Titanium & Hydrometallurgy
Titanium’s performance characteristics in acidic oxidizing and mildly reducing environments make it applicable to numerous currently defined and many projected hydrometallurgical applications. With titanium’s current and projected availability and price stability increased use in pressure leach, piping systems and electrorefining is practical. Titanium has a low density, .163 lb. per cubic inch, versus iron, as […]
Acid Dissolution of Metal & Mineral Samples by Microwave

Objective Reduce the time, complexity and expense of dissolving metal and mineral samples in solution in preparation for chemical analysis. Approach In earlier research, the Bureau of Mines developed a rapid and inexpensive method for the dissolution of mineral and metal samples in plastic pressure bottles heated in a boiling water bath. Using this technique, […]
Leaching Manganese
Domestic mines account for a mere 2 pct of the manganese consumption in the United States. Although plentiful supplies of manganese are readily available from several foreign countries, the Nation’s vulnerability to sudden cessation of foreign shipments plus the current trade imbalance has stimulated a renewed search for economic methods of producing manganese from domestic […]
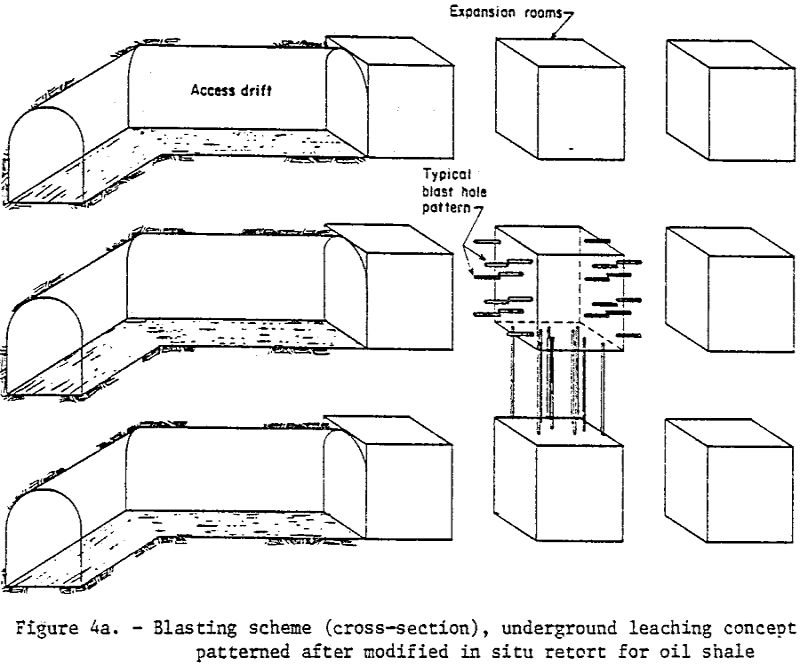
Ferric Chloride Leaching

Primary lead is commercially produced from lead sulfide concentrates by a smelting process consisting of sintering, blast furnace reduction, and refining. The pyrometallurgical method is low cost and requires relatively little energy, but generates gaseous sulfur dioxide and particulate lead, which must be controlled to prevent air pollution. Because of the difficulties in meeting regulations […]
Vanadium & Uranium Extraction
Addition of vanadium to iron and steel gives improved product properties such as increased strength, improved machinability, reduced distortion, simpler heat treatment, better weldability, increased wear resistance, better control and uniformity of hardness penetration and gradient, smoother and better finishes, and reduced flaking or spalling of carburized surfaces. Consequently, vanadium-steel alloys are used in the […]
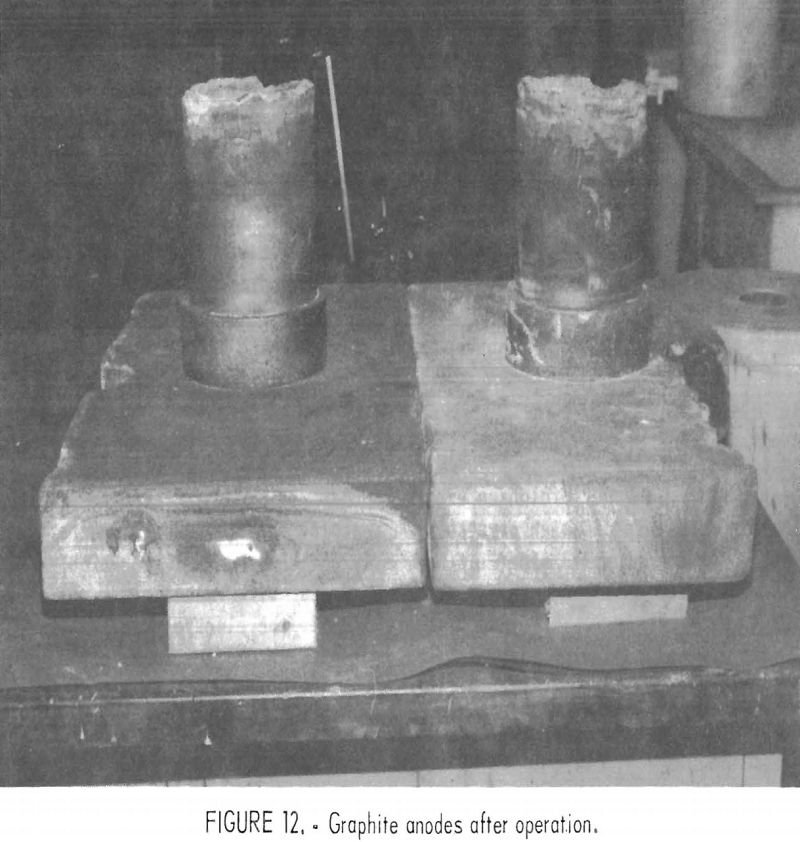
Electrolytic Method for Recycling Scrap Batteries
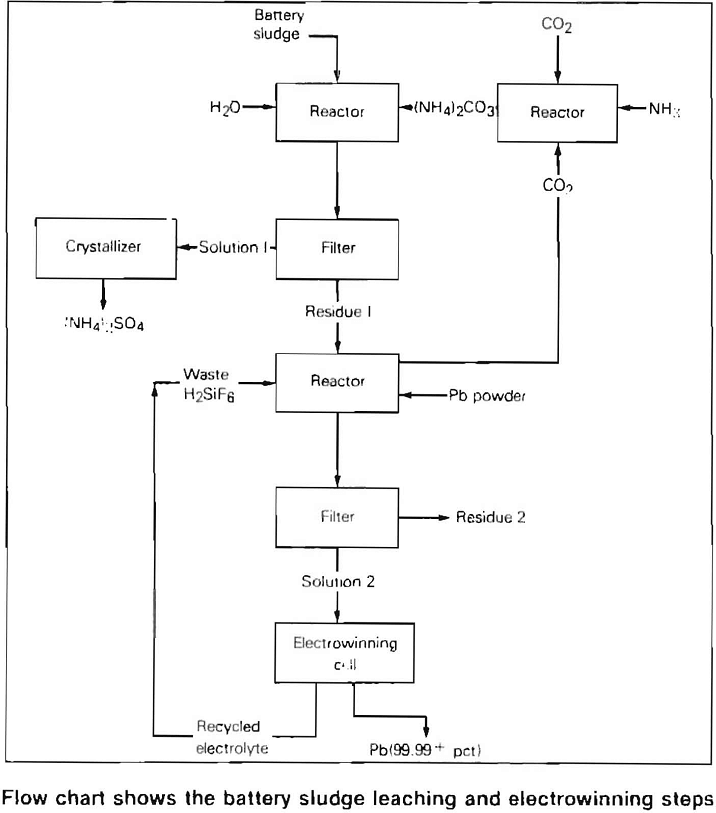
