Dense-Heavy Medium Separation HMS / DMS Process
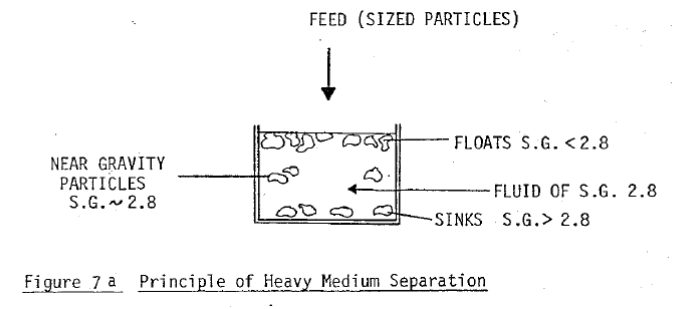
HMS and DMS are acronyms for Heavy (Dense) Medium Separation and is applied to the process of pre-concentration of minerals – mainly the production of a high weight, low assay product, which may be rejected as waste. In principle it is the simplest of all gravity processes and is a standard laboratory method for separating minerals […]
Agglomeration of Particles
Agglomeration is the formation of aggregate by the sticking together of feed and/or recycle materials, and it includes the formation of agglomerate nuclei. The main objective in agglomerating fines being the conversion of ores, minerals and chemicals of undesirable fineness into agglomerates characterised by a size consistency desirable for subsequent use or processing. In metallurgical […]
Factors Affecting Filtration Rates and Cake Moistures

Here is a list of all Factors Affecting Filtration Rates and Cake Moistures in plants or laboratory de-watering systems and processes. Particle Size of Solids Generally the large the particle size, the higher the filtration rate in Kg/m2/h and the lower the cake moisture. However, the validity of the last statement depends on other factors, […]
Filtration – Leaf Filter Testing
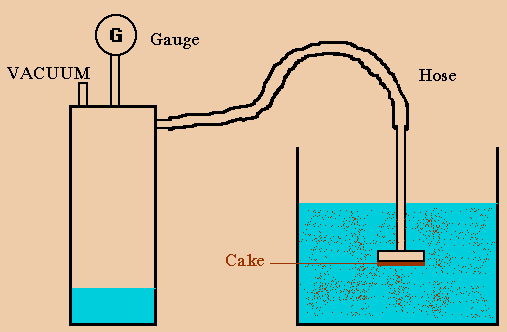
Filtration is defined as the separation of insoluble solids from a liquid by forcing a portion of the liquid through a porous medium by a pressure differential, while the solids are trapped on the surface or in the depth of medium. The two main methods that exist to create the required pressure differential are: Application […]
Types of Crushers
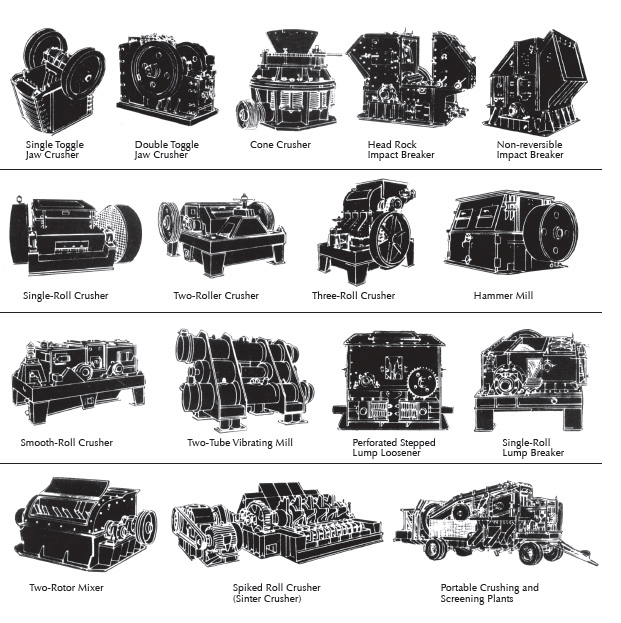
Crushers may be divided into three general classes, with respect to the manner in which they do their work: Pressure Crushers: This category embraces the several types of gyratory crushers and jaw crushers, as well as the double crushing rolls, with either smooth or corrugated shells. Impact Crushers: This division is represented chiefly by the […]
Impact Crusher Working Principle

Starting from the base working principle that compression is the forcing of two surfaces towards one another to crush the material caught between them. Impact crushing can be of two variations: gravity and dynamic. An example of gravity impact would be dropping a rock onto a steel plate (similar to what goes on into an […]
Principle of Operation of Hydrocyclone
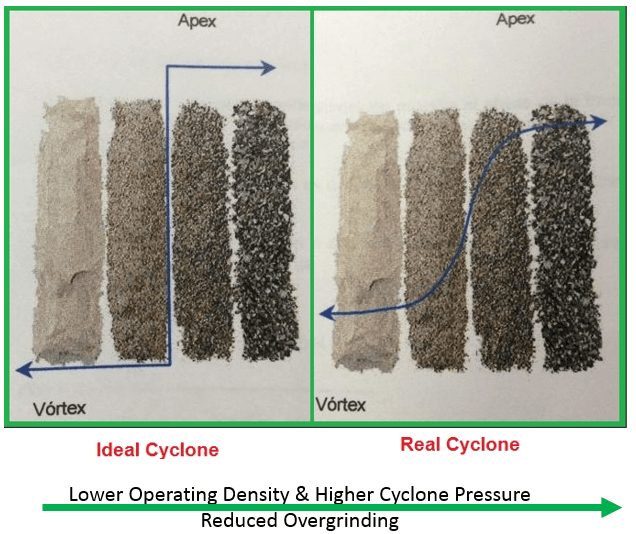
The Principle of Operation of Hydrocyclone is, in simple terms, the forces of gravity and centrifuge to separate large or heavy particles from smaller and lighter one. When sized correctly will “cut” like the ‘real cyclone’ below VS the imaginary ‘ideal’ one on the left. Hydrocyclones are preferred units for sizing or desliming large […]
Froth Flotation System

Successful industrial practice has shown that froth flotation sytem needs to be viewed both at the plant level and at the research level as a highly interactive system consisting of equipment, chemistry, and operational factors. A long history of plant tests has shown rather clearly that it is not very fruitful to work in any […]
Flotation Machines

Industrial flotation machines can be divided into four classes: mechanical pneumatic froth separation column air-lift matless As pneumatic and froth separation devices are not commonly used in industry today, no further discussion about them will be given in this module. The mechanical machine is dearly the most common type of flotation machine currently used in […]
Flotation Frothers – Frothing Agents
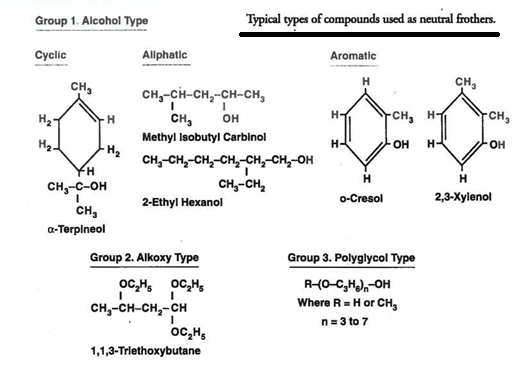
The next reagent that is added is the Flotation FROTHER. The frother strengthens the surface tension of the air that is injected into the flotation cell. As the air rises in the shape of bubbles, they come into contact with the mineral laden collector which attaches itself to the air. The bubble will continue to […]
