Cyanide Regeneration Processes and Methods

Cyanide regeneration offers a practical means of overcoming the otherwise heavy cyanide consumption frequently encountered in the treatment of gold and, especially, silver ores, where cyanicides (cyanide consuming minerals) are present. Miscellaneous processes used for the extraction of gold and silver values by hydrometallurgical means are also discussed in this chapter. These include the carbon-cyanidation, […]
Cyanide Gold Dissolution

Manufacturing Cyanide Sodium cyanide is a white, deliquescent, crystalline material easily soluble in water. The basic sources are alkalis or alkaline earths, atmospheric nitrogen, and carbon. In the United States it is derived (1) from sodamide which is produced from sodium and ammonia. The sodamide is heated with charcoal, and the resultant soda cyanamid is […]
Amalgamation Process of Gold

The use of direct amalgamation following stamps or primary mills and the use of barrel amalgamation for treating jig and corduroy concentrates. Precipitation of gold and silver on zinc dust or on zinc shavings is fully treated, from the clarification and de-aeration of cyanide solutions to the cleanup and melting of the bullion. The use of […]
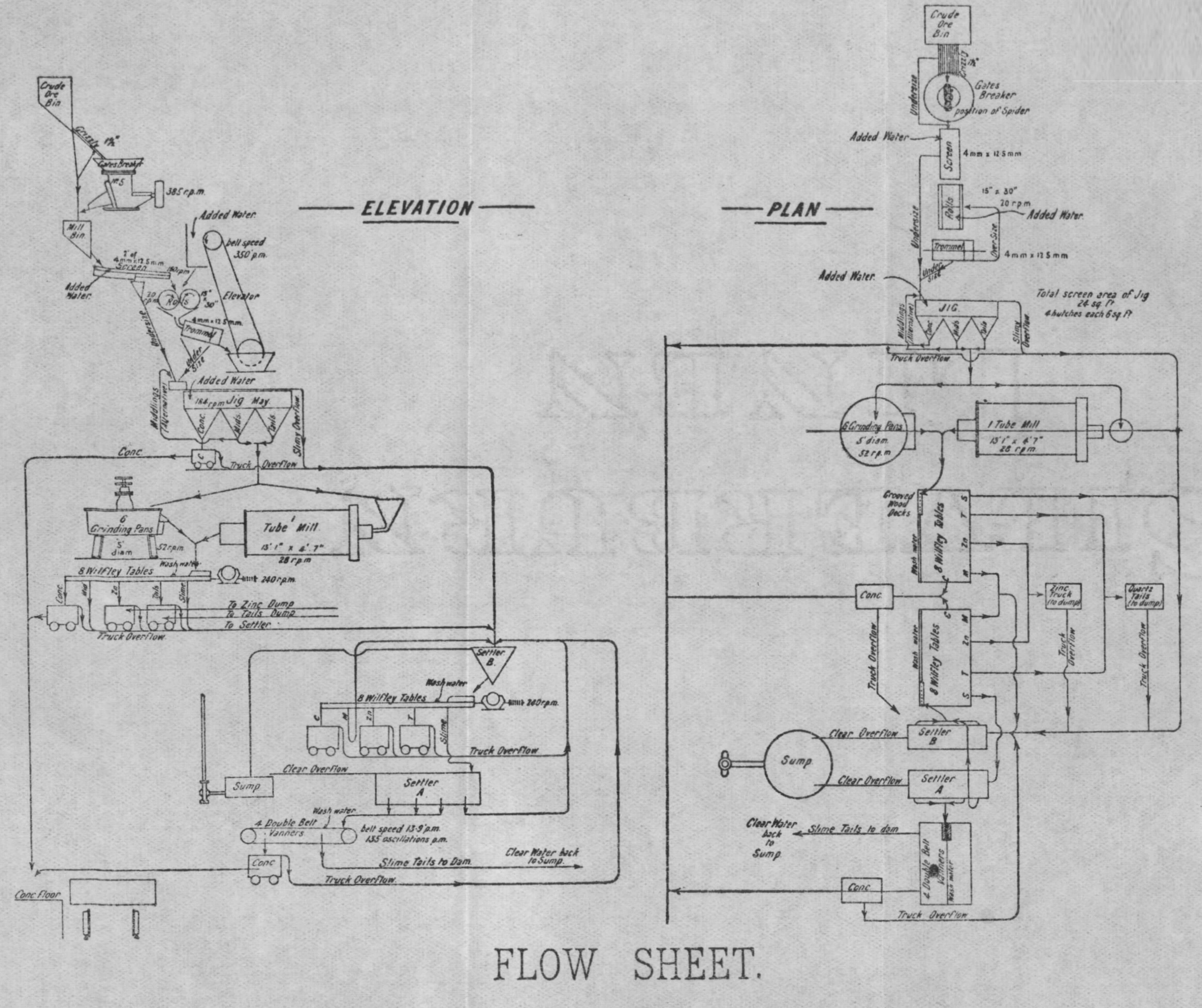
Long Ball Mills
Estimating Ore Reserves
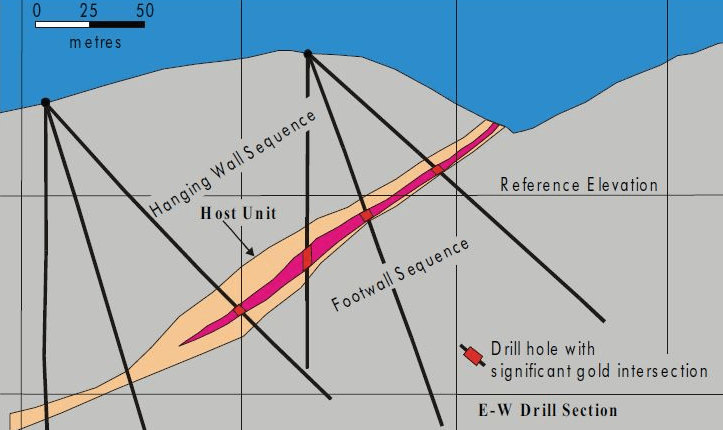
The methods of sampling and ore reserve estimating used can fall into two divisions because of the difference in occurrence, manner of prospecting, and methods of mining: that for the underground operations and that for a shovel operations. The orebodies may be divided into three classes: Replacements of limestone, replacements of porphyry, and replacements of contact breccia. […]
Gold Ore Roasting Techniques

