Refining Electrolytic Copper
The object of refining copper in the reverberatory furnace is to obtain a metal which will have the highest attainable degree of malleability, ductility and electric conductivity, and present at the same time a level surface when it solidifies in the mold after casting. These desirable physical properties are governed by the character of the […]
Copper Refining: Explained Step-by-Step
In refining copper, the metal is melted down in a reverberatory furnace in a more or less oxidizing atmosphere and then further subjected to an oxidizing smelting in order to eliminate the common impurities, most of which have a stronger affinity for oxygen than has copper. In these operations some of the copper is oxidized […]
How to Remove Arsenic, Antimony & Bismuth from Copper

The ores of copper are usually associated with minerals containing arsenic, antimony and bismuth. Whatever the means adopted for extracting the copper, these metals are usually found, to a greater or less extent, in the product. There is, however, usually some elimination in the various metallurgical operations to which the ores are subjected, and some […]
Copper Ore Heap Leaching Agglomeration
How is Copper Ore Processed
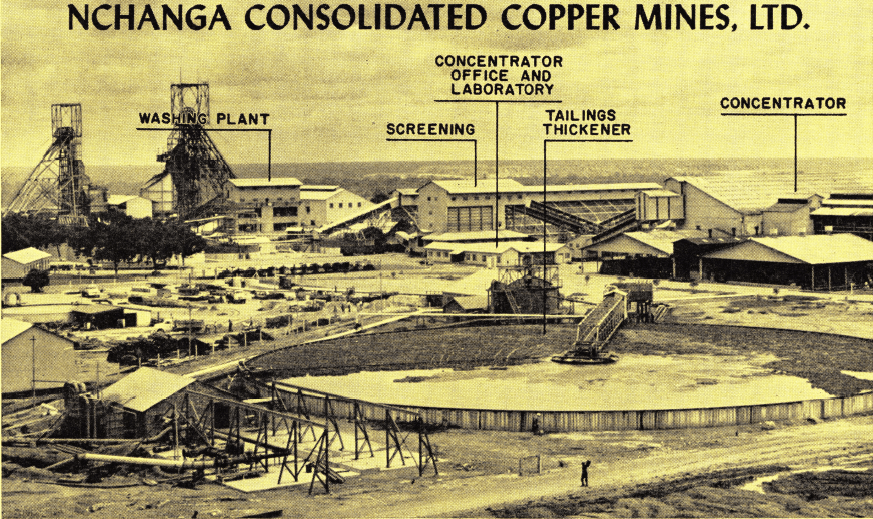
In 1948 Trefoil was privileged to publish an Engineering Notebook Bulletin on Development and Pilot Plant Operations at the Nchanga Consolidated Copper Mines Ltd., Chingola, Northern Rhodesia. This article was authored by Mr. H. L. Talbot, then Consulting Metallurgist to the Anglo-American Group of Companies in Northern Rhodesia. It is now our privilege to bring […]
Flotation Uranium bearing Copper ore
Uraninite and masuyite are the major uranium minerals, essentially fine grained, in the ores studied. Over 40% of the uranium is distributed in the -8µm fractions compared with copper, which is concentrated mainly in the +8-20µm range. Uranium is concentrated mainly in the copper ore zones, with only marginal levels in the gold-only ores. Poor liberation […]
Segregation Process of Mixed Sulphide Copper Ore
