Acid Leach Processing of Arsenic Rich Copper Wastes
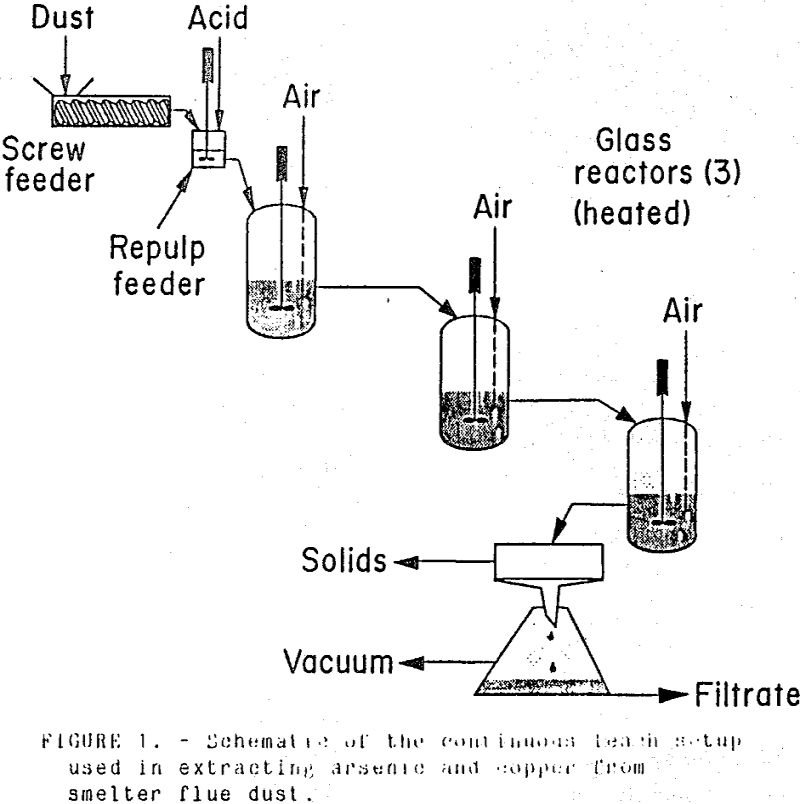
Arsenic, copper, and molybdenum were effectively removed from arsenic-bearing flue dust using a three-stage continuous sulfuric acid leach. Leach conditions to maximize arsenic and copper extraction while minimizing bismuth extraction were determined: 25-wt pct H2SO4, 20- to 25-wt pct solids, a leach temperature of 55° C, and a 30-min residence time. These conditions yielded arsenic, […]
Germanium Gallium Ore Leaching with Sulfuric Acid

A sulfuric acid leach technique for extracting gallium and germanium from Apex ore without the use of a reducing agent, such as SO2, was investigated. Leaching studies showed that with increasing sulfuric acid concentrations, gallium extraction increased to over 95%, while germanium extraction reached a peak of 71% before decreasing to less than 50%. It […]
Germanium Extraction from Zinc Hydrometallurgy
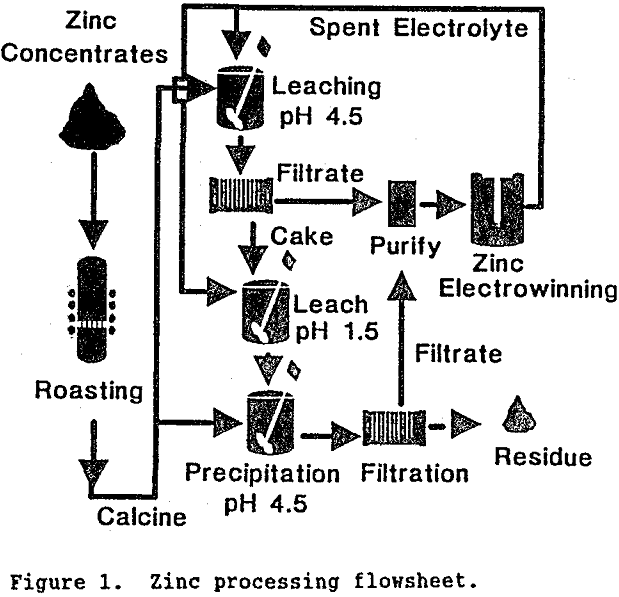