In the case of many complex gold and silver ores roasting before cyanidation is essential if satisfactory extraction of the precious metals is to be obtained. In such cases no practical amount of grinding or prolonged contacting of the raw ore with cyanide solution will affect more than a certain low extraction; in other cases, […]
Gold Metallurgy & Leaching in Cyanicides

Cyanidation as applied to ordinary gold and silver ores is a relatively simple process. When cyanicides {cyanide-consuming elements) are encountered in small amounts in the treatment of such ores, the various schemes already discussed, such as use of a lead salt or wasting barren solution, can usually be resorted to and successful operation maintained. When, […]
Gold Flotation
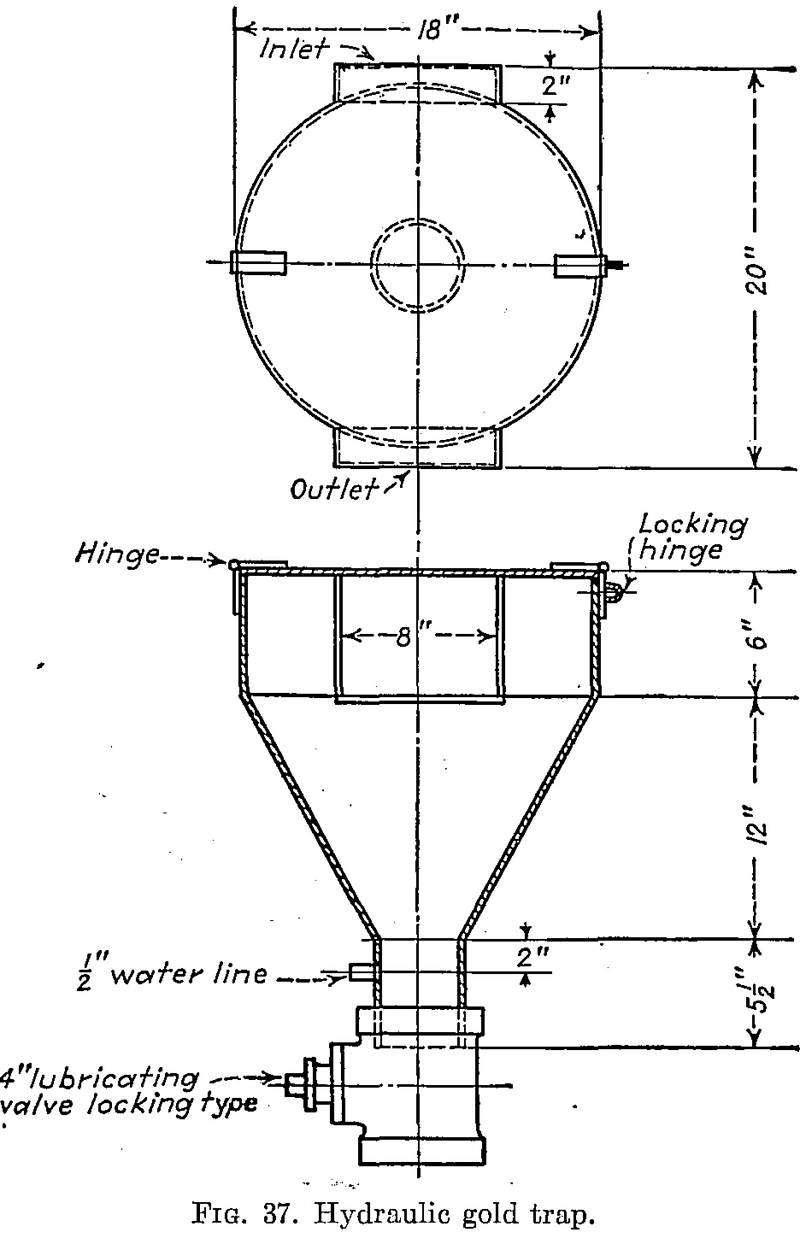
Though the gold recovery methods previously discussed usually catch the coarser particles of sulphides in the ore and thus indirectly recover some of the gold associated with these and other heavy minerals, they are not primarily designed for sulphide recovery. Where a high sulphide recovery is demanded, flotation methods are now in general use, but […]
CCD Filtration System

Slime treatment, as commonly used by metallurgical engineers, includes thickening, agitation, and filtering and as applied, to cyanidation also includes washing by continuous countercurrent decantation (C.C.D.) and/or filters. “Slime” is the general term used to describe the finer portion of pulp in a combination sand and slime-treatment plant and is usually finer than 100 mesh. […]
Vat Leaching of Finely Crushed Gold Ore

Vat leaching is carried out in vats ranging in capacity from 30 to 1200 tons. Sand for leaching is separated from slime in cones, V boxes, classifiers, and in collecting vats filled by distributors—the overflow in each case being slime or finer portion of the ore. As a rule, leaching is a simple process, involving […]
