Effect of Feed Size in Comminution
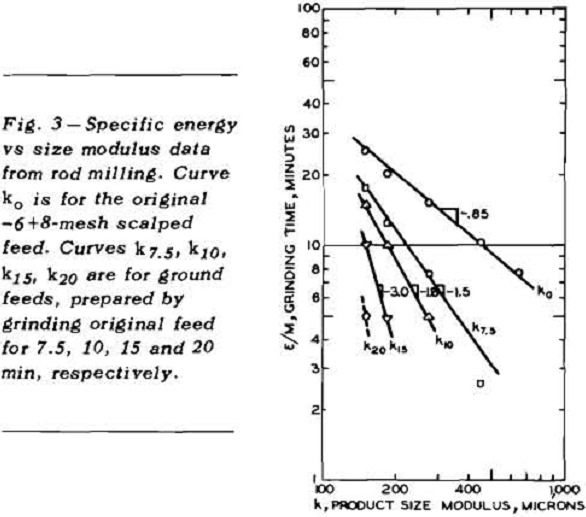
The feed size cannot be neglected in any case where the effective size modulus of the feed is not too much coarser than the size modulus of the product. This can be illustrated in the second experiment of Fuerstenau and Cohen where the feed is considered to be the original -6 +8-mesh material. However, one […]
Single Impact Testing of Grains of Brittle Materials
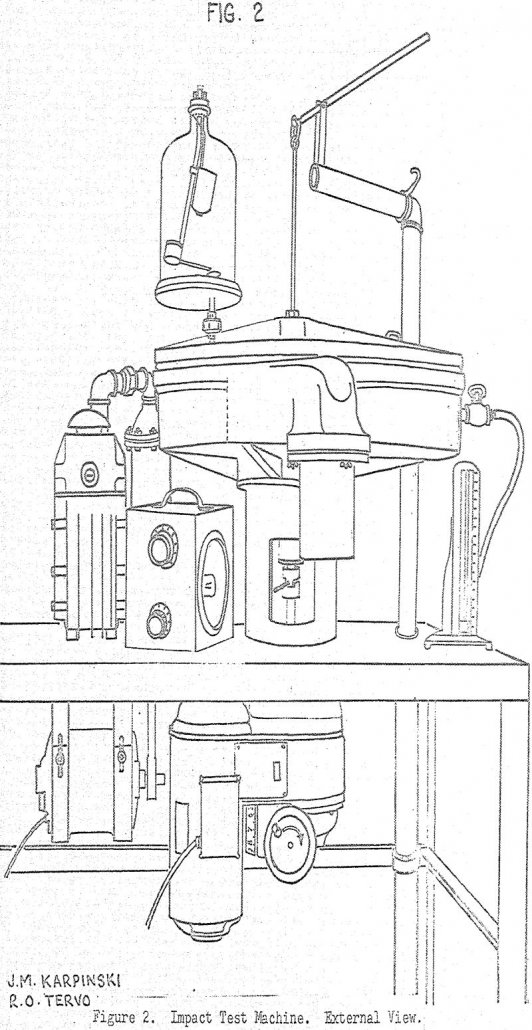
A method and equipment have been developed for measuring the impact strength of grains of brittle materials. It is shown that brittle materials develop a characteristic particle size distribution when fractured by impact. A simple mathematical model has been found to describe this distribution, and one of the parameters of the model has been designated the […]
Rotary Percussion Rock Drilling
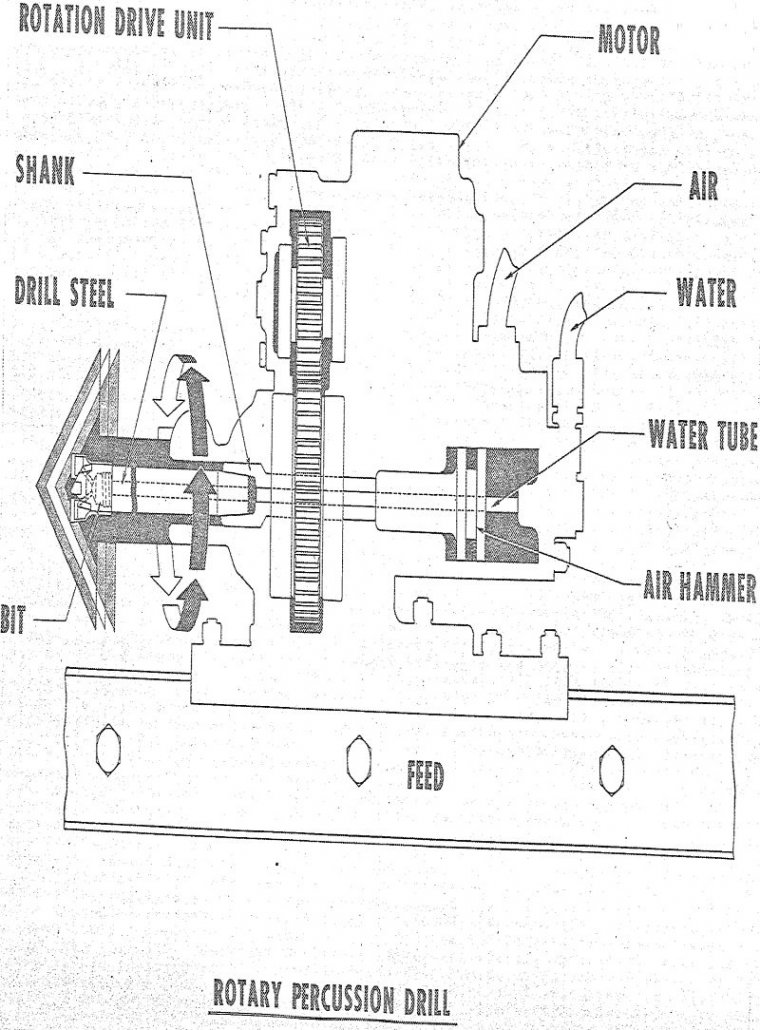
“Rotary percussion” implies two types of energy, rotary and percussion. Into these categories fall rock drills of varying sizes. The larger ones drill above 6″ diameter holes; the medium size, 2 ¾-” to 4 ½” holes; and the smallest, 1 ¼” to 2″ holes. Essentially, the larger holes are drilled with down-the-hole drills using tri-cone […]
Ropes for Drum and Koepe Friction Hoists
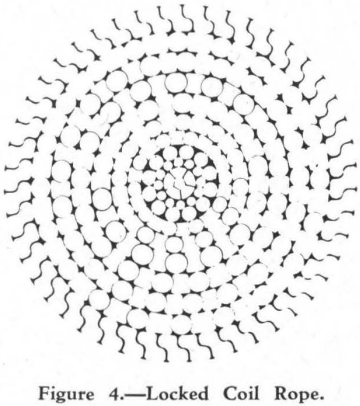
Four basic designs of ropes are now employed for hoisting duties: Six-strand, round strand ropes with fibre cores. Six-strand, triangular strand ropes with fibre cores. Non-rotating, multi-strand ropes. Locked coil ropes. Very solid and reliable ropes can be obtained with this simple geometric design of strand. Owing to the fact that the wires in the […]
Reagent Testing – How to Analyse Results by Statistics
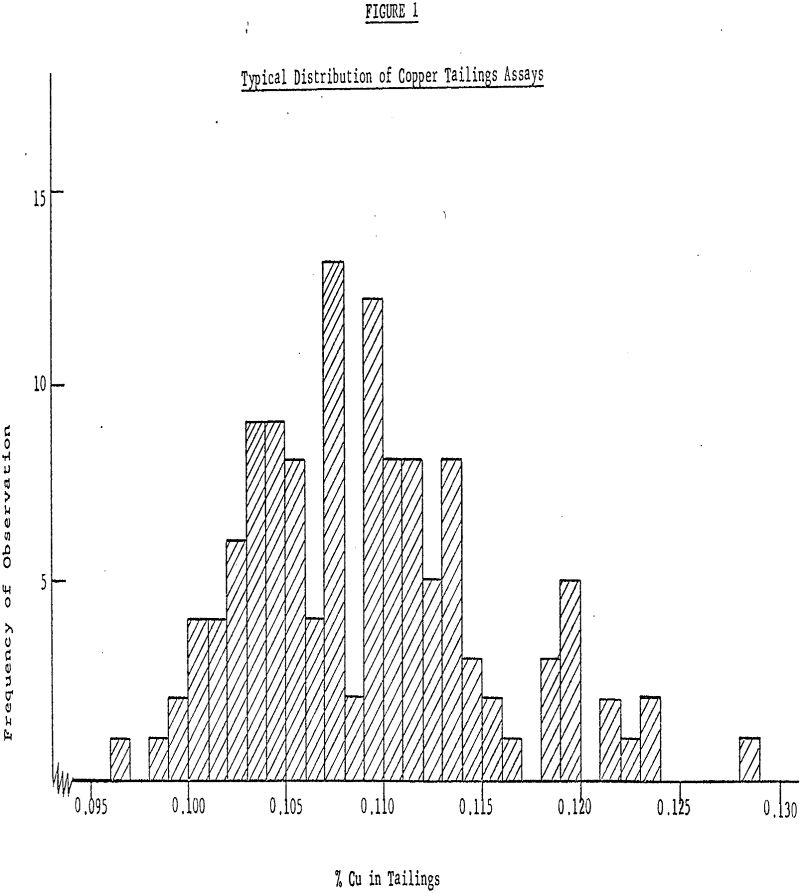
In the operation of today’s large scale ore-processing mills, it is extremely important to have some way of making an objective evaluation of the performance of the available flotation reagents. While Reagent Testing the use of Statistics is necessary for Result Analysis. Attempts to do this may often result in inconclusive findings since the magnitude […]
