Small Gyratory Crushers
The Allis-Chalmers (Type R) Small Gyratory Reduction Crusher is designed for large capacity, fine crushing and incorporates many improvements over other gyratory type crushers previously manufactured by this company. The most distinctive feature of the Type R Crusher is the built-in, oil filled hydraulic jack used for fast, positive change of crusher setting while crusher […]
Effect of Copper Sulfate on Zinc Sphalerite Flotation
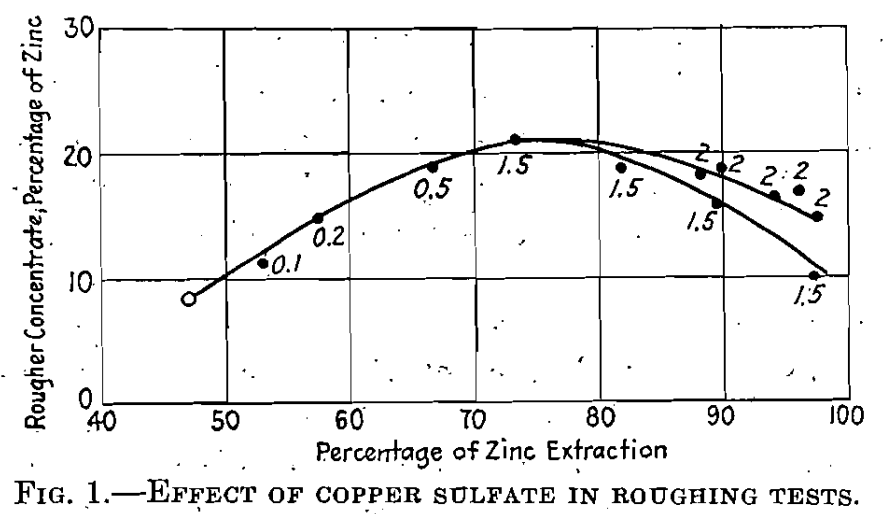
As an example of the beneficial effect of copper sulfate in the activation of zinc sphalerite toward flotation, the series of results shown in Fig. 1 is of interest. These represent rougher tests on a sample of heavy pyritic ore. The particular sample in question contained about 5.6% zinc as marmatite; and was treated in a circuit […]
Rocks and Mineral Identification Table
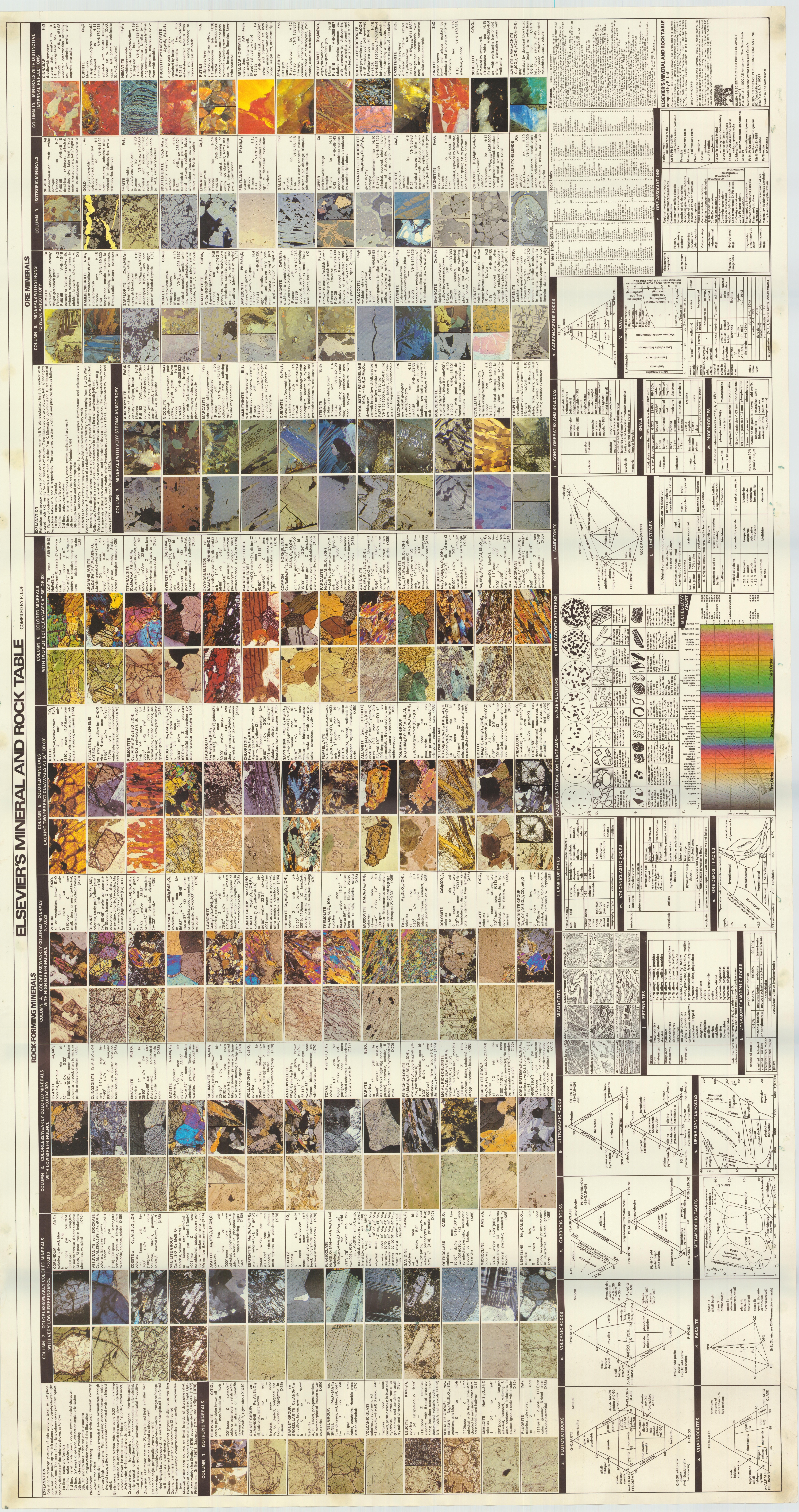
It is strongly recommended to the student of this book that he obtain specimens of rock, not labelled, and study their features with a view to naming them. The Table for Identification of Rocks will help in naming them. It may here be mentioned that the identification of rocks presents peculiar difficulties. Rocks are not […]
Mica Mineral Types
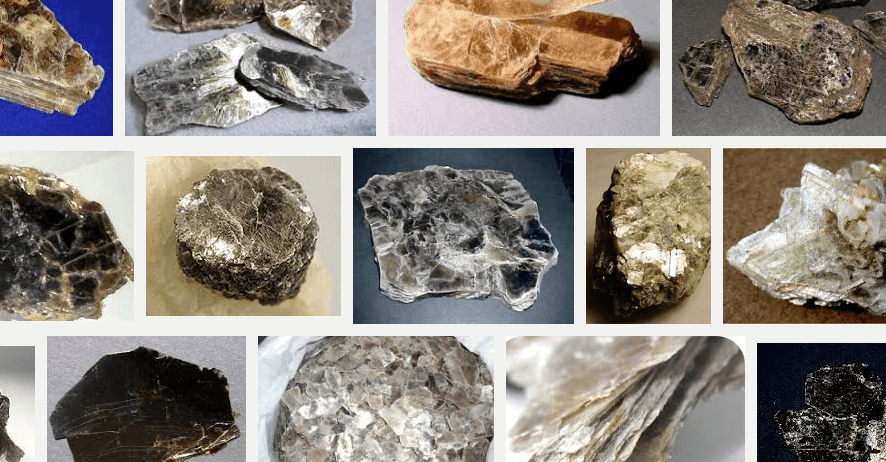

