 Two general classifications of gearing are used for ball Mill drives. These are the spur gear and the helical gear. Helical gearing may be either of the single helical or double helical (Herringbone) design.
Two general classifications of gearing are used for ball Mill drives. These are the spur gear and the helical gear. Helical gearing may be either of the single helical or double helical (Herringbone) design.
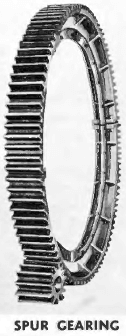
SPUR GEARS
These are generally furnished on the smaller diameter mills using V-belt drives or reducer drives. Spur gears and pinions are cut with teeth of the full depth involute tooth form thus assuring maximum tooth strength and long wearing life. The main gear is cut from a special Meehanite metal casting and is constructed split and reversible. The pinion is cut from a steel forging bored, keyseated and mounted on the pinion shaft. The pinion is also reversible.
All spur gears and pinions are carefully machined and the teeth are accurately cut to obtain proper tooth profile and spacing, thereby utilizing the maximum potential tooth strength and wear rating.
HELICAL GEARS
Helical gears are used for the larger diameter mills which are to be direct connected to a low speed motor. There are primarily two main reasons for use of helical gearing on this drive arrangement. F irst, in order to permit higher gear ratios than are obtainable from a practical standpoint with use of the spur gear. This in turn permits the use of a higher speed and less expensive motor. Second; in order to take advantage of the smoother continuous overlapping tooth action of helical gearing so essential where there is no intermediate transmission element such as a V-belt drive or speed reducer.
irst, in order to permit higher gear ratios than are obtainable from a practical standpoint with use of the spur gear. This in turn permits the use of a higher speed and less expensive motor. Second; in order to take advantage of the smoother continuous overlapping tooth action of helical gearing so essential where there is no intermediate transmission element such as a V-belt drive or speed reducer.
All helical gears and pinions are cut with the full depth tooth form. The main gear is cut from a special gear steel casting and is made split and reversible. The pinion, usually integral with the pinion shaft, is cut from an alloy steel forging and heat treated prior to cutting the teeth. The pinion shaft is double ended so it is also reversible.
All ball Mill gearing is designed in accordance with sound engineering principles and at the same time with consideration given to the long range economics involved. Extremes such as excessively high ratios or a very low number of teeth in the pinion are always avoided. This is done to provide allowance for such later changes in power or capacity requirements as changing the mill speed through the use of different sized pinions. Therefore, complete replacement of the main gear and pinion is not required.
Furthermore, all gears and pinions are of ample proportion to withstand the dynamic overloads encountered in this service and to provide satisfactory performance under the conditions peculiar to mill operation.
PINION SHAFTS
As mentioned above pinion shafts used with helical gearing are usually forged integral with the pinion. For other drives the pinion shaft is carefully turned and key-seated to accommodate the pinion for press fit.
GEAR GUARD
A plate steel gear guard, generally in the form of a full circle is furnished to protect the gear from entrance of dirt or foreign material It is furnished with an inspection door and a door to be used for the application of gear lubricant. It is made dust resistant for operations under extremely dirty and dusty conditions. The gear guards are designed to be mounted independently of the mill proper.
SPECIAL FEATURES
Where specific conditions call for special features, these can be provided. For example: Splitters for distributing mill discharge to two separate classifiers; Rubber lining of heads, shells or feeders for resistance against abrasion or corrosion; sectionalizing for transportation restrictions special designs for metal reclaiming work; discharge trommels and elevators; heavy duty scrubber applications.