Expansible Shale Prospecting

Field criteria are needed to help the prospector recognize a potentially expansible shale, clay, or slate. Certain criteria have proven useful in California even though the physical-chemical mechanisms of expansion are not. thoroughly understood. Three conditions must be satisfied before expansion can take place. The raw material must partially fuse at a low temperature (1800-2000°F.). […]
Particle Size Reduction with Roller Mill
For reasons well known to Mining Engineers, fine grinding in the wet form is quite universal in plants engaged in the extraction of metallic values from crude ores. In the processing of non-metallic and industrial minerals, however, fine grinding in dry form is the more common method. The crude materials generally contain less moisture than […]
Factors Affecting the Angle of Slope in Open-Cast Mines
The problems of slope stability in open-cast mines are examined. A criterion, the instantaneous stripping ratio, is suggested for use in the design of pit slopes and as an index of control at all stages of the exploitation of the ore body. This criterion may also be related to safety and to the maximizing of […]
Low Alkali Portland Cement
The concurrent observation of the phenomena of alkali-aggregate reaction and development of efficient dust collection systems on rotary-kilns made mandatory the process modifications to produce low alkali cements. Such low alkali cements as were available prior to these recent changes were either the rare result of low alkali raw materials, the loss of alkalies, with […]
Cultured Quartz
The technique of growing crystals from the melt, such as KI, NaBr, was already commercially in use. Quartz could not be so grown, since its utility depends on the form stable below 573° C, and, even if it could be grown from an extraordinarily viscous melt, the higher form passing through this transition becomes twinned. […]
