
Gold Sulfite
Sulphites of Gold, alkaline sulphites, or sulphur dioxide, which reduce gold trichloride easily, do not produce the same effect on a solution of an alkaline

Sulphites of Gold, alkaline sulphites, or sulphur dioxide, which reduce gold trichloride easily, do not produce the same effect on a solution of an alkaline
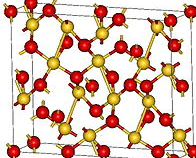
Aurous Oxide, Au2O This gold oxide is prepared by decomposing aurous chloride, AuCl, or the corresponding bromide by potash in the cold (Berzelius) when a

Cyanogen and gold unite in two proportions, forming aurous and auric cyanides, but the latter is only known with certainty in combination. Aurous Cyanide, AuCy,

Gold Protobromide, AuBr, is a yellowish-green powder obtained by heating the tribromide to about 140°. It is insoluble in water, but is decomposed by it,
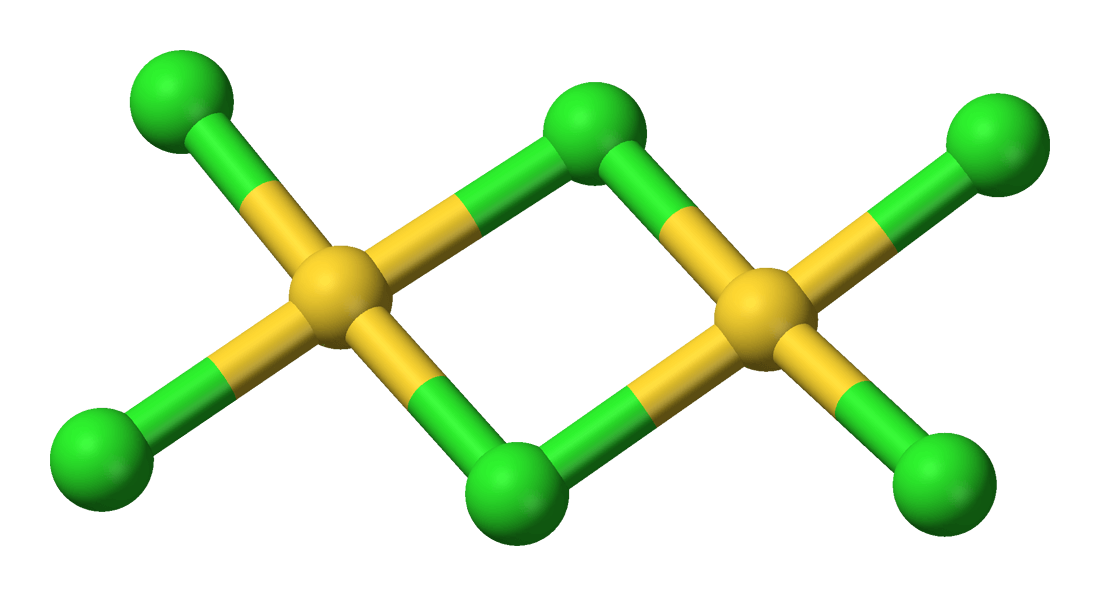
Gold Monochloride or Aurous Gold Chloride “AuCl” is a salt is prepared by heating the trichloride to 185° in air for twelve hours. It is non-volatile and

The boiling point of pure gold has not been determined; calculated according to Wiebe’s formula it would be about 2,240°, or nearly 500° above the
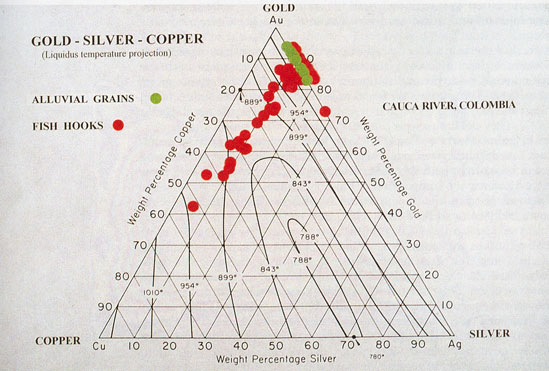
Gold and Copper Alloys dissolve in one another in all proportions, forming a complete series of homogeneous alloys, which are less malleable, harder, more elastic,
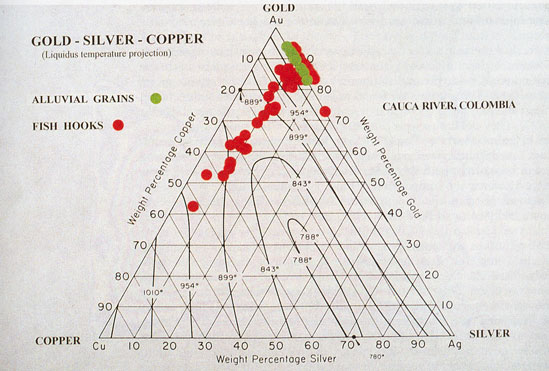
Gold and silver unite in all proportions, yielding alloys which are harder, more fusible, and more elastic than either metal. The hardest is that containing

Gold can alloy with almost all other metals, but most of the bodies thus formed are of little or no practical importance. Tin, zinc, arsenic
Gold is readily soluble in aqua regia, or in any other mixture producing nascent chlorine, among such mixtures being solutions of: nitrates, chlorides, and sulphates