Carbon Monoxide Gas

Take a few crystals of oxalic acid and put them into a dry test-tube, then add a few drops of strong sulphuric acid to them and heat gently over a bunsen flame; an effervescence takes place and a gas is given off, which upon applying a lighted taper to the mouth of the tube will […]
Chlorine Gas
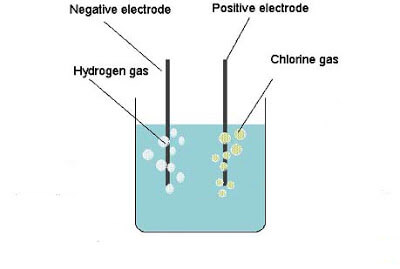
Chlorine is a heavy gas, being about 2½ times heavier than air, so that it can be collected by downward displacement. Weigh out about 30 grams of manganese dioxide and about the same quantity of sodium chloride; mix them well together in a mortar, and transfer to a large flat-bottomed flask. Fix up your apparatus […]
Hydrochloric Acid Gas
Our Hydrochloric Acid Gas experiment starts when you place a little sodium chloride in a test-tube and add a drop or two of strong sulphuric acid; an effervescence follows and a gas is given off with a strongly acid pungent odour. NaCl + H2SO4 = NaHSO4 + HCl Set up your apparatus in the same […]
Bromine Gas
In the preparation of bromine, fix up your apparatus as for the preparation of nitric acid, surrounding the receiver with cold water. Mix about 4 grams of manganese dioxide with 2 grams of potassium bromide, transfer to the retort carefully, and add a little strong sulphuric acid; then replace the stopper in the retort and […]
Iodine Gas
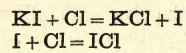
Mix about 1 or 2 grams of potassium iodide with about twice its weight of manganese dioxide, and transfer the mixture to a flask fixed on a retort stand, then add a few c.c. of strong sulphuric acid (do not fit a cork into the flask); violet fumes soon appear, and condense in the neck of […]
Hydrofluoric Acid, Silicon Fluoride
Hydrofluoric acid can be prepared by the action of sulphuric acid on fluorspar (calcium fluoride), but glass apparatus cannot be used in the preparation on account of the action of this gas on the glass. Take a small round piece of sheet lead about 3 inches in diameter, and with the pestle press the centre […]
Sulphur Dioxide Gas
Fix up your apparatus as in the preparation of carbon dioxide, only set your flask on a retort-stand, so that it can be heated. Take about 20 grams of copper shavings or clippings and put them carefully into the flask, add through the thistle funnel about 60 c.c. of strong sulphuric acid, and heat up […]
Sulphur Trioxide Gas
The Sulphur Trioxide Gas Laboratory experiments starts when you pour about 10 c.c. of strong Nordhausen sulphuric acid (H2S2O7) into a small retort to which is attached a receiver; heat the retort carefully, and fumes of sulphur trioxide will pass over and condense to a white crystalline solid in the receiver. H2S2O7 = H2SO4 + […]
Analyse & Assay Refined Lead

In preparing a sample of refined lead for analysis, it is necessary to exercise great care to avoid contamination, as the amounts of the various impurities present in market lead are very small. The lead is cut into convenient-sized pieces, which are flattened out with a hammer, so that, on putting the lead through the […]
Silver Fineness Determination
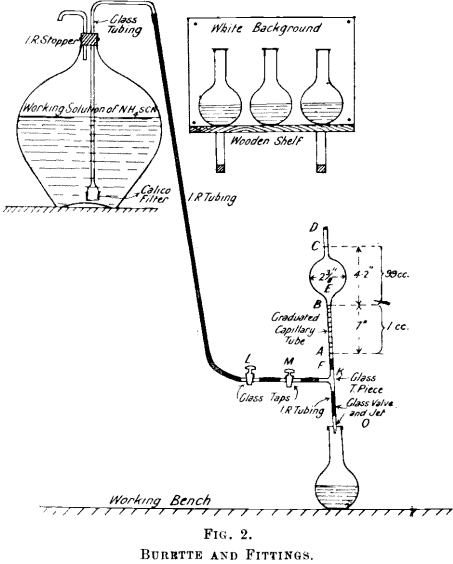
This excellent volumetric method commends itself as a means of estimating the fineness of silver—firstly, owing to the large number of possible impurities which do not affect its accuracy (these impurities include Cu—up to 70%— Au, Pb, Zn, Bi, Cd, Fe, Mn, Sb, and As) ; secondly, the method combines accuracy with speed. The above […]
