Processing Bastnasite Ore
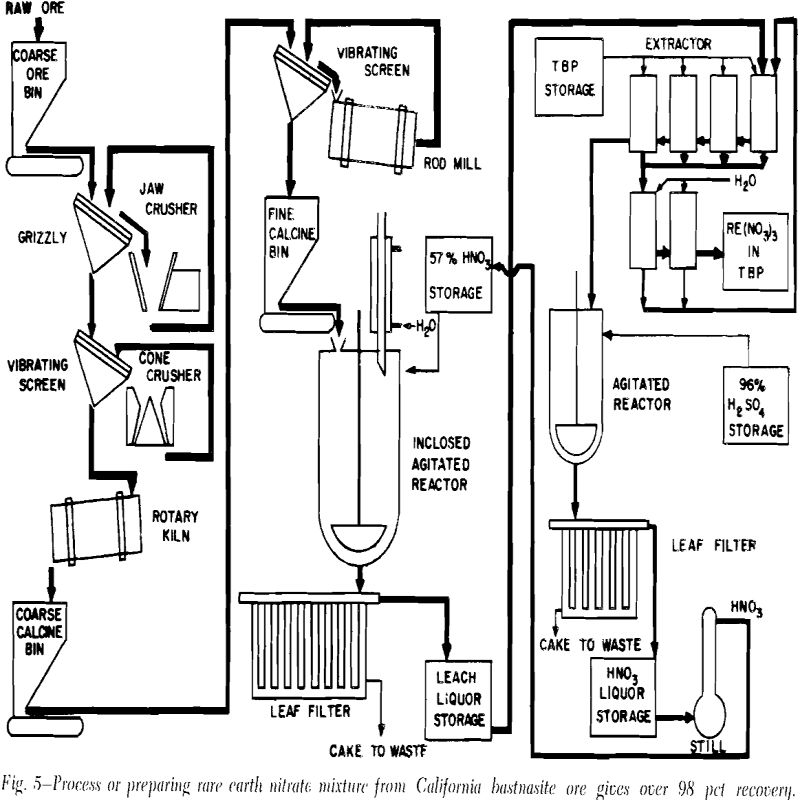
Average composition of ore from the San Bernardino deposit is less than 0.1 pct ThO2, 25 to 35 pct calcite, 10 pct rare earth oxides, 15 to 20 pct silica, and 30 to 40 pct barite. Rare earth content of the ore analyzes 50.7 pct CeO, 4.2 pct Pr6O11 11.7 pct Nd2O3, 1.3 pct Sm2O3, […]
Heavy Rare Earths Separation by Ion Exchange
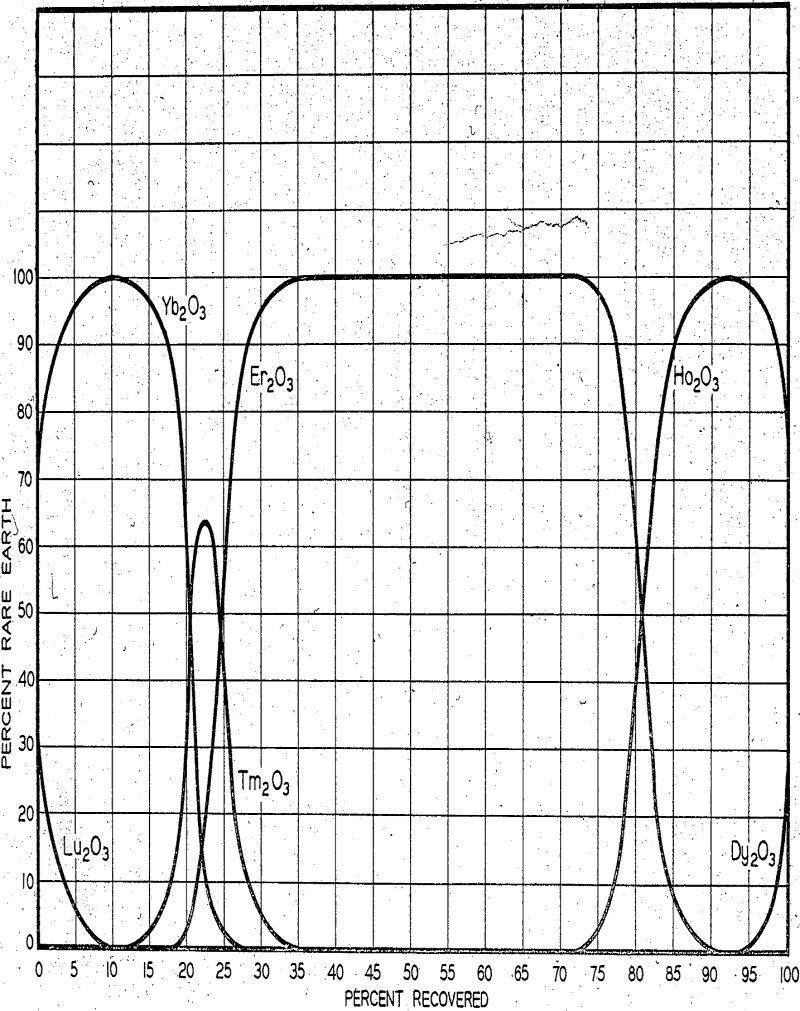
The equipment for the separation of the rare earths consists of nearly 200 columns thirty inches in diameter by twenty feet high. They are constructed of materials which will not contaminate the rare earth products. Most of the cation exchange resin in the plant is a styrene-divinylbenzene sulfonic acid resin such as Amberlite IR-120 and […]
Continuous Filtration of Precipitates

