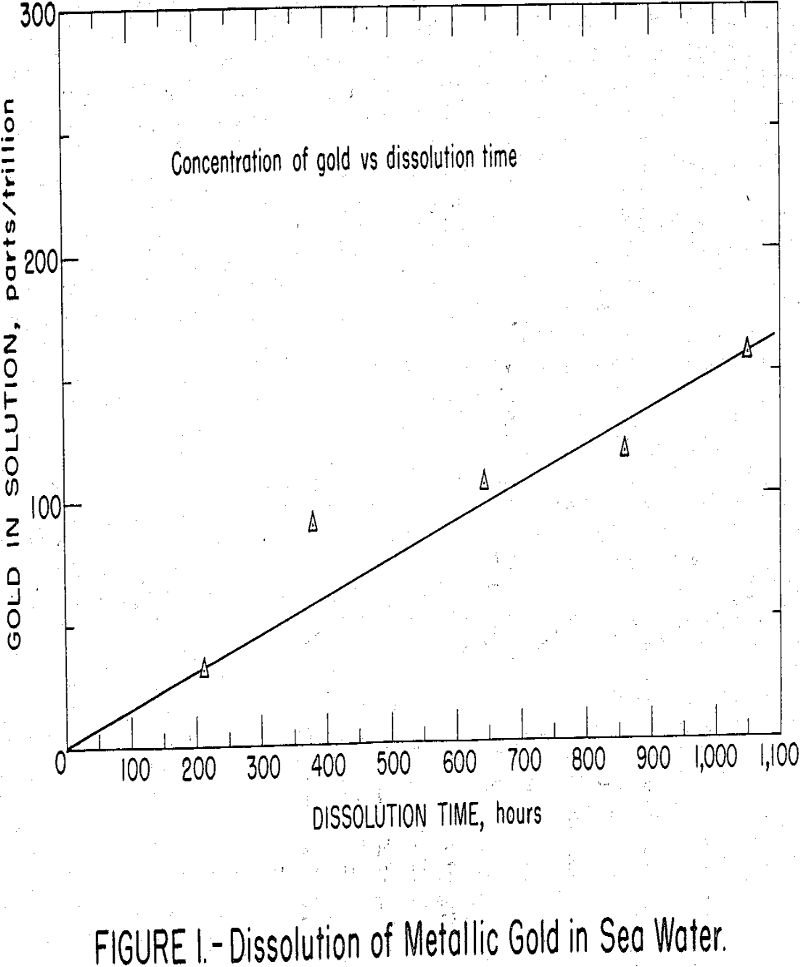
Interest in the recovery of minerals from sea water has been stimulated in recent years by proposals for large-scale water desalination plants that would yield both fresh water and enriched brine. Extraction of selected mineral components from the brine or the sea water feed might help pay for the fresh water. Additionally, by processing sea […]
Functional Mineral Pigments
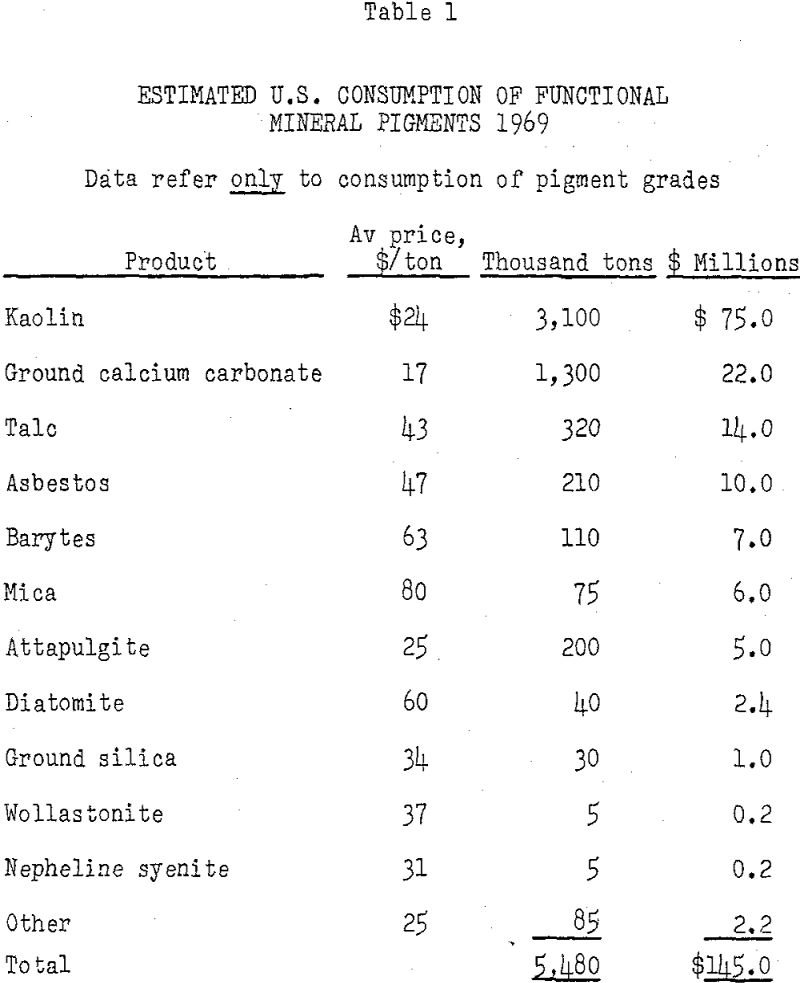
Functional mineral pigments are used in large quantities in paint, paper, plastics, rubber, textiles, agriculture, and several other industries. Originally extender pigments were employed only to lower cost. They were thought of merely as adulterants to replace more expensive prime pigments and binders. However, over the years their role has become better understood, and today […]