Electrolytic Method for Recycling Scrap Batteries Objective To devise an economical, environmentally acceptable method for recycling scrap lead-acid batteries. Approach A combination electrorefining-electrowinning method for recycling lead metal and sludge from scrap batteries was devised which produces a 99.99 + percent pure lead product and eliminates the lead and sulfur oxide emissions that are […]
Carbon Adsorption of Gold
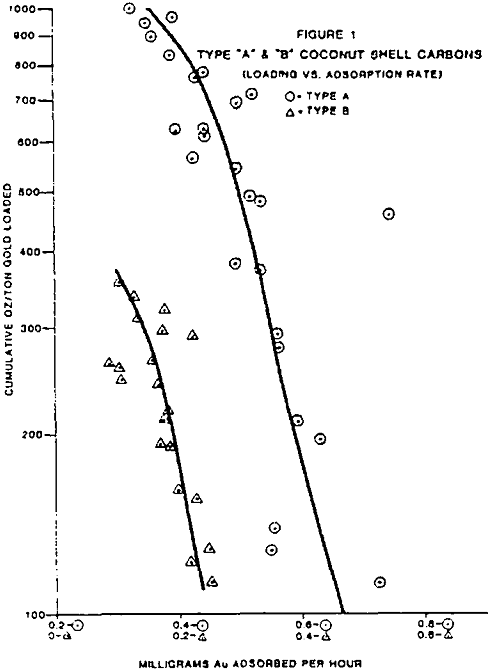
The procedures and tests descriptions are given for the ultimate gold carbon loading tests and the dynamic gold carbon loading tests. A 4.5 parts per million gold solution was prepared by dissolving fine (-200 mesh) gold powder in a sodium cyanide solution made with deionized water at pH 10.5 (lime adjusted). This gold feed solution […]
Biological Leaching of Manganese Ores
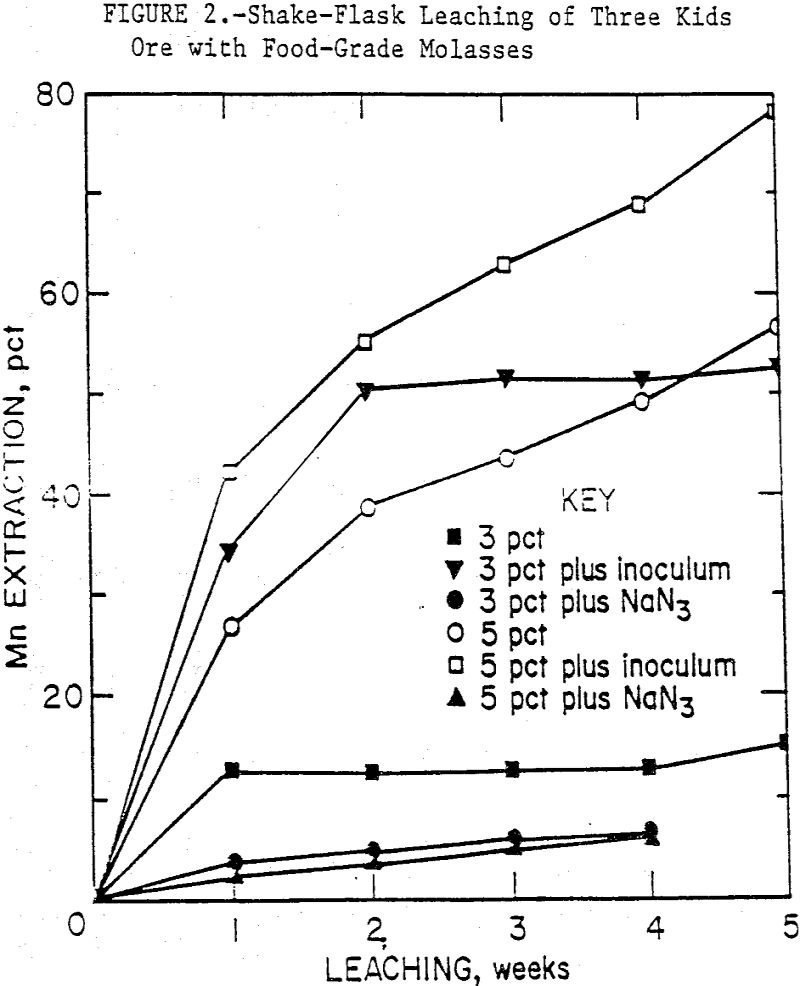
Biological leaching of low-grade ores has been gaining interest and acceptability in recent years. Sulfide ores, which are subject to oxidation of specific bacteria such as Thiobacilli, are being bioleached commercially. Other ore types, especially oxides and silicates, have been examined for their leachability by microorganisms. Ehrlich (1980), Holden and Madgwick (1983), Groudev (1987), and […]