Advances in hydrometallurgy during recent years resulted in greater attention being focused on the various unit operations involved. Some steps, similar to normal beneficiation practice—crushing, grinding, classification, etc. are well known.Others —roasting, leaching—have recently been intensively investigated from both theoretical and practical viewpoints. Less well-studied are such operations as precipitation and precipitate filtration. Continuous Filters […]
Fluidized Bed Chlorination of Rutile
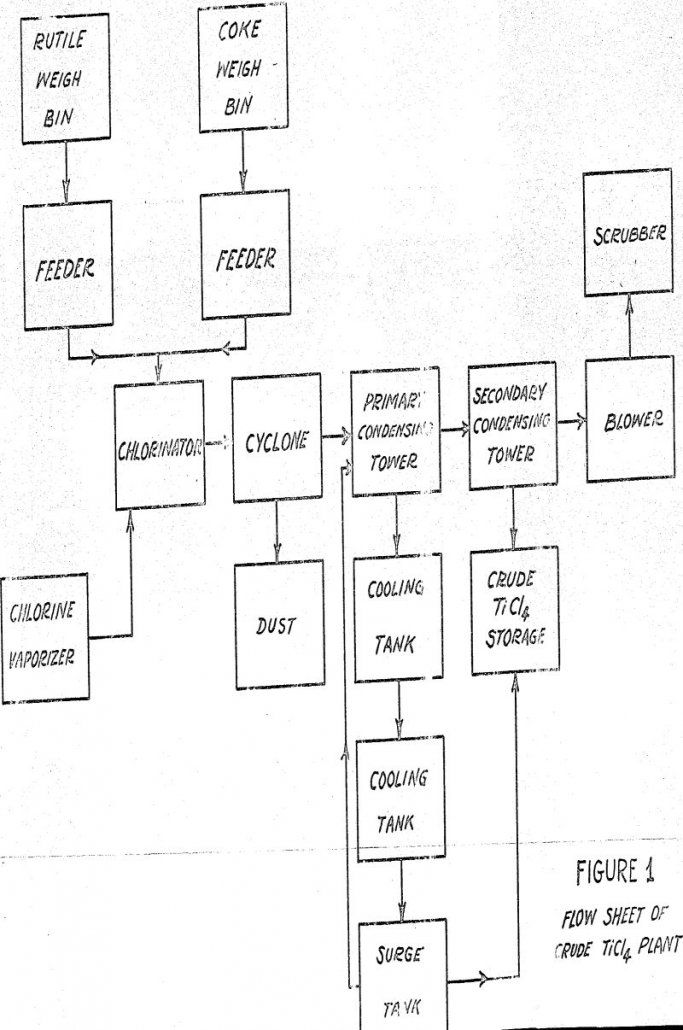
Starting with rutile, containing more than 95% TiO2 and of the proper particle size, the commercial production of titanium tetrachloride via fluidized bed chlorination is relatively very simple and economical. As compared to shaft chlorination, it operates at a much higher capacity for given sizing of equipment, and appears more foolproof, requiring less attention. At […]
Copper-Nickel Ore Processing
