Froth Flotation Process
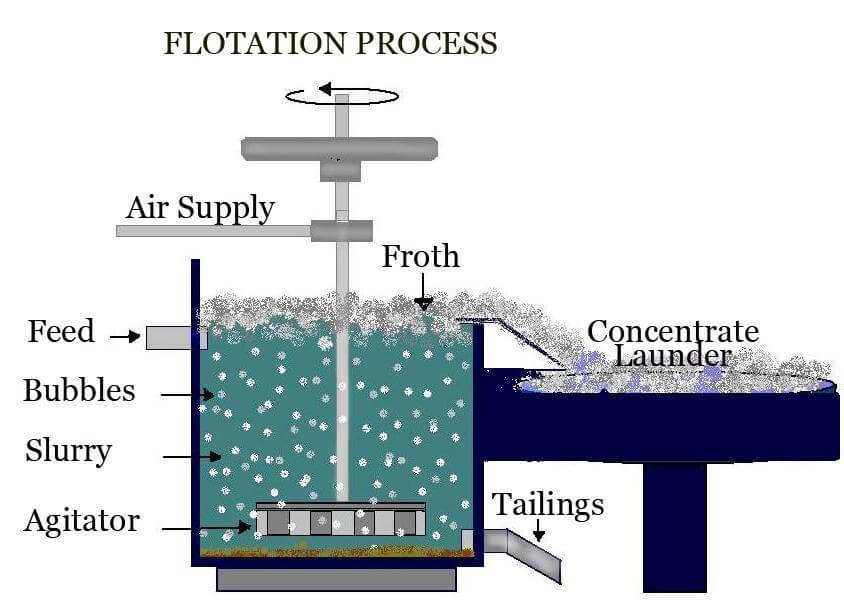
The Froth Flotation Process is about taking advantage of the natural hydrophobicity of liberated (well ground) minerals/metals and making/playing on making them hydrophobic (water-repel) individually to carefully separate them from one another and the slurry they are in. For this purpose we use chemicals/reagents: Frothers (MIBC) is what allows the formation of air bubbles. Think […]
Sulfide Ore Treatment Gold – Silver – Copper – Cobalt – Zinc Recovery
A procedure was developed for recovering gold, silver, cobalt, copper, and zinc from a massive sulfide ore by a hydro-metallurgical process. The procedure consists of (1) oxygen pressure leaching; (2) iron, arsenic, and copper removal from the leach solution by precipitation; (3) selective extraction of cobalt and zinc from solution; (4) electro-deposition of the cobalt […]
Electronic Ore Sorting Copper Ore
This process uses electronic ore sorting or “pre-concentration” as an added step before normal concentration to develop a processing system for the native copper ores. Successful ore sorting can lead to cost reductions in the following areas: Materials handling, and hoisting (if sorting is done underground). Capital and milling operations. Mill tailings disposal, as well as […]
Acid Leaching – Copper Ore Treatment Method
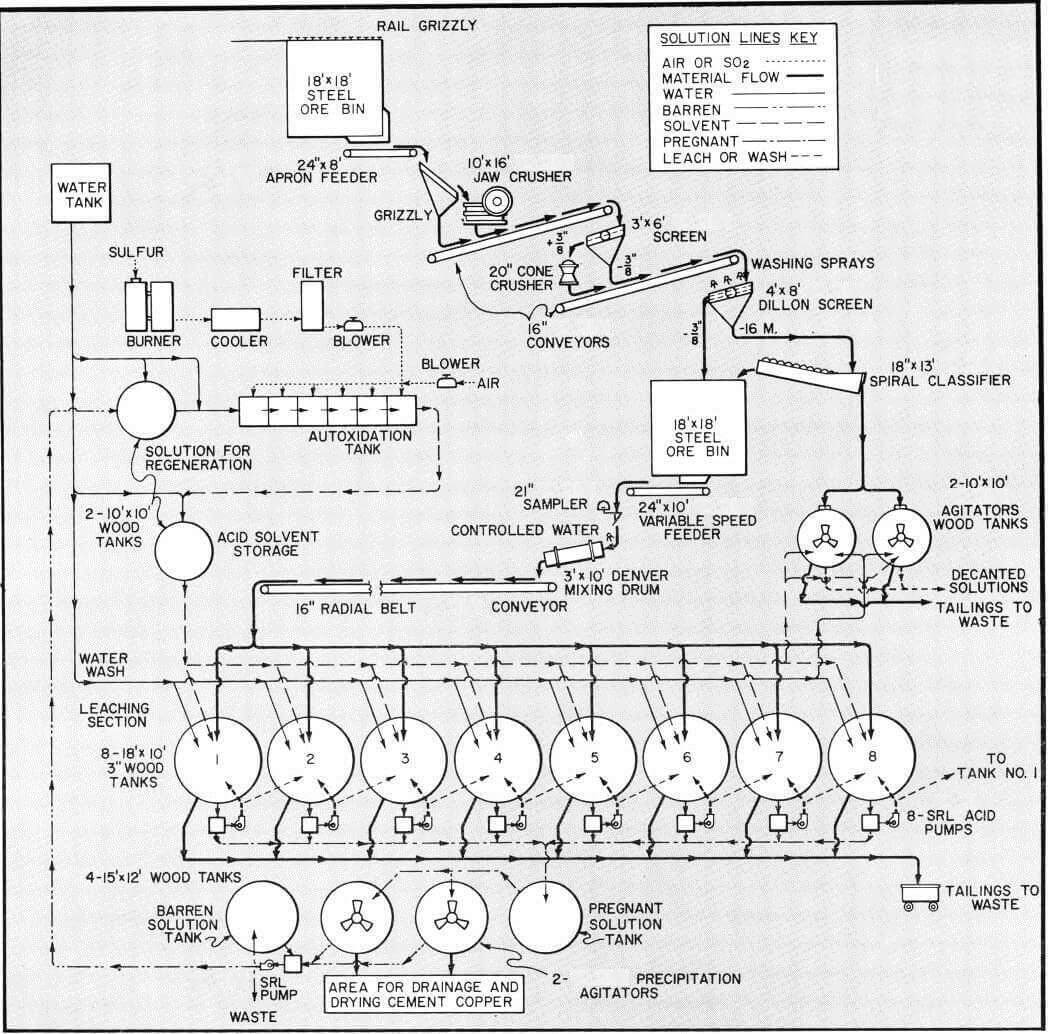
The treatment of copper ores, both oxides and sulfides by means of flotation, hydrometallurgy or other processes has been well established for many years. Flotation has been applied generally to the treatment of sulfide ores, both in small and large scale operations. Hydrometallurgical methods alone or in combination with flotation have mainly been applied to […]
Copper Electrolytic Refining Process Explained
Experiments on a Porphyry Copper Ore: This research was done partly in the non-ferrous laboratory of the Department of Metallurgy of Columbia University, under the direction of Dr. Edward F. Kern, and completed elsewhere. Acknowledgment is due to Prof. Arthur L. Walker, Dr. Edward F. Kern and Dr. William Campbell of the Department of Metallurgy, for their […]
