General Solubility Rule

The 8 General Solubility Rules. These are the reason why we can determine clearly the endpoints of reactions. For instance the endpoint of the titration of AgNO3 against Cyanide is determined by the indicator KI. This is because after the endpoint the excess Ag+ in solution combines with I- to form Agl which is insoluble. […]
Wet Lead Assay Method
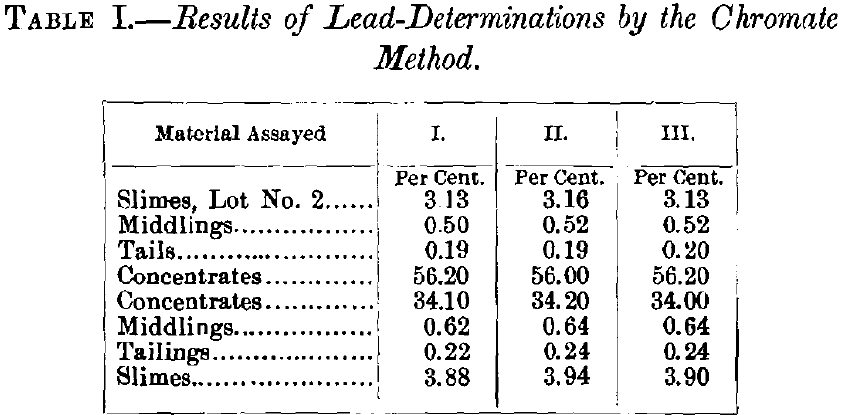
For a number of years I have used for the commercial wet assay of lead generally the ammonium molybdate, and occasionally the ferrocyanide method. These well-known methods need no detailed description here. In the ore-selling and ore-buying establishments of the West, 90%, of all wet lead-assays are made by one or the other, and at […]
Silver Sulphide Assaying

There has been considerable discussion of late as to the best assay method for determining the silver-contents of sulphides of silver resulting from the leaching of silver-ores, and also as to the relative merits of the crucible and the scorification-method for the determination of the silver-contents of ores. Owing to the great depression in the silver-market, these […]
Alundum Extraction-Thimble Used in the Copper Assaying
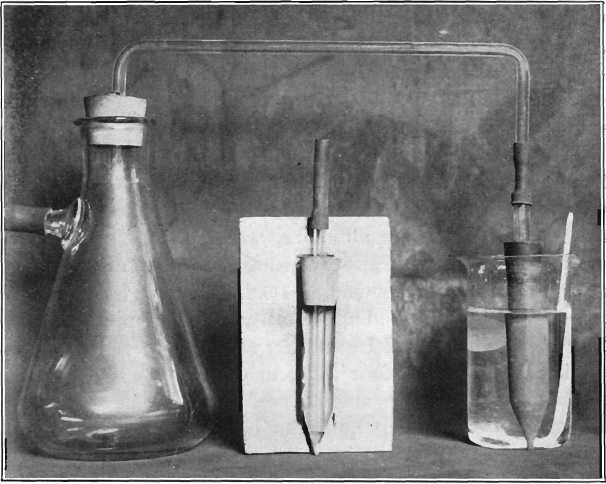
The photograph, Fig. 1, shows the apparatus a little less than half size, consisting of a filtering-flask fitted with rubber stopper through which passes a bent glass tube, and an extraction-thimble fitted with rubber stopper through which passes a glass tube of 0.25-inch bore. Both tubes are connected by a short piece of rubber tubing. […]
Gold Solubility in Nitric Acid of Copper-Bullions-Alloys
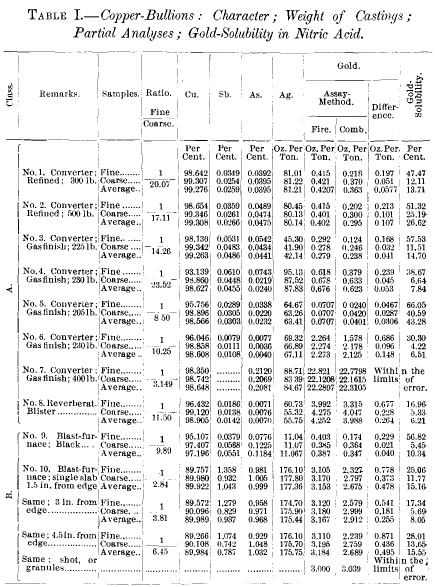
In a paper, entitled A Uniform Method for the Assay of Copper Material for Gold and Silver, A. R. Ledoux invited the assayers of this country to contribute to a symposium, in which the results of their assays of given samples of copper-matte and metallic copper would be made comparable. This symposium appeared about one […]
Flux
Methods of Precipitate Refining FLUXES FOR METALLURGY Recovery of Precious and Secondary Metals from Electrolytic Copper Refining PRECIOUS METALS REFINING PRACTICE CALCULATING-DETERMINING SLAG DENSITY Flux SLAGS AND FLUXES IN PYROMETALLURGICAL PROCESSES
Recovering Silver from Photographic Materials

The Dangers Of Nitric Acid Nitric acid can kill if swallowed! Nitric acid can be absorbed through the skin, causing nitric acid poisoning. WEAR RUBBER GLOVES! Always use nitric acid in a well-ventilated area. Do not breathe the fumes! Nitric acid can ruin your clothes and shoes. Always add nitric acid to water. Never add […]
Arsenic Determination/Assaying
An assay method to measure arsenic using a MHS-10 and AA200 and Mercury Hydride System. Sample Preparation -Sample Weights to be used: Heads…………….. 0.3 g Cu Con……………..0.1 g Zn Con……………..0.2 g Knelson…………….0.3 g Core…………………0.1 g STANDARD MP-1a ……………0.1 g Cu Con Check Sample………..0.1 g Weigh the samples into 250 ml low form beakers. Add 10 mL Acid […]
Sodium Borohydride Make-up
Sodium Borohydride Solution Make-up Weigh 5 g of Sodium Borohydride and 2.5 g of KOH into a glass funnel inserted into 250 mL volumetric flask. Add distilled water to rinse the Sodium Borohydride / KOH into the flask. (If you are making a 10 g batch, dissolve the reagents in a beaker prior to transferring […]
Analysis for (Cu, Pb, Zn, Fe, Cd) by ATOMIC ABSORPTION
Sample Preparation for assaying Copper/Lead/Zinc/Iron/Cadmium by AA: Weight 0.1 – 0.25 g of sample into a 300 ml tall form beaker Add 5 ml Conc. HCL + 5ml Conc. HNO3. Place samples on a padded hotplate in a fume-hood. Turn the hotplate from 1 switch to 2 switches. Bring to dryness. Avoid sample spitting by […]