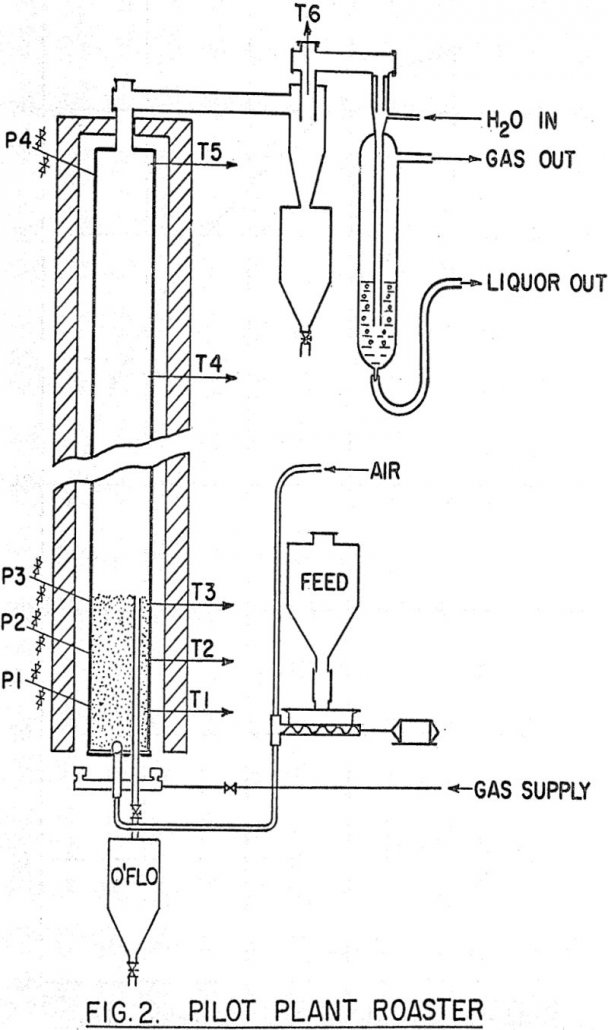
A nickel-copper sulphide concentrate was treated in a pilot plant at Warren Spring Laboratory during 1961, by a hydrometallurgical roast-leach-solvent extraction process devised to cleanly separate the metal values, and produce acid sulphate liquors containing the metals. It is shown that 86 percent of the nickel and 95 percent of the copper could be leached […]
How to Recover Molybdenum in Oxidized Ore
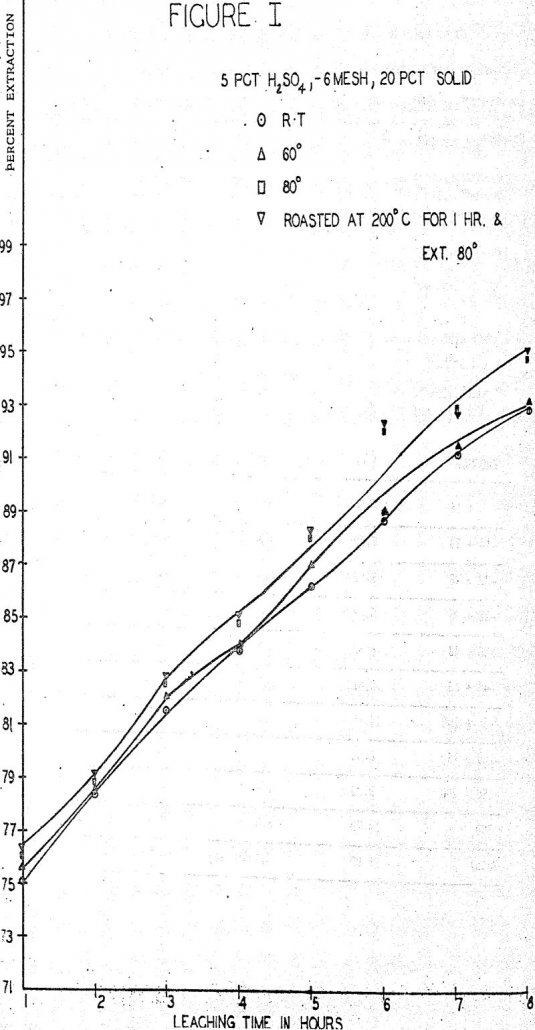
A study of some variables affecting the recovery of molybdenum from oxidized molybdenum minerals was made. The effects of variations in contact time, temperature, pulp density, particle size, and solvent concentration on the recovery of molybdenum using acid and alkaline solvents were investigated. Chemical analyses, screen analyses and microscopic examinations were made and the presence […]