Germanium is an important strategic metal used in fiber optics, infrared detectors, and semiconductor devices including transistors, diodes, and rectifiers. Substitution for germanium cannot be made without substantial loss in performance in most cases. Germanium is generally not concentrated naturally, although trace amounts are found in many minerals. Germanium is produced almost exclusively from waste […]
Apatite Leaching using H2SO4 & Methanol
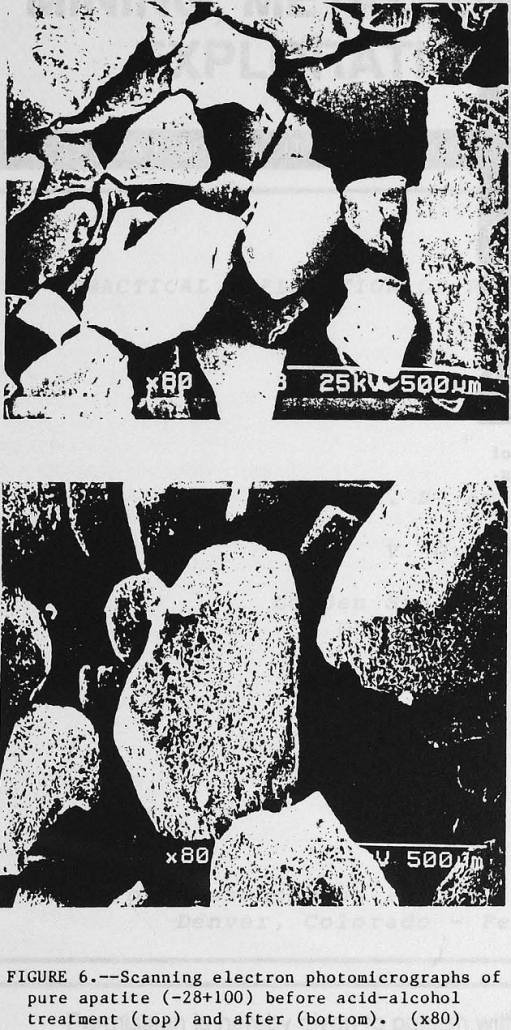
Current practice for the production of wet-process phosphoric acid (H3PO4) involves leaching beneficiated phosphate rock with aqueous H2SO4. Typical processing involves mining the ore, also called matrix, using a dragline, then forming a water-based slurry to facilitate pumping the ore to a beneficiation plant. Phosphate values contained in the minus 150-mesh fraction of the ore […]
Recover Anhydrous ZnCl2 from Aqueous Solutions
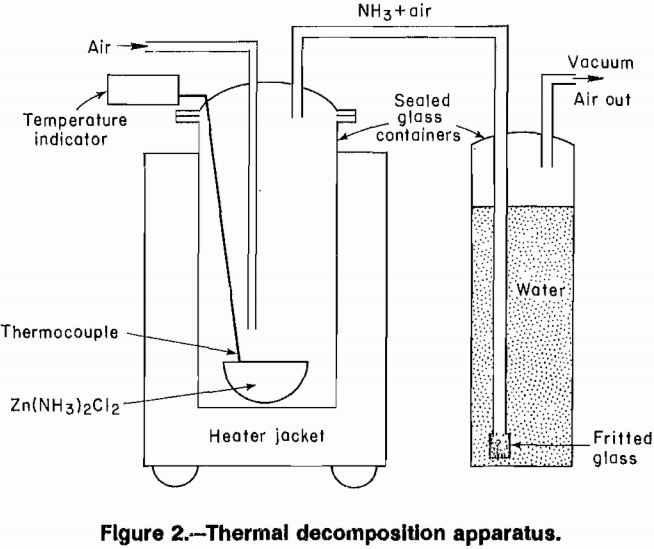
At the present time, zinc is produced commercially by a roast-leach zinc electrowinning process. The primary source is high-grade concentrates of the mineral ZnS. Concentrates must contain low levels of iron to avoid formation of zinc ferrites during roasting because zinc ferrites are not amenable to leaching and cause decreased zinc recovery. Also, SO2 is […]
