Increased recycling of waste paper has been emphasized in recent years in both the USA and Canada for environmental and economic reasons. Removal of ink particles from the waste paper pulp is therefore necessary. One of the most promising methods for ink removal is froth flotation. Our study investigated the feasibility of a simplified flotation scheme which showed that about 90-92% ink removal can be achieved while 95-97% ink removal is achievable if a hydrophobic polymer is used ahead of flotation.
Experimental Techniques
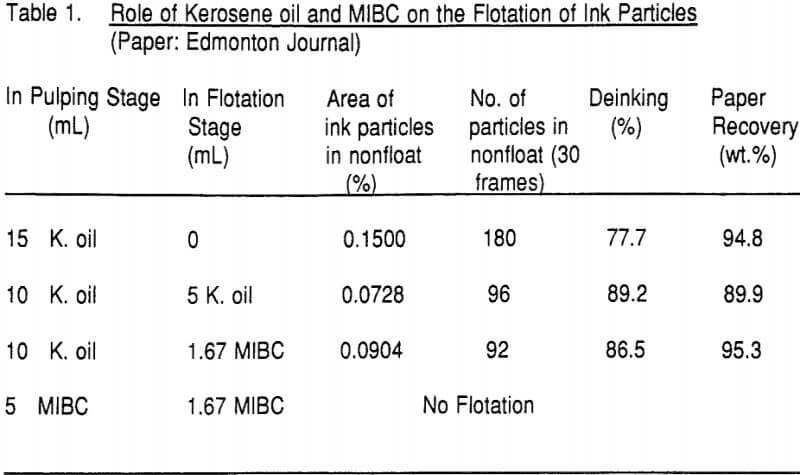
(1N) NaOH and (1:1) HCl were used for pH adjustment. A blend of one part of methyl iso-butyl carbinol (MIBC), supplied by Terochem Scientific, Ont., Canada, and two parts of kerosene oil or kerosene oil alone was used as the flotation reagent.
20 g of shredded paper was placed in a Hobert mixer and the required amount of de-ionized water was added to make 5 wt.% solids concentration. Pulping pH was adjusted and a part of the required amount of flotation agents was added while mixing at 200 rpm for 15 minutes. The mixture was then kept soaking for 16 hours. The mixture was further pulped in two stages: one at 200 rpm for 30 minutes and the other at 400 rpm for 15 minutes. Pulping was done at two different stages for better separation of the ink particles and to avoid breakage of the ink particles. The pulp was then transferred to the flotation machine and diluted to 0.35 wt.% solids.
The degree of deinking of the pulp was estimated on the basis of the percent reduction in particle area and calculated as follows:
Deinking (%)= aF – aP/aF x 100
Where aF= ink particle area% in feed
ap= ink particle area% in non-float
Results and Discussion
There are basically two steps: the first step is pulping and the second is flotation. The effect of pH, reagent type and concentration on each step has been investigated.
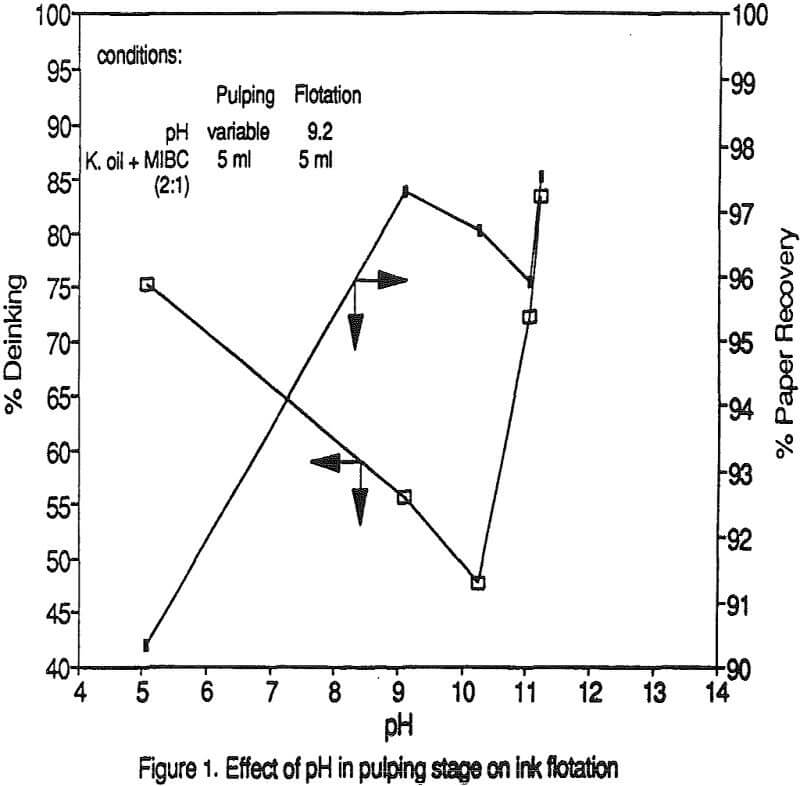
In industrial practice pulping is done in batches by filling the pulper with the waste paper, water and chemicals and then pulped for one hour. Similarly in the present work, pulping has been carried out for one hour. The effect of pH has been determined by the performance in the flotation step. The ink liberation from the newsprint plays a vital role in the flotation process.
The effect of pH on flotation indicates that the flotation pH has a significant role in the process of ink removal. Though the pulping is done at pH of 11.2, where ink particles are well liberated, there is no flotation in the acidic pH. It is found that there is a threshold pH below which selective separation of ink particles is not practicable since both pulp and ink float together. .
The role of kerosene oil on deinking of photocopy waste paper (xerographic paper) has been tested. As the paper used had prints only on one face, the particle area percentage is only 0.015%. Around 71.8% of ink can be removed with kerosene oil and a very clean pulp with only 0.004% ink particle area can be obtained.