Dragscraper for Stockpiling, Reclaiming and Blending
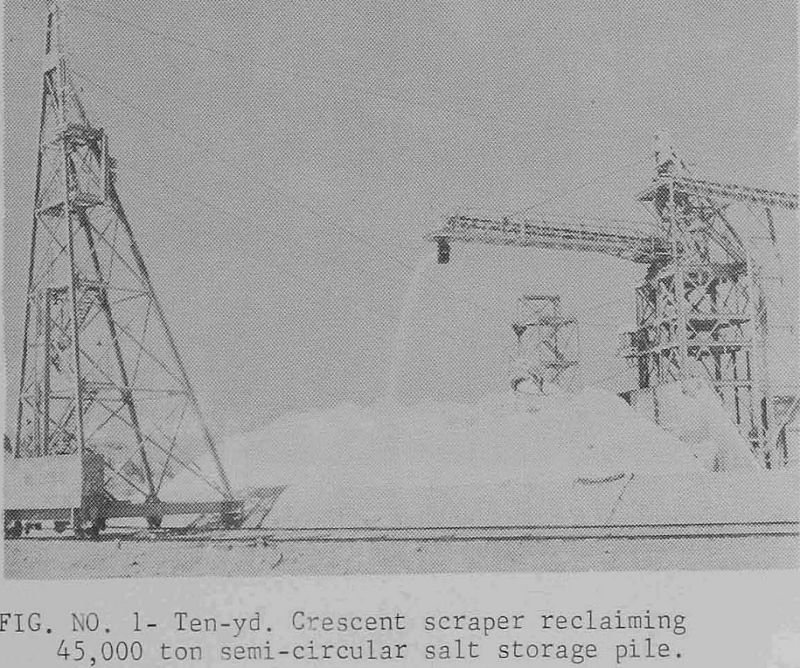
Today more than ever, there is an increased demand for higher plant production capacities and efficiencies to offset the increasing costs for labor and materials. Plants involved in processing large volumes of bulk materials are particularly interested in more efficient material handling systems to (1) reduce labor and maintenance costs, (2) improve blending of non-uniform […]
Crushing & Grinding of Gypsum

In the crushing and grinding of metallics for beneficiation, the sizing is normally done to liberate the metals or sulphides for further processing to improve recoveries of the basic