Copper Electrolite Solution Filtration
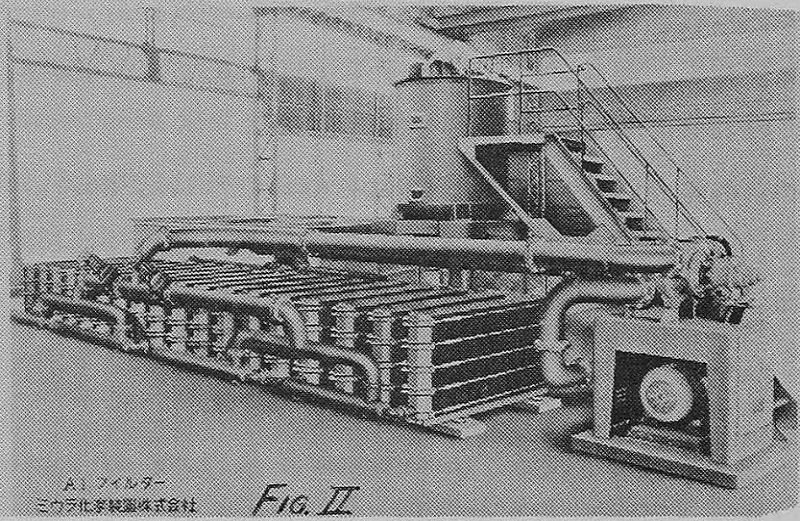
The electrolyte in-between the active electrodes must be purged with higher velocities to maintain a high concentration of the desirable copper ion in the liquid film adjacent to the cathode and the sulfate ion in the liquid film at the anode. This higher velocity also carries away from the cathode the undesirable impurities released from […]
Grinding Circuit Control – South Africa
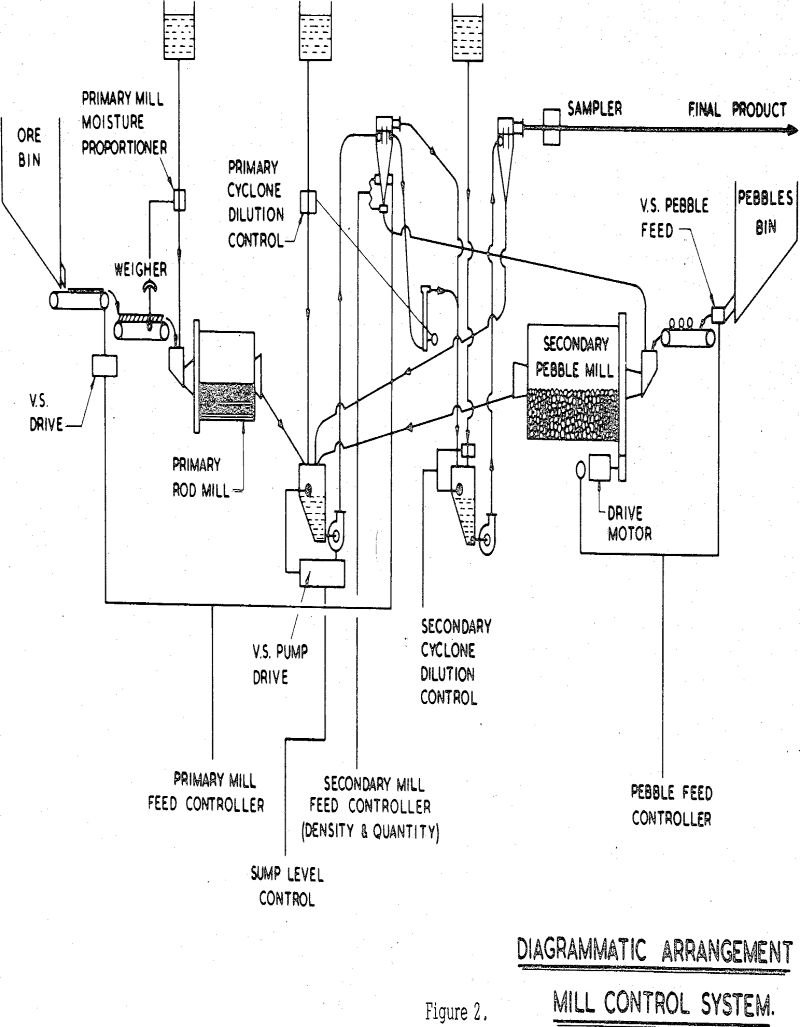
In a minerals-recovery context, the object of exercising control over milling operations must be threefold. To achieve maximum recovery at minimum operating costs and making maximum use of installed equipment. Milling is one of a sequence of operations which have as their objective the economic recovery of minerals from mined ores. All operations in the […]
Using a Crusher to Control Autogenous Grinding Circuit
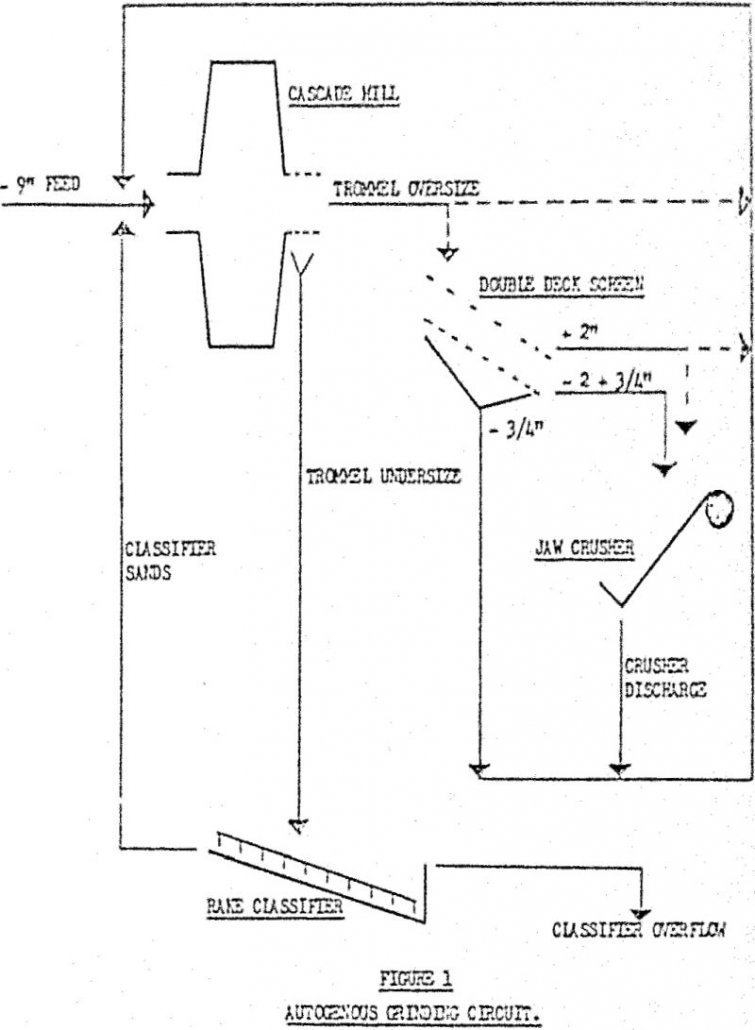