Solvent Extraction – Predicting Equilibrium Values
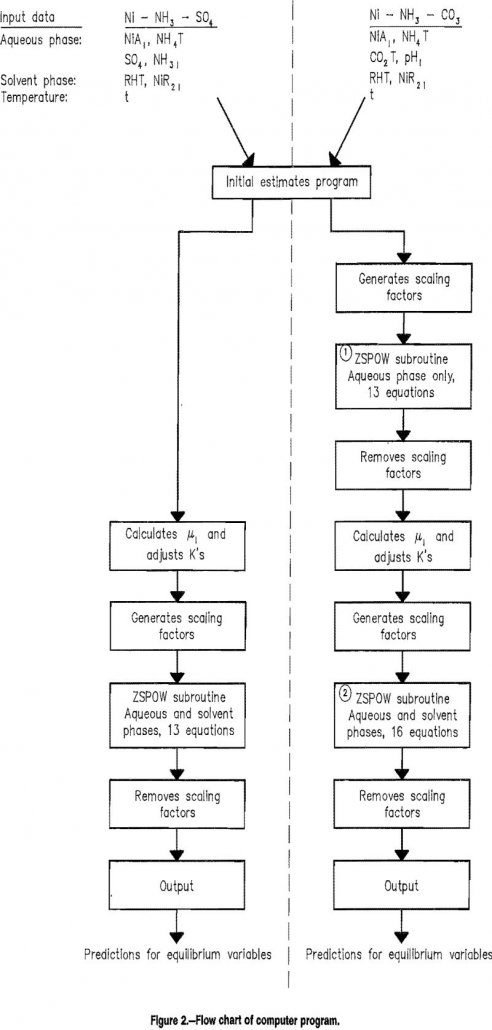
Trends in extractive metallurgy in recent years from milling and smelting of high-grade ores toward heap leaching and electrowinning of low-grade or marginal ores, have resulted in increased reliance on solvent extraction as a key part of profitable operations. Consequently, solvent extraction processes and reagents have been extensively studied, resulting in greatly improved techniques and […]
Biosorption of Metal Contaminants Using Biomass
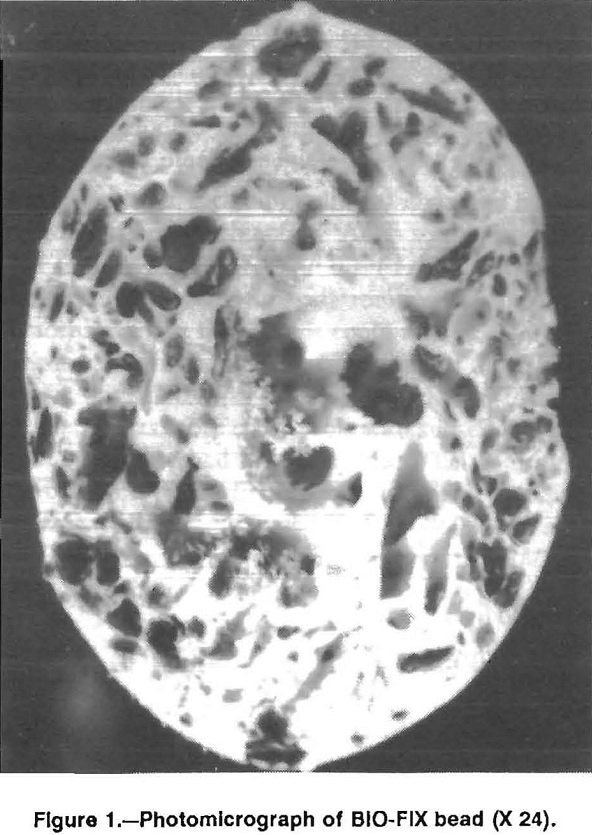
The removal of toxic metal contaminants from aqueous waste streams is one of the most important environmental issues facing the United States today. Although this issue has been addressed for many years, effective treatment options are limited. Chemical precipitation, ion exchange, reverse osmosis, and solvent extraction are the most commonly used procedures for removing metal […]
Cyanide Leach in Cold Temperatures
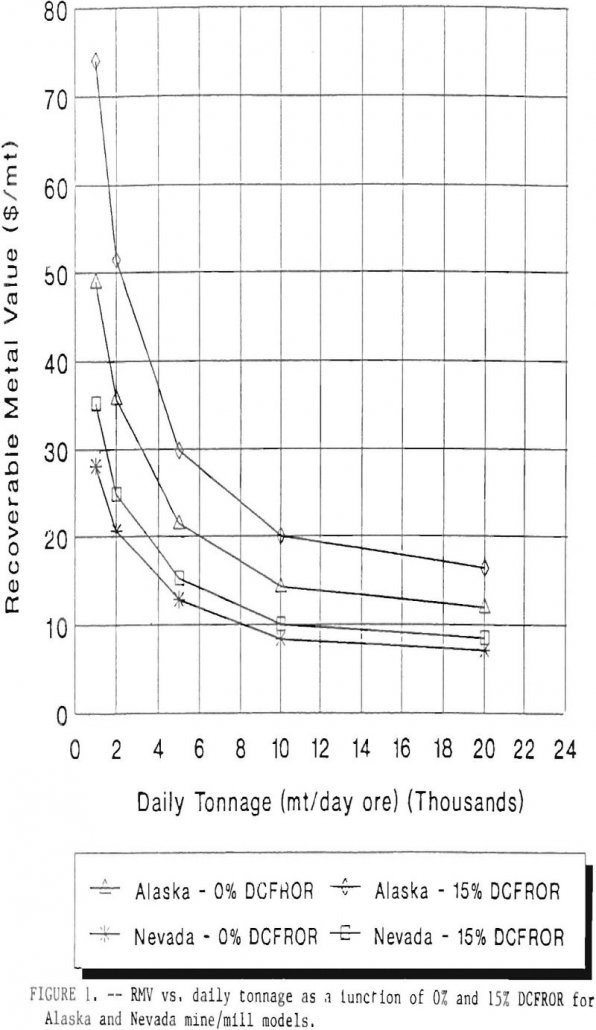