metals or minerals. The objective is to reduce the ore in size through various closely controlled stages to that degree of fineness which gives an economic […]
Automatic Control of Crushing and Grinding Facilities
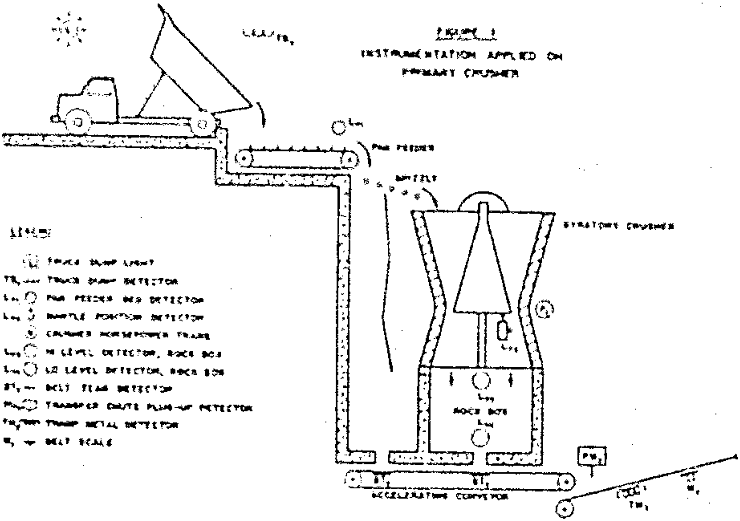
During the past two years, there has been an increasing acceptance of process automation among ferrous, non-ferrous and non-metallic rock processing operations in an attempt to keep total unit costs in line in a market situation where labor and material costs are rising almost daily. The experienced crusher or mill designer and operator should know […]
Beneficiation of Kaolinite Clay from Silica Sand Washings
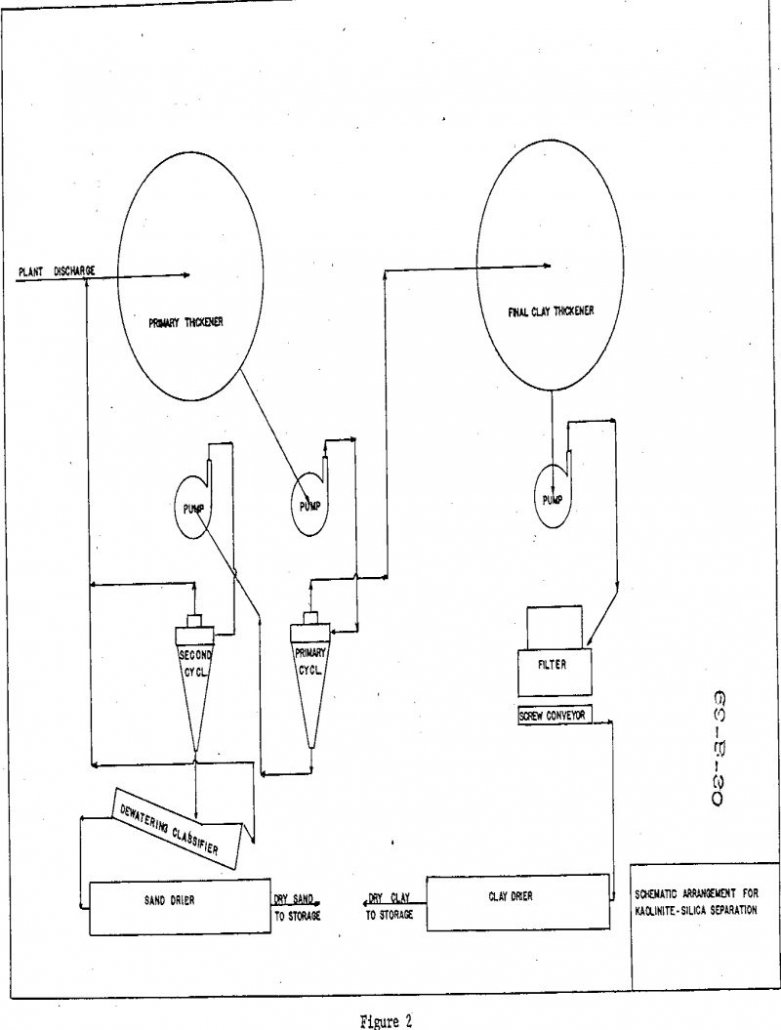