In an autogenous grinding circuit in which feed at approximately nine inches top size is reduced to a size suitable for subsequent processing, the build-up of a “critical size” fraction in the media causes problems. A “critical size” fraction has been defined as, “media too small to effect reduction by impact grinding of ore coarser […]
Feed-Forward Control for Grinding Circuits
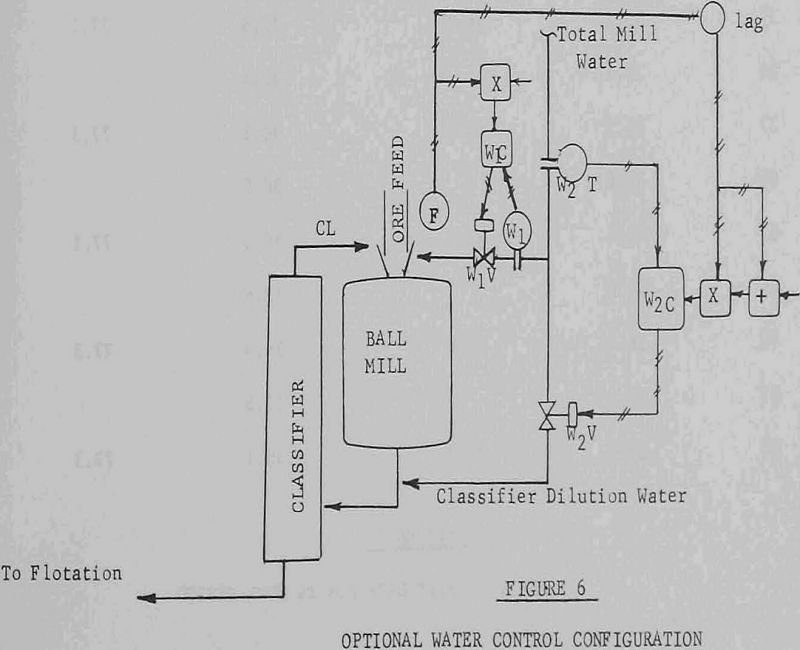
Feed-forward control ( i.e. the forward flow of information in a control system ) is a simple and flexible approach to over-all control of a ball mill-rake classifier grinding circuit. The system described here uses mill power, feed rate, mill dilution water flow rate, and classifier dilution water flow rate only, to control mill load, […]
Large Tonnage Fine Crushing Plants – Trade-Off Study
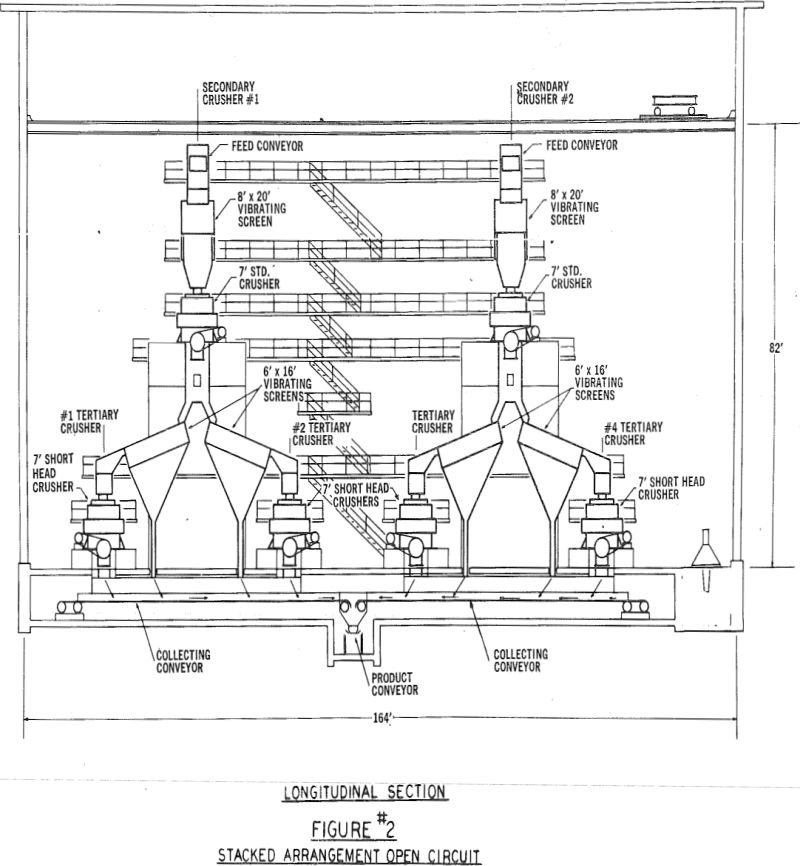
Common practice for size reduction of run-of-mine or run-of-pit ore in preparation for subsequent treatment utilizes a three-stage system. First stage, or primary breaking is generally carried out with jaw or gyratory crushers. The usual output from this stage provides a feed for fine crushing in the size range of 6 to 10 inches. Factors […]