In October of 1987, the U.S. Bureau of Mines (Bureau) initiated a study on the applicability of cyanide technology to the Alaska mineral industry. The study included the collection and analysis of cyanide literature and leaching costs, as well as the generation of several generic feasibility studies. Although other methods of cyanide use in the […]
Thiocyanic Acid in Ion Exchange & Solvent Extraction of Metals

Metal separations and metal recoveries by ion exchange and solvent extraction of their thiocyanate complexes are widely practiced in analytical chemistry as well as in some industries. Consequently, a critical review of the chemistry of thiocyanic acid and thiocyanates is presented in the second part with the aim of providing a clearer understanding on the […]
Precipitation of Mercury in Cyanide Gold Leaching
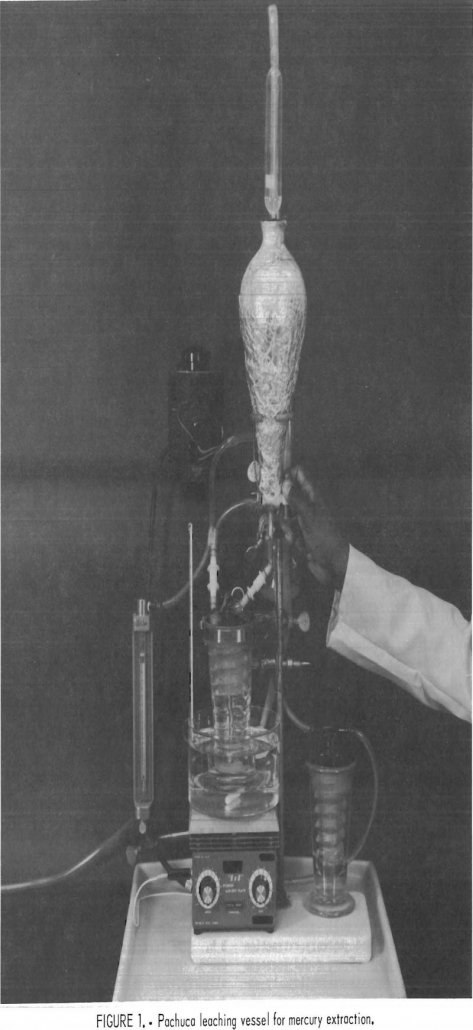
Numerous low-grade gold-silver ore deposits are being mined and milled throughout the Western United States. In addition to gold and silver, many deposits contain as much as 15 ppm of mercury. During cyanidation, 10 to 30 pct of the mercury and 85 to 90 pct of the gold are typically solubilized. The reactions for gold […]