Silica sand has been mined in Illinois from the St. Peter Sandstone since the turn of the century, especially in the area around Ottawa on the Illinois River in the north-central part of the state. Production of this sand, consumed mainly by the glass and foundry industries but also sought after for many other uses, […]
Wet Autogenous Grinding in Tumbling Mills
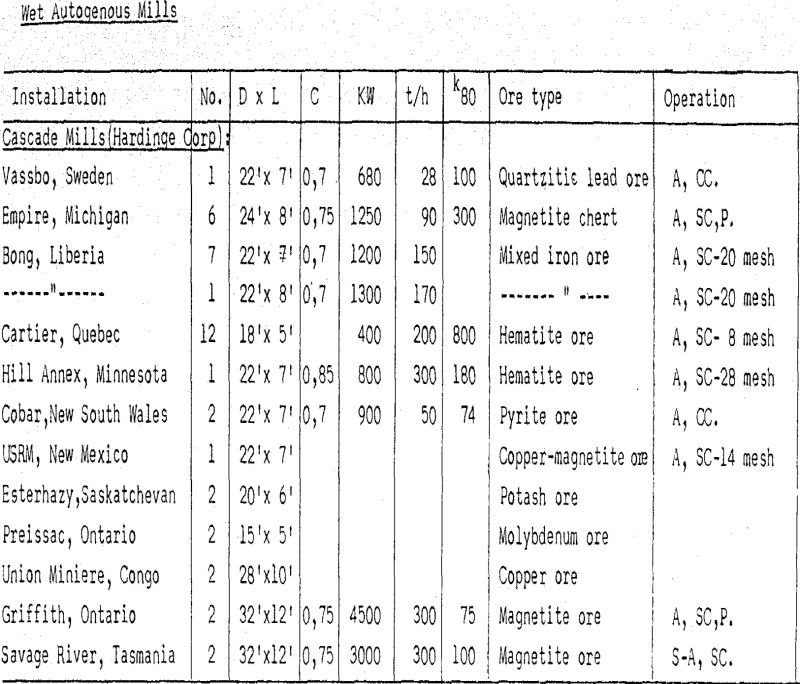
The autogenous grinding method has been progressively employed in mineral dressing plants during the last 15 years. The term has been used with somewhat different meanings. In this paper the author will use it in the most restricted way, for processes where run-of-mine ore (rock) in one step is reduced to a grind product by […]
Water in Fluorspar Flotation
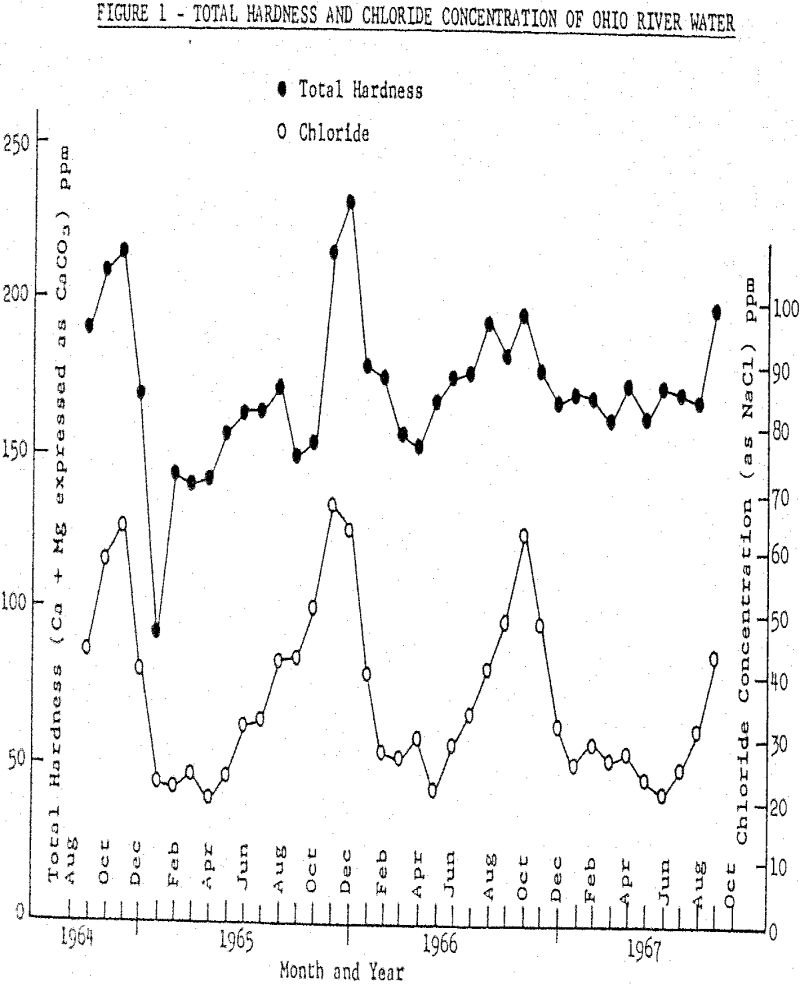