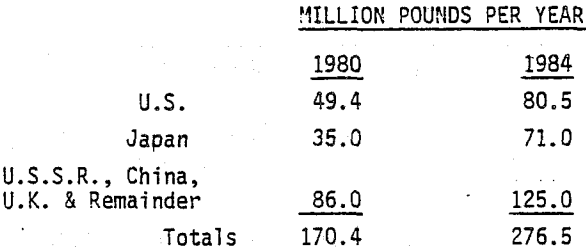
Selective In Situ Leach Mining of Manganese Ores
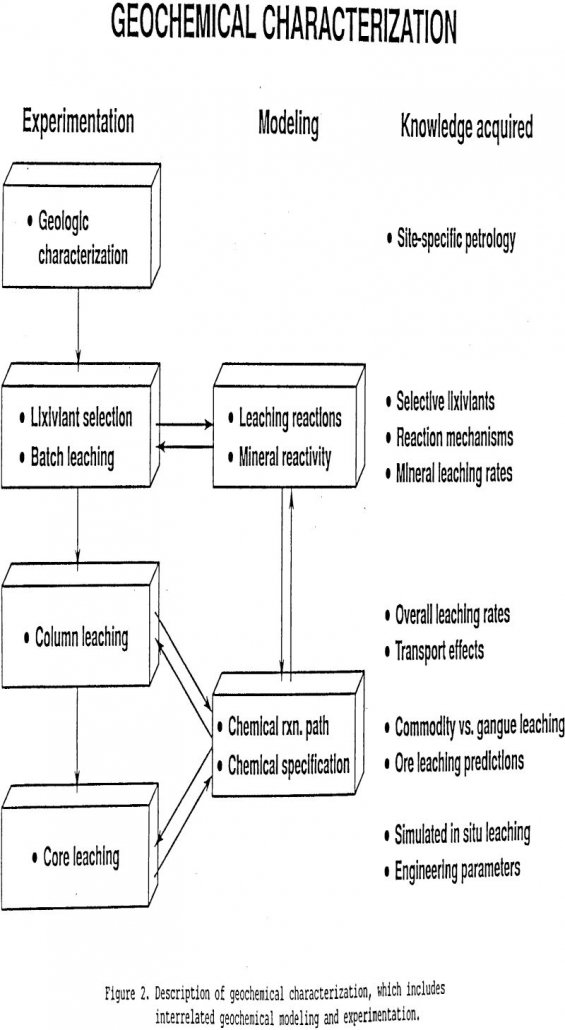
The Bureau of Mines is conducting research to develop cost effective, environmentally compatible advanced mining technologies for the selective extraction of critical and strategic metals. Critical and strategic metals (e.g. manganese, cobalt, and chromium) are essential to domestic steel, aerospace, electronic and defense-oriented industries. The United States no longer has high-grade deposits of these minerals […]
Unsaturated Setting Affects in Situ Copper Leaching
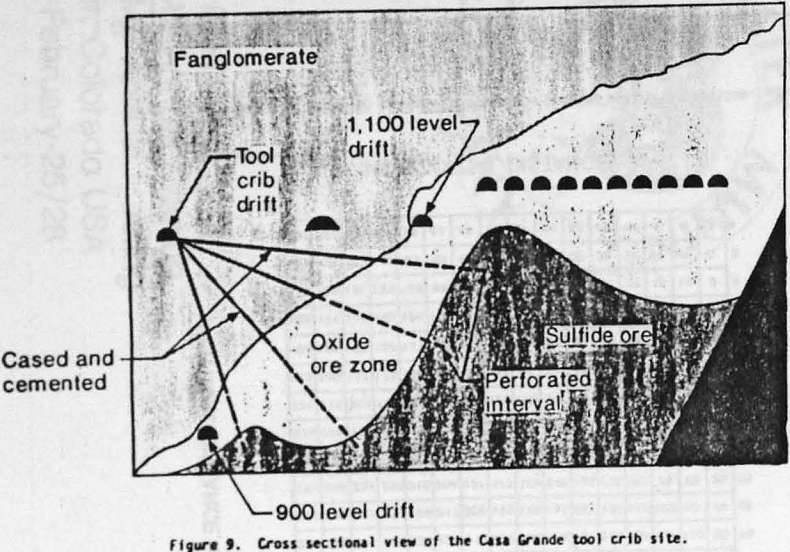
Hydraulic properties and characteristics of copper ore associated with the Casa Grande deposit at the Casa Grande mine are investigated by the Bureau of Mines to assess permeability and its impact on flow capacity during in-place, copper leaching operation. The copper ore is a heterogeneous, unsaturated, and fractured medium in which the permeability is dominated […]