Use LIX-64 Extractant for Copper Pilot Plant Data
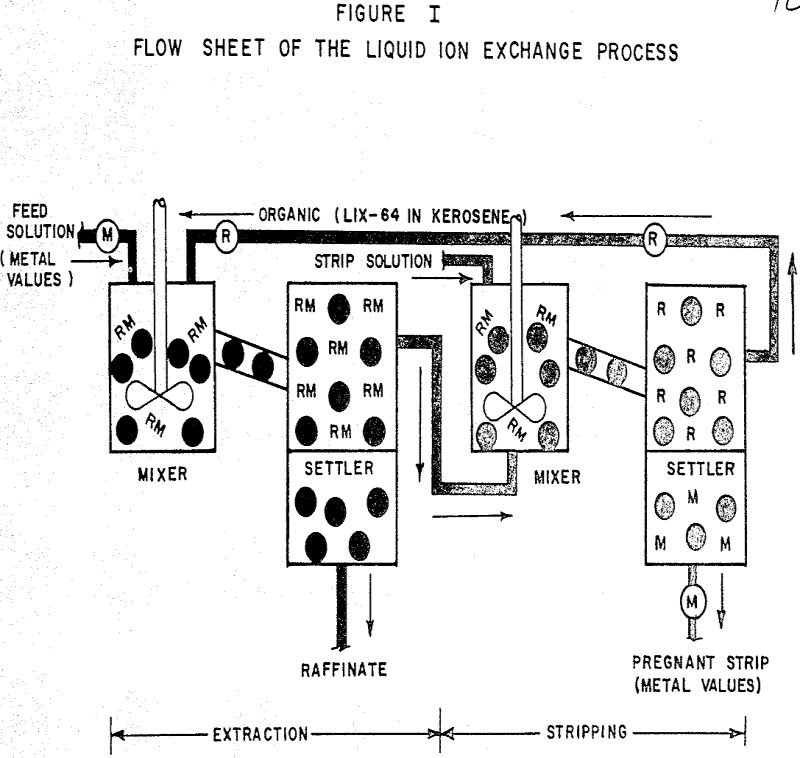
Design parameters for scale-up to commercial plants are presented and discussed along with a revised capital cost estimate. The future pilot program is discussed, including minor design changes and the effect of entrained organic on dump leaching efficiency. Description of The Liquid Ion Exchange Process In the extraction section, a water-immiscible organic solvent (normally kerosene) […]
Chemical Mining
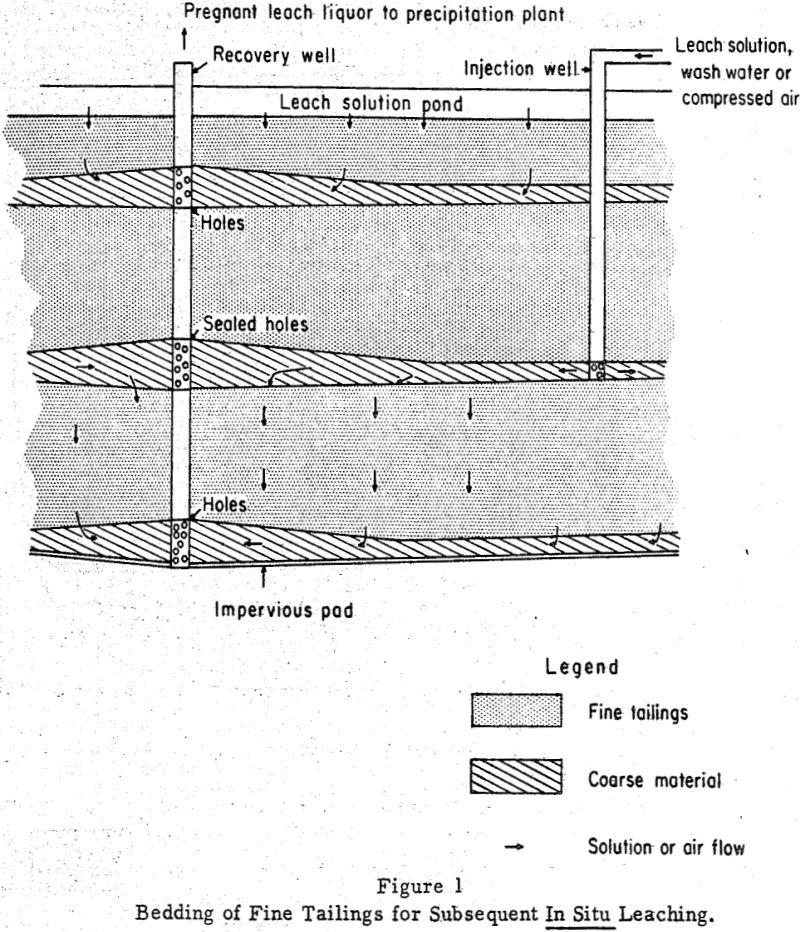
Chemical mining is the in situ extraction of metals from ores located within the confines of a mine (broken or fractured ore, stope fill, caved material, ores in permeable zones) or in dumps, prepared ore heaps, slag heaps, and tailing ponds on the surface. These materials represent an enormous, untapped, potential source of all types […]
