How to Recover Lead & Copper from Blast Furnace Matte
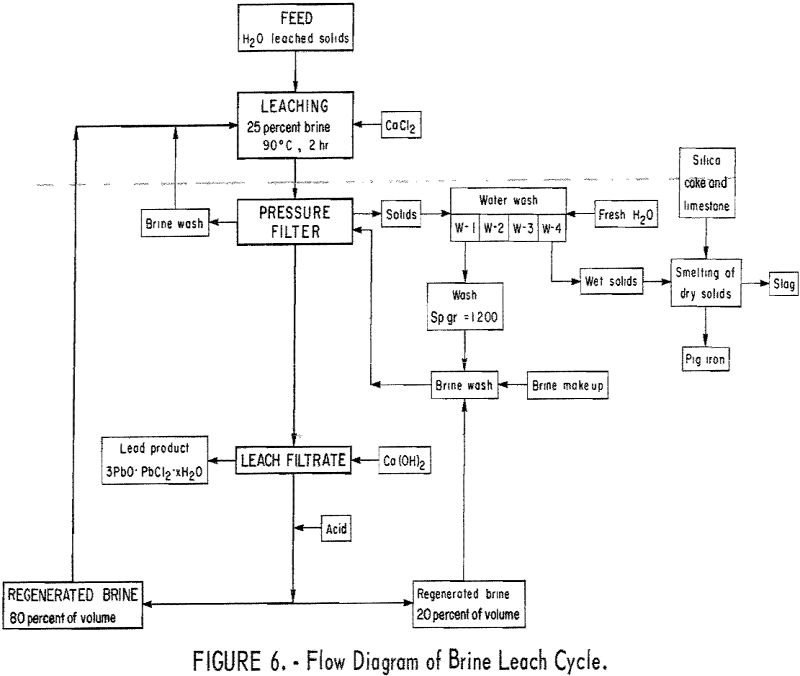
This research has shown that & solid waste byproduct from secondary lead smelters can be successfully processed to recover copper and lead that is lost during smelting. The major steps in the process and the products recovered are as follows: Copper and lead sulfides in blast furnace matte are converted to sulfates and iron sulfide […]
Electrorefining Vanadium Scrap

A molten-salt electrorefining process was developed which provides a practical way for reclaiming vanadium from scrap generated in the processing of ductile vanadium into bar, sheet, wire, and other shapes. Refining produced extremely ductile vanadium with a purity range of 99.93 to 99.95 percent. The process was particularly effective in reducing the interstitial elements, carbon, […]
Recover Copper from Oxides using Iron and Steel Scrap
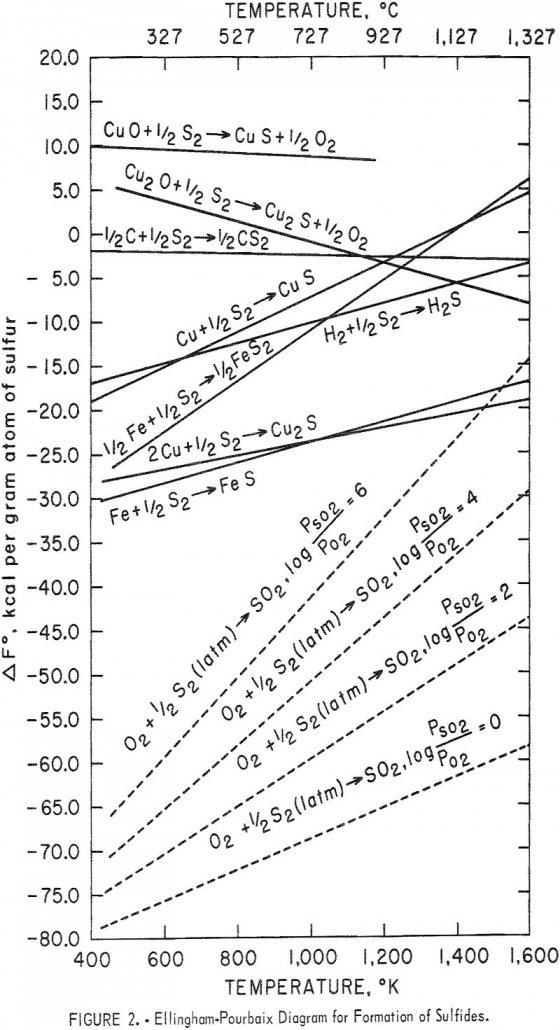
For the past two decades, about one-third of the copper consumed in the United States has been imported. In order to meet the Nation’s demand, new and improved methods of copper extraction must be found. Ferrothermic extraction is one possibility; the Bureau of Mines undertook this investigation to determine the principles and optimum conditions of […]
Method for removing aluminum from diecast scrap
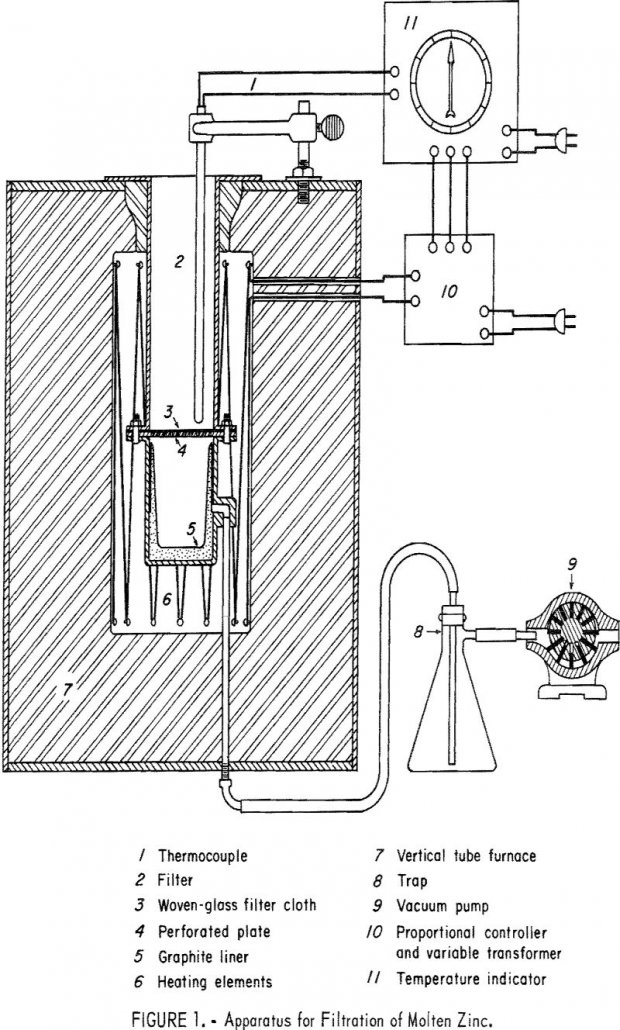
