Cassiterite & Wolfram and Scheelite Leaching – Oxide
Natural cassiterite on account of its crystalline nature is extremely difficult to dissolve in acids or alkalies. Artificial cassiterite on the other hand is amorphous
Natural cassiterite on account of its crystalline nature is extremely difficult to dissolve in acids or alkalies. Artificial cassiterite on the other hand is amorphous
Leaching, often gold, is the process of extracting a soluble constituent from a solid by means of a solvent. In extractive metallurgy, of gold, it
To perform Gravity separation of heavy minerals in the range 600 microns to 12 microns and to simulate gravity recovery performance on a sample hoping

This Laboratory Magnetic Separator is a high intensity dry device which uses a rotating iron disc to concentrate the magnetic field and remove the magnetic particles
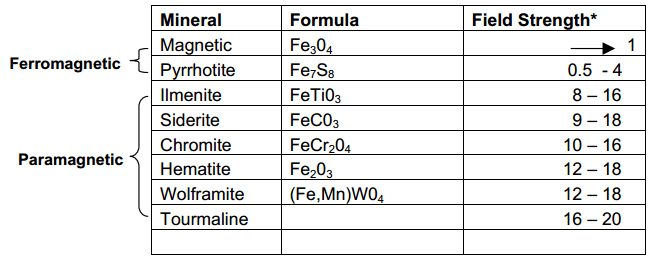
Magnetic separation is a process used to separate materials from those that are less or nonmagnetic. All materials have a response when placed in a
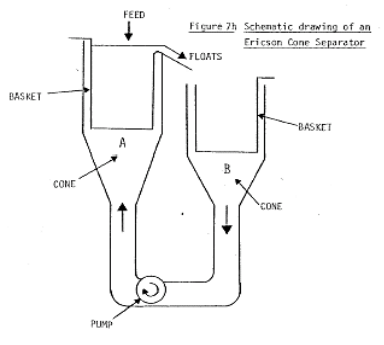
Where large samples (both in top size and weight) have to be examined it is not practical to use heavy liquids (being both expensive and
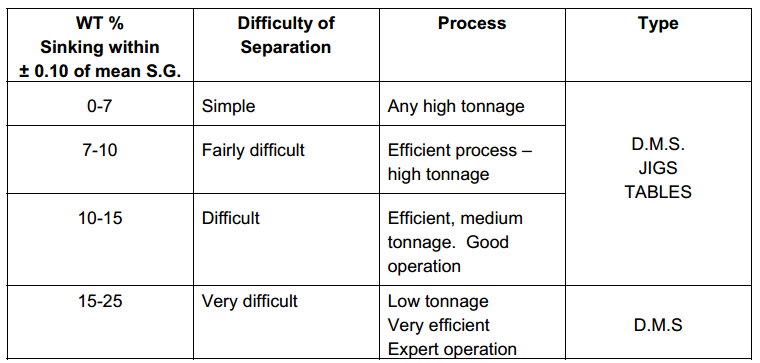
The three types of curve described so far completely define the behaviour of the material in a heavy liquid under ideal sink-float conditions. In practice,
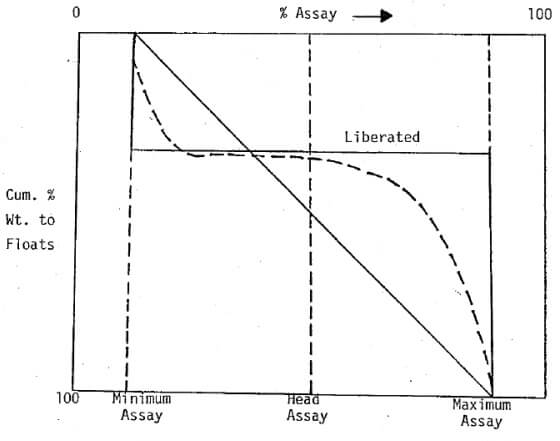
The incremental assays obtained for each S.G. are plotted against the average cumulative % weight of sinks and floats. This curve shows the assay of
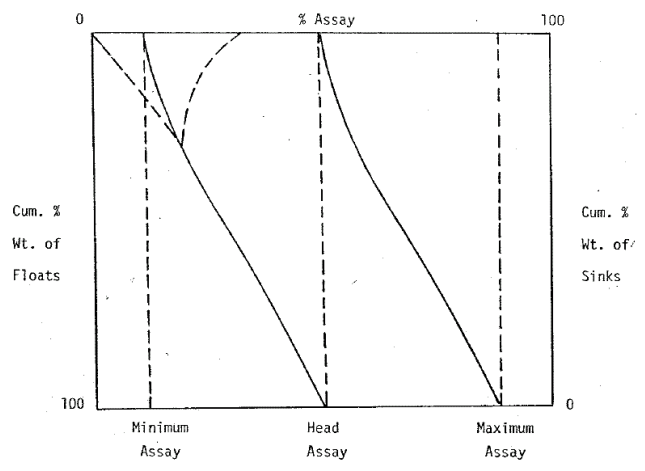
The cumulative % assay of the floats or sinks is plotted against the cumulative % weight of the floats or sinks. These curves indicate cumulative
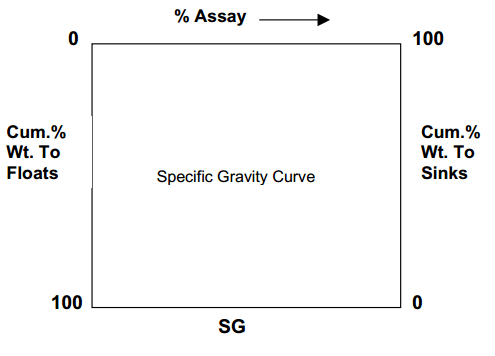
Heavy liquid data can also be interpreted by washability curves. To plot these curves, the axes shown here. The cumulative % wt. Floats or