Mica type minerals make a group of silicates of alumina, with potash, iron, magnesia; characterized by easy cleavage into thin, flexible, elastic sheets. Mica gives off water when strongly heated. Muscovite Muscovite, or white mica, (K,H) AlSiO4, is colorless, sometimes gray, brown, ruby, etc.; powder, white; luster, glassy or pearly; H = 2 to 2.5; G […]
Zirconium Minerals

Zircon and Zirconium Minerals; ZrSiO4 are colorless, pale yellow, grayish, yellowish green, brownish yellow, reddish brown; powder, white or nearly so; luster, like diamond, or glassy; H = 7.5; G = 4.68 to 4.70; crystals, tetragonal; cleavage, imperfect; composition silicate of zirconia (ZrO2).—Found in igneous rocks of the acidic kind, for example, syenite, and especially in […]
Pyroxene Mineral Group

The mineral pyroxene is a name applied to a group of silicates that are similar in composition to the hornblende group, but not so often containing soda and potash. Cleavage pieces show angles of 93° and 87°, thus making nearly square edges, a clear distinction between them and the sharp and obtuse edges of cleavage […]
Group Different Feldspars Minerals

Feldspars constitute a group of similar minerals, which may be described as silicates of aluminum and either potash or soda or lime. Color, white, or pale shades of yellow, red, or green, sometimes gray; powder, white; luster, glassy; usually opaque; H = 6 to 6.5; G = 2.55 to 2.75; crystals, in the monoclinic system (orthoclase) […]
Cryolite

Cryolite; Na3AlF6. — Color, snow-white or ice-like, sometimes reddish, brownish, or even black; luster, glassy and greasy; H = 2.5; G = 2.95 to 3; cleavage, perfect; looks rather like quartz, but distinguished by softness and good cleavage; composition, a fluoride of sodium and aluminum. Used as a solvent in the manufacture of aluminum. Aluminum […]
List Antimony Minerals Group

Tetrahedrite or Gray Copper Ore Part of the list of all Antimony Minerals Group is Cu2Sb8S7. — Color, grayish or grayish black; powder, grayish or grayish black, sometimes inclining to brown or reddish; luster, metallic; H = 3 to 4; G=4.4 to 5.1; no cleavage; composition, about 52% copper, and, in addition to the antimony […]
List Arsenides Minerals

Arsenide minerals are compounds of the metals with arsenic. The list of nearly all these minerals have a metallic luster, i.e., the peculiar shining appearance of metals. Smaltite CoAs2. — Color, tin-white to steel- gray; the white color is seen in the larger crystals, but since smaltite is usually massive (i. e., in a mass […]