Zinc-base die-cast scrap represents the largest single source of secondary zinc. A large part of the die-cast scrap originates from grills, fuel pumps, carburetors, trim, and hardware from scrapped automobiles and other machinery, or from punchings or factory rejects of these components. A typical mixture of die-cast scrap contains from 3 to 5 percent aluminum […]
Recycle & Recover Titanium Chlorination Residues
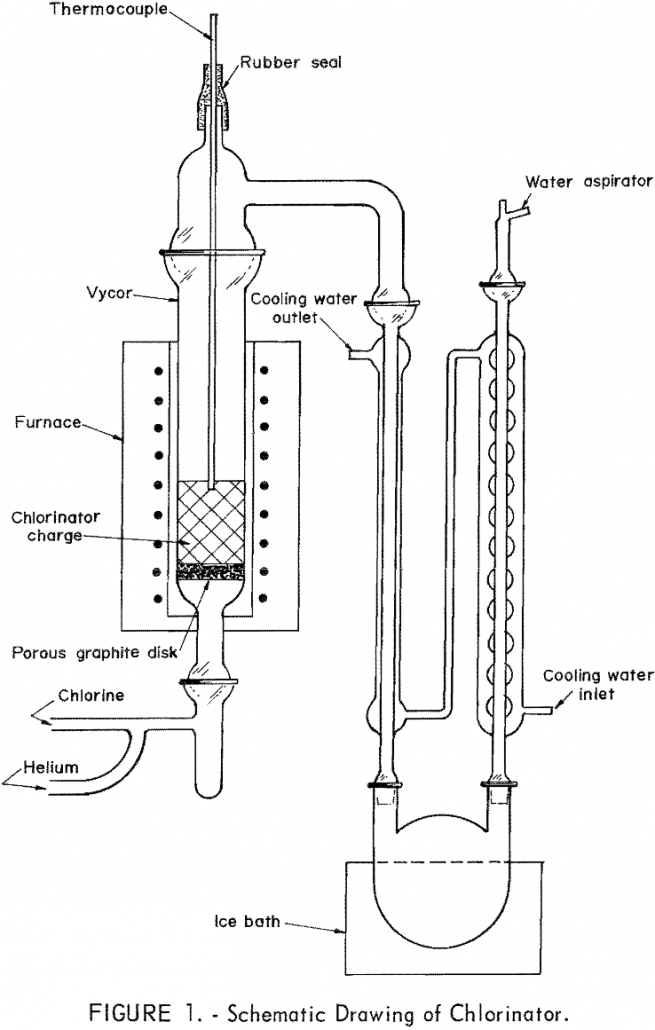
Approximately one-half of the weight of the sludge generated in the commercial production of purified TiCl4 from rutile can be recycled with a coincident diminution of waste disposal problems and the more efficient utilization of TiO2 and carbon in the processing operation. The sludge can be separated into soluble and insoluble fractions by water leaching, […]
How to Dismantle Junk Cars for Scrap

The proposed complete dismantling of the car removes all copper-containing parts; hence, the bales prepared from the clean ferrous metals should contain only the 0.07 percent copper that is in solid solution in the steel. As the baled steel weighs 2,614 pounds, it contains about 1.8 pounds of copper. If the upper limit of high-quality […]
Scrap Tire Distillation

Destructive distillation was demonstrated to be a technically feasible method of disposing of and obtaining potentially valuable products from scrap automobile and truck tires. The relative amounts of the various products were shown to be highly dependent on the temperature of carbonization. Highest yields of liquid products were obtained at 500° C and highest yields […]