Method of Precipitating Copper
During the last few years we have been doing considerable experimenting on methods of precipitating copper. The first patent on precipitating from sulphate solutions by heating with SO2 under pressure was taken out by us (U. S. Pat. 723,949). This reaction, CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O = Cu + 2H2SO4, is interesting, but there are […]
Leaching Copper: Iron form Electrolyte
The solvent we would use; how we would precipitate the copper from the solution, and what we would do with the iron in the electrolyte. Without going into the details of the reasons, we decided that sulphuric acid would be the most satisfactory solvent and that we would recover the copper from the solutions by […]
How to Recover Copper from Solution
At the beginning of our investigation we seriously considered what I called the “brutal method” of leaching, namely, the manufacture of sulphuric acid, the solution of the copper from the ore with such acid, and the precipitation of the copper by metallic iron, with the resultant complete, or nearly complete, destruction of both acid and […]
Overpoling Electrolytic Copper
The current meaning of the term, copper overpoled in the reverberatory furnace, is that poling has been carried beyond the tough-pitch stage, with the result that the reduction has been carried too far, causing the copper to become porous and brittle, and thus unfit for industrial purposes. It will be shown that the brittleness of […]
Assaying Gold & Silver from Copper Alloys
The so-called “combination method” is generally used in assaying bar copper for silver. It has been modified from time to time. Briefly outlined as now practiced, it is as follows: One A. T. of the borings is dissolved in dilute nitric acid. When solution is complete the liquid is boiled and then filtered to remove […]