Water has received little attention as a variable in flotation, even though it is a known fact that water hardness often has an adverse effect on purity and recovery, particularly on the flotation of non-metallic minerals. Because of this fact, process water used in some flotation plants is treated to reduce hardness to an acceptable […]
Chrysocolla Sulfidization and Flotation
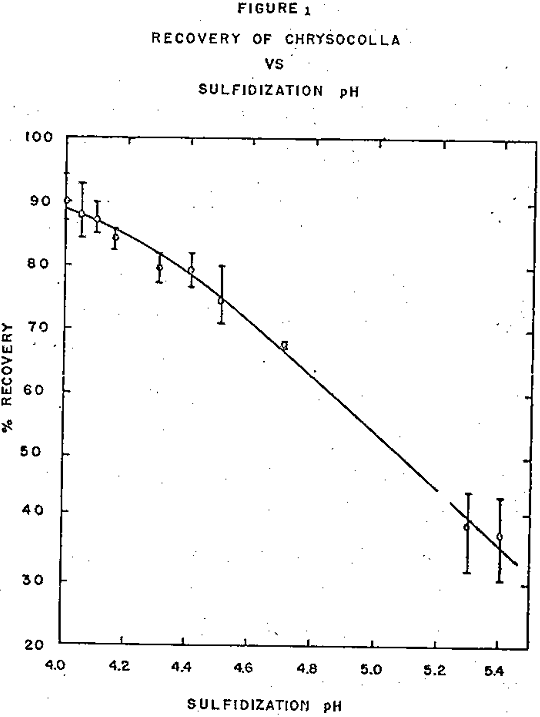
Studies of sulfidization and flotation of chrysocolla involving the use of pH and sulfide ion instruments, a Zeta meter, microflotation techniques, and sensitive determinations of adsorbed sulfur have given new insight into the mechanism of the process. Factors that affect the recovery of sulfidized chrysocolla by flotation appear to be the pH at which it […]