Building a Junk Car Incinerator
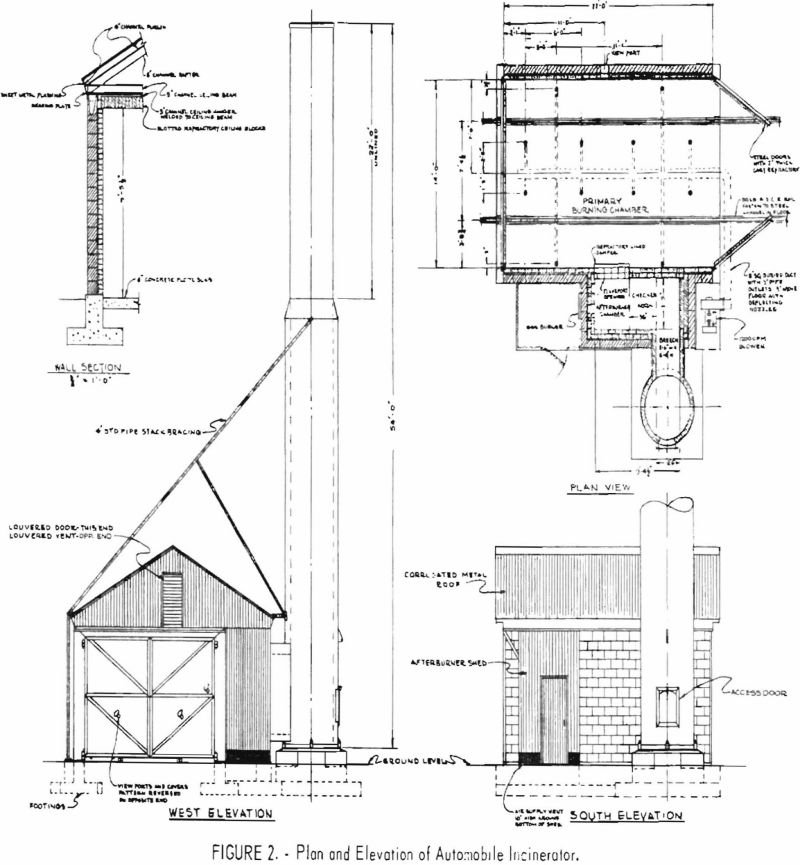
Congress, by the Solid Waste Disposal Act of 1965, delegated to the Bureau of Mines responsibility for conducting research on solid waste problems. The accumulation of abandoned automobiles is one of these problems, and this paper reports the efforts of the Bureau’s Salt Lake City Metallurgy Research Center in attempting to resolve the abandoned car […]
How to Recover Cadmium & Nickel from Scrap Batteries
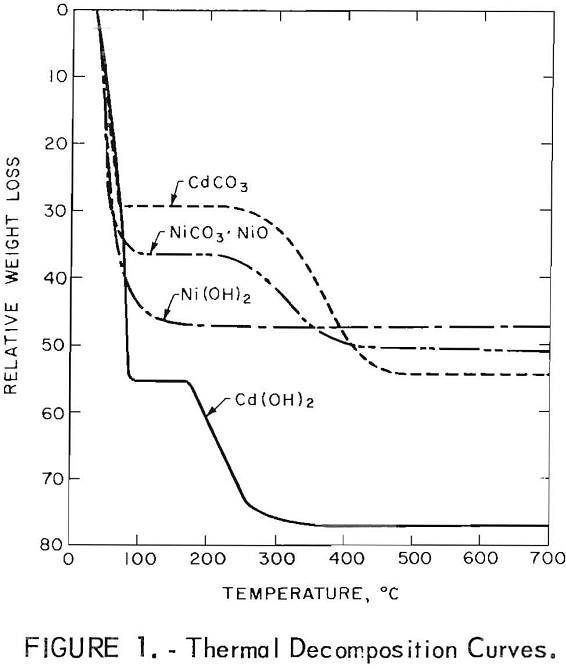
The manufacture and use of nickel-cadmium alkaline storage batteries in the United States began to grow at a rapid pace in the late 1950’s. The batteries have found use in a wide variety of consumer appliances, electronic units, industrial equipment, communication devices, and space applications. The U.S. Department of Defense is the biggest single user […]
How to Recover Copper from Slag by Flotation

The bulk of the world’s output of copper is produced by smelting copper sulfide flotation concentrates in reverberatory furnaces, followed by oxidizing the matte to blister copper in a converter. Slags produced in the converter are too high in copper to be sent to the dump and are returned to the reverberatory furnace for recovery […]
