Hoisting Ore in Mining
Auxiliaries Actuated by Oil under 135 lb. Pressure When steam is used by the auxiliaries, which operate brakes, clutches, etc., it constitutes an important percentage of the total power used by the engine. The condensation is great and continuous, and since the controlling valves can have no lap, but must be set “line and line,” […]
Ore Tramming in Mining
The ore deposits of the Warren district, in which the mines of the Copper Queen Consolidated Mining Co. are situated, have been described in a number of technical publications, and will not be discussed here in detail. Certain of their characteristics, however, control methods of underground transportation and hoisting of ore. In the Copper Queen […]
Quicksilver Ore Mining & Reduction Method
The low cost of mining was the principal consideration, since, with mercury’s price per pound, the total gross value of the ore did not exceed too much per ton. Square setting and filling was out of the question, so various attempts with cheap methods were made, among them a shrinkage system. None gave satisfaction on account […]
Rotary Rock Drill
In drilling for water and oil to reasonable depths through the generally soft yielding clay and sand formation of the Coastal Plain of Texas, Louisiana, and Mississippi, the rotating method of drilling was adopted, principally on account of the easy and quick penetration, and the low cost of the drilling plant. In favorable ground, free […]
Cost of Stoping for Underground Mining
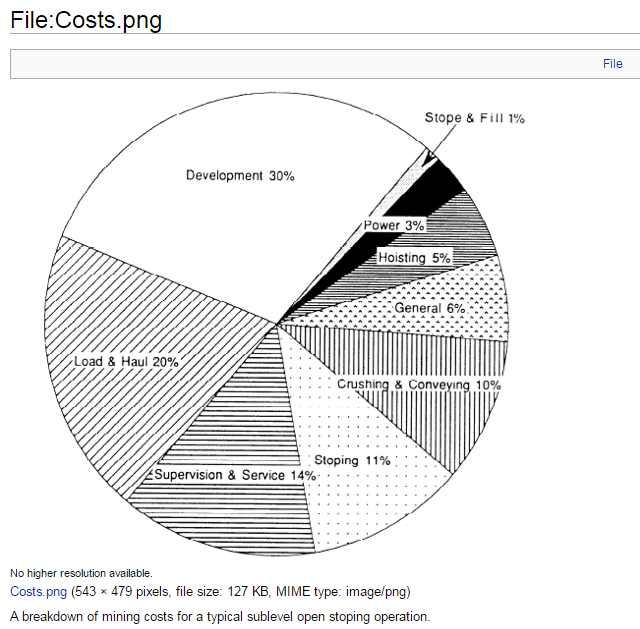
Stoping cost is one of the largest of the items comprising the total cost of producing ore. The cost per ton of ore mined is important but may be overemphasized if the more important cost, that per unit of metal recovered, is thereby overlooked. A given stoping method may give a low cost per ton […]
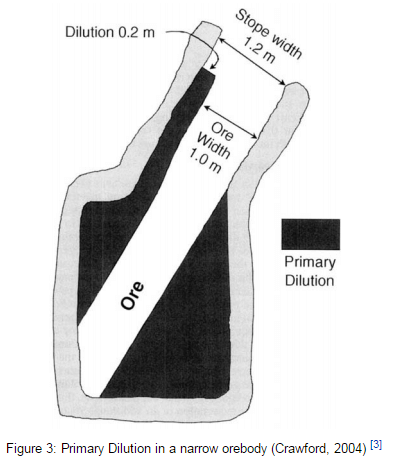
Ore Dilution & Recovery in Mining

Recovery and dilution usually are interrelated; with some methods of stoping a high recovery involves contamination of the ore from the walls or capping, and often clean ore can be obtained only by leaving some ore in the mine. In open-stope mines the greatest loss of ore is that tied up in pillars left for […]
Compare Stoping Methods of Mining
The foregoing descriptions and discussion of the different stoping methods and practices and the accompanying tabulated data indicate the conditions under which they may be applied and serve as a basis for comparing them. Stoping costs will be presented later. Direct comparisons of the different methods are difficult because these methods and variations thereof are […]
Costs of Mining Methods
To compare properly two different methods of mining, it is not wise to attempt to calculate the total cost of each, but rather to compare the costs of those operations that are differently executed in the two methods under consideration. When any method is in operation the proper way to reduce the total cost is […]
Backfilling Mining Stopes
Stope filling has been discussed by Jackson in an earlier paper. Filling long has been recognized as the most effective method of permanently supporting the walls of mine workings and minimizing movement and subsidence. It is used alone in cut-and-fill stoping and in conjunction with framed timbers in square-set stoping for support of weak walls […]
Drilling & Blasting of Underground Stopes
Drilling in stopes is done with pneumatic-feed stopers, light handheld hammer drills of the jackhammer type and heavier plugger machines, drifters of the Leyner type mounted on crossbars or on columns, and drifters (and, now, only occasionally, piston drills) mounted on tripods; more recently, with the more extensive use of bort instead of carbon for […]
