Why Oxygen is Important in Cyanidation
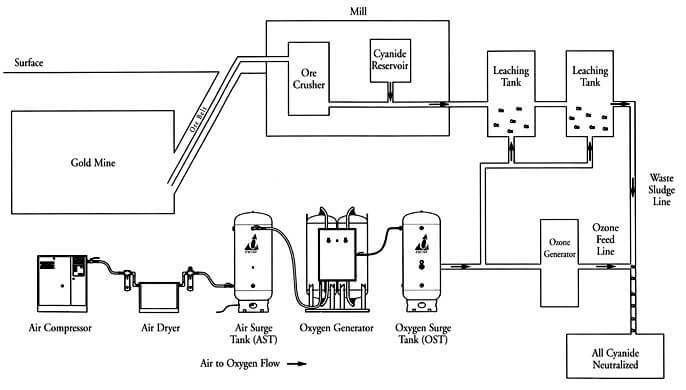
The Rule and Function of Oxygen in Cyanidation.—Oxygen appears to be an indispensable factor, either directly or indirectly, in the dissolution of gold and silver by cyanide solutions, except in the case of the haloid compounds of silver. Whether the action of oxygen in the dissolution of gold be a direct one, as illustrated by the […]
Effect of Cyanide on Steel and Iron Minerals Leached by Cyanide

The corrosion of black rolled mild steel in sodium cyanide solution is negligible. A piece of steel suspended in a sodium cyanide solution maintained at 0.05% NaCN and 0.001% CaO, in the presence of air, lost 0.002% of its weight in two weeks, this was equivalent to a penetration of 0.76 micron per year.Oxidized iron minerals […]
Cyanide Leaching and Decomposition of Pyrrhotite

Research on cyanidation methods brought considerable discussion on the reactions involved in the leaching and decomposition of pyrrhotite in cyanide solutions. Pyrrhotite has one loosely held sulphur atom which readily reacts with cyanide to form thiocyanate: Fe5S6 + NaCN = NaCNS + 5 FeS The ferrous sulphide oxidizes rapidly to the sulphate which reacts with cyanide to […]
Eliminating Copper from Gold Ore

When reviewing Methods of Eliminating Copper from Gold Ores we see that several methods have been suggested to eliminate copper from ores prior to cyanidation. Preliminary extraction of the copper with sulphuric or sulphurous acids may be applicable to ores containing oxidized copper minerals such as malachite, azurite and chrysocolla but these acids have but little […]
Titration of Cyanide Solutions Containing Dissolved Copper

When silver nitrate is added to sodium cuprocyanide of the composition Na2Cu(CN)3, an appreciable amount must be added before a precipitate comes down. The reactions are believed to be as follows: 2 Na2Cu(CN)3 + AgNO2 = 2 NaCu(CN)2 + NaAg(CN)2 + NaNO3 On further addition of silver nitrate, a precipitate of CuCN begins to come […]
Chemical Reaction of Copper Minerals and Cyanide

In discussing the Reaction Products from Copper Minerals and Cyanide you will find that when an excess of copper mineral is acted upon by cyanide solution, dissolution of copper continues at a decreasing rate until equilibrium is established and no more copper goes into solution. The rate will vary with the particular mineral used as […]
Iron in Cyanidation -Ferrocyanide Compounds

Practically all ores treated by the cyanidation process contain iron minerals. In addition, the equipment in cyanidation plants with which cyanide solutions come in contact is made largely of iron and steel. Fortunately, cyanide solutions have very little action on metallic iron and most iron minerals, otherwise the cyanidation process would be impractical for die […]
Silver & Gold Cyanide Leaching of Copper Ore

Much work has been done on the effect of copper in cyanide solutions on the leaching of gold. It is generally accepted that copper in cyanide solutions can form complex ions such as Cu(CN)2-, Cu(CN)3=, and Cu(CN)4=-, although Cu(CN)3= is considered the most probable of these. According to leach scientists, the complex having an empirical formula […]
Free Cyanide Titration: Pyrrhotite & Sodium Sulphide, Thiosulphate, Thiocyanate, Ferrocyanide

When cyaniding a precious metal ore containing pyrrhotite, various compounds such as, thiosulphate, thiocyanate, ferrocyanide and soluble sulphide are formed and found in the cyanide solution. Soluble sulphides, if present at all, are found only in relatively small amounts; on the other hand thiosulphate, thiocyanate and ferrocyanide have been found in solutions in amounts of […]
Gold/Silver Leaching with Sodium Zinc Cyanide

Dissolution of Precious Metals in Sodium Zinc Cyanide: The dissolving effect of sodium zinc cyanide on precious metals has been the subject of much discussion. According to one researcher, pure K2Zn(CN)4 in the presence of oxygen dissolves gold with the formation of gold potassium cyanide and zinc oxide. Another researcher compared the dissolving effects of KCN and […]