Chromium Electroplating
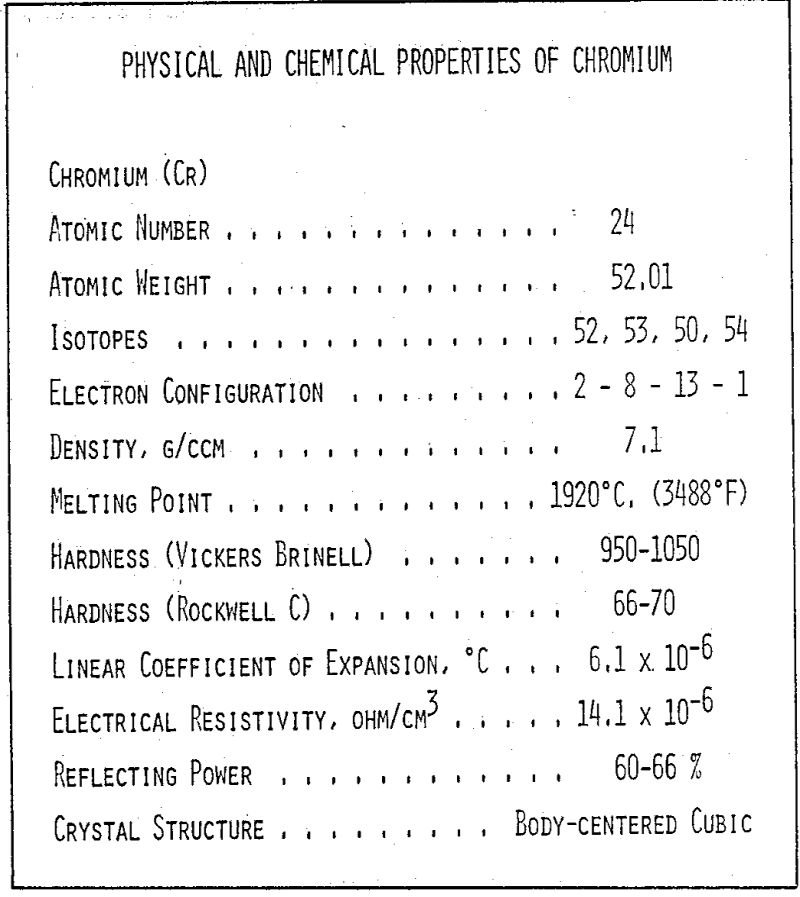
Electroplating is a widely utilized but little understood process, the fact that the average person is in contact with dozens of plated items daily without even being aware that they are electroplated is evidence of the success of the process, although a complete explanation of electrodeposition involves thermodynamics and modern theories of bonding and catalytic […]
Bulk Sampling Method
Bulk sampling is define as the “process of extracting a small fraction of material from a large bulk sufficiently representative for the intended purpose”. Today’s pressing need for simple, effective and reliable sampling systems is intensified by the growing demand for quality control as a means to cope with inflation, competition and rapidly increasing consumption […]
Blasting Mechanics
The term “powder factor” is almost universally accepted as the measure of the efficiency of a blasting program. It represents the economics of blasting since it designates quantity of explosive (thereby providing quality control in rock fragmentation) in terms of the associated volume broken. It is the wide use of this concept that explains the […]
Conveyor Belt Scale Design
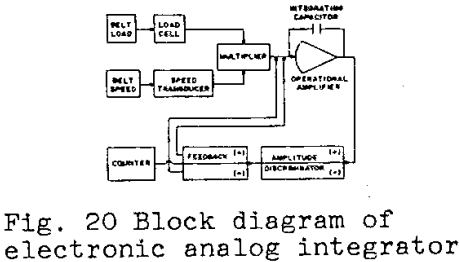
Weight may be defined as the gravitational attraction or earthpull on a body (mass). Thus, from a practical viewpoint, a scale or other form of weighing device is a means for determining mass. Weighing devices fall into two principal categories: (1) gravimetric; and (2) non-gravimetric or nuclear devices. At present, after many centuries of use, […]
Using Platinum Electrodes to Indicate Redox Potential

Platinum electrodes are not inert as originally thought to be. The reactivity of platinum electrodes can explain their erratic behavior in many electrochemical measurements of metallurgical interest, e.g., in flotation systems, streaming potential measurements, contact-angle measurements, and in leaching systems. Experimental Procedure A rotating platinum electrode was used in many of the measurements to study […]
