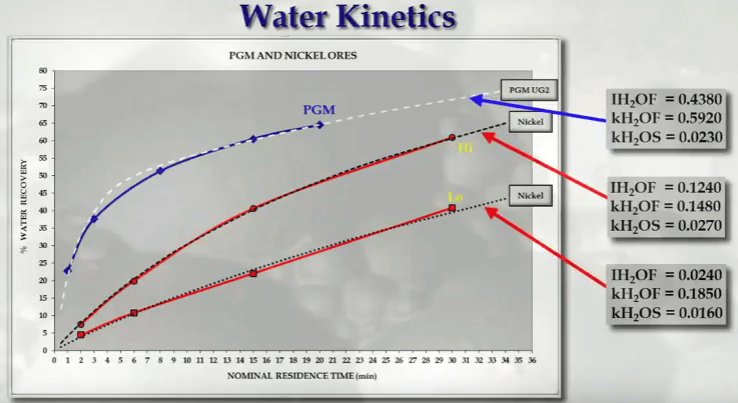
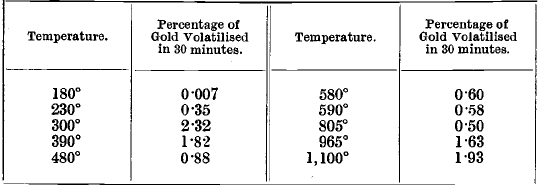
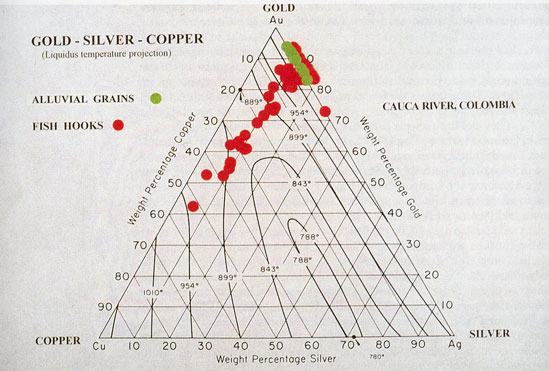
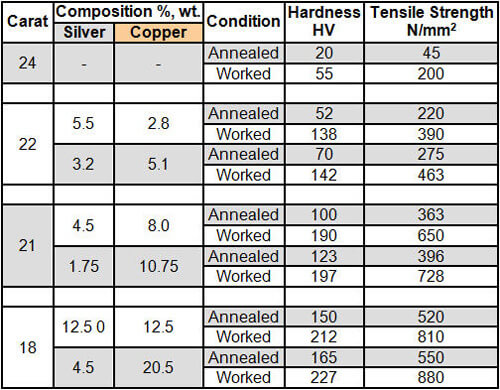
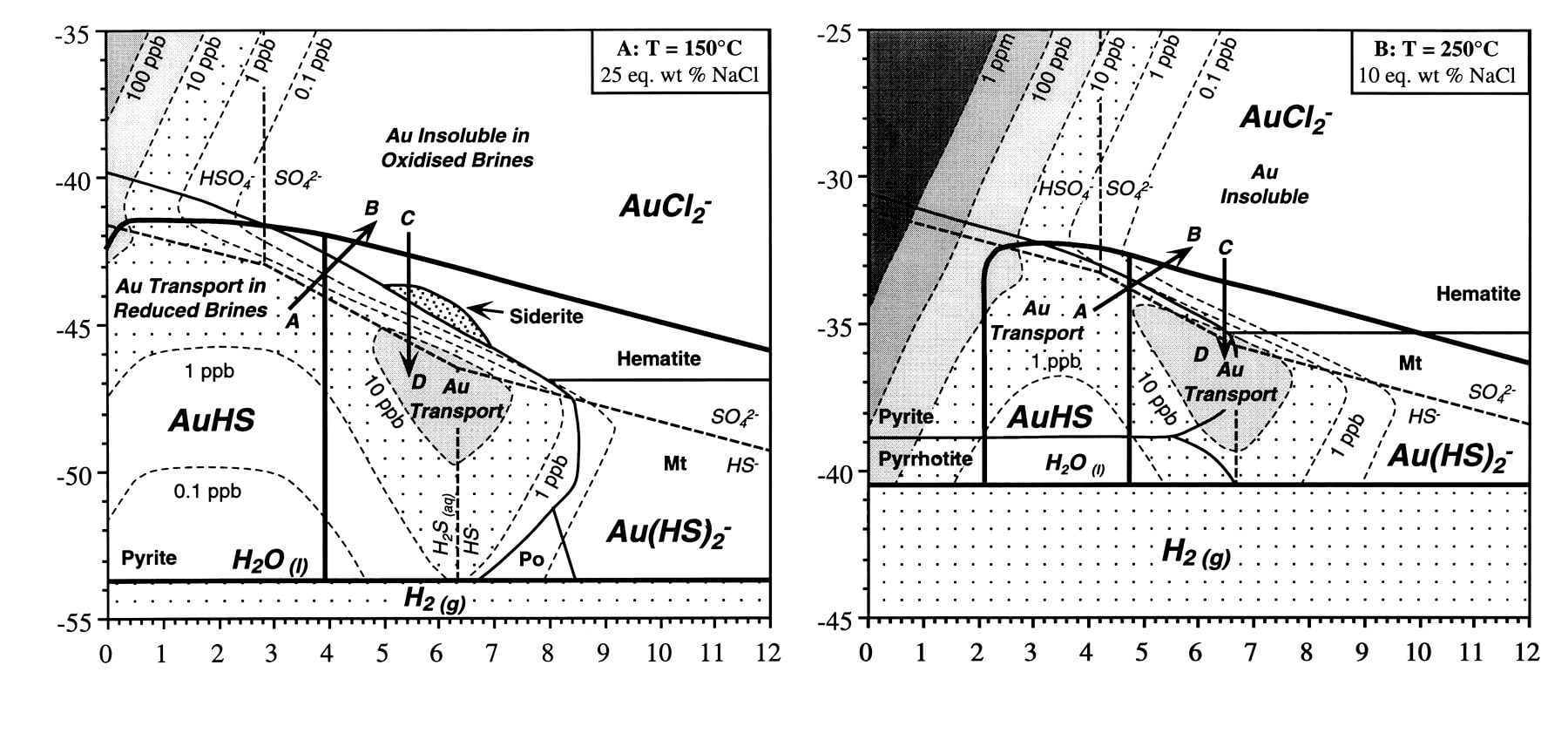
Flotation Kinetics: Mass & Water Recovery VS Entrainment & Mineralogy
This covers the recovery of entrained solids with water and the relationship between mineralogy and flotation performance; both are described in terms of flotation kinetics. The starting points for the relationship between mass and water recovery other products of a flotation rate test. In addition to concentrate mass, metal or mineral and floatable gangue. If … Read more