Hydrochloric Acid Leaching of Iron from Aluminous Clays

Pennsylvania has ample reserves of high-alumina clays which are potential sources of alumina, but many of these clays contain large amounts of iron, which makes them unsuitable for treatment by acid processes. Of all the clay minerals tested, only gibbsite exhibits high acid solubility. Kaolinite, diaspore, and boehmite, which are the major alumina-bearing minerals in […]
Removal of Iron from Aluminum Sulfate Solutions
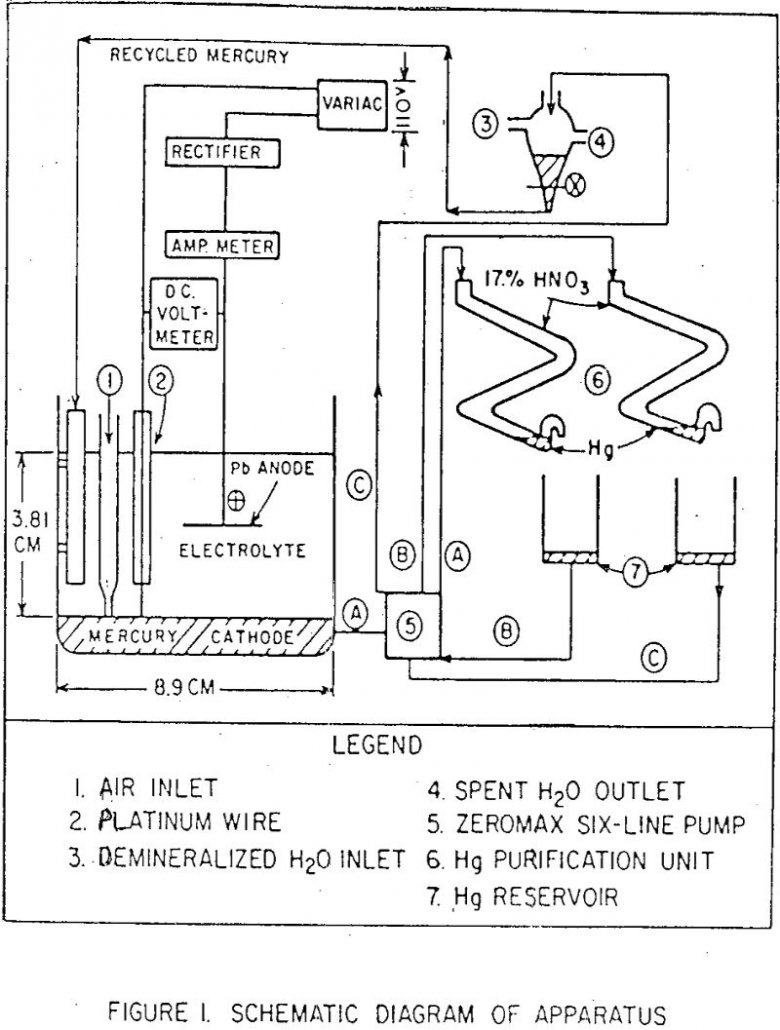
A study on the sulfuric acid extraction of alumina from some Pennsylvania ferruginous clays indicated that the published electrolytic method seems to be more efficient than the known chemical methods for removing iron from the leach liquor. The main disadvantages of the chemical methods are the consumption of excessive amounts of reagents and/or the precipitation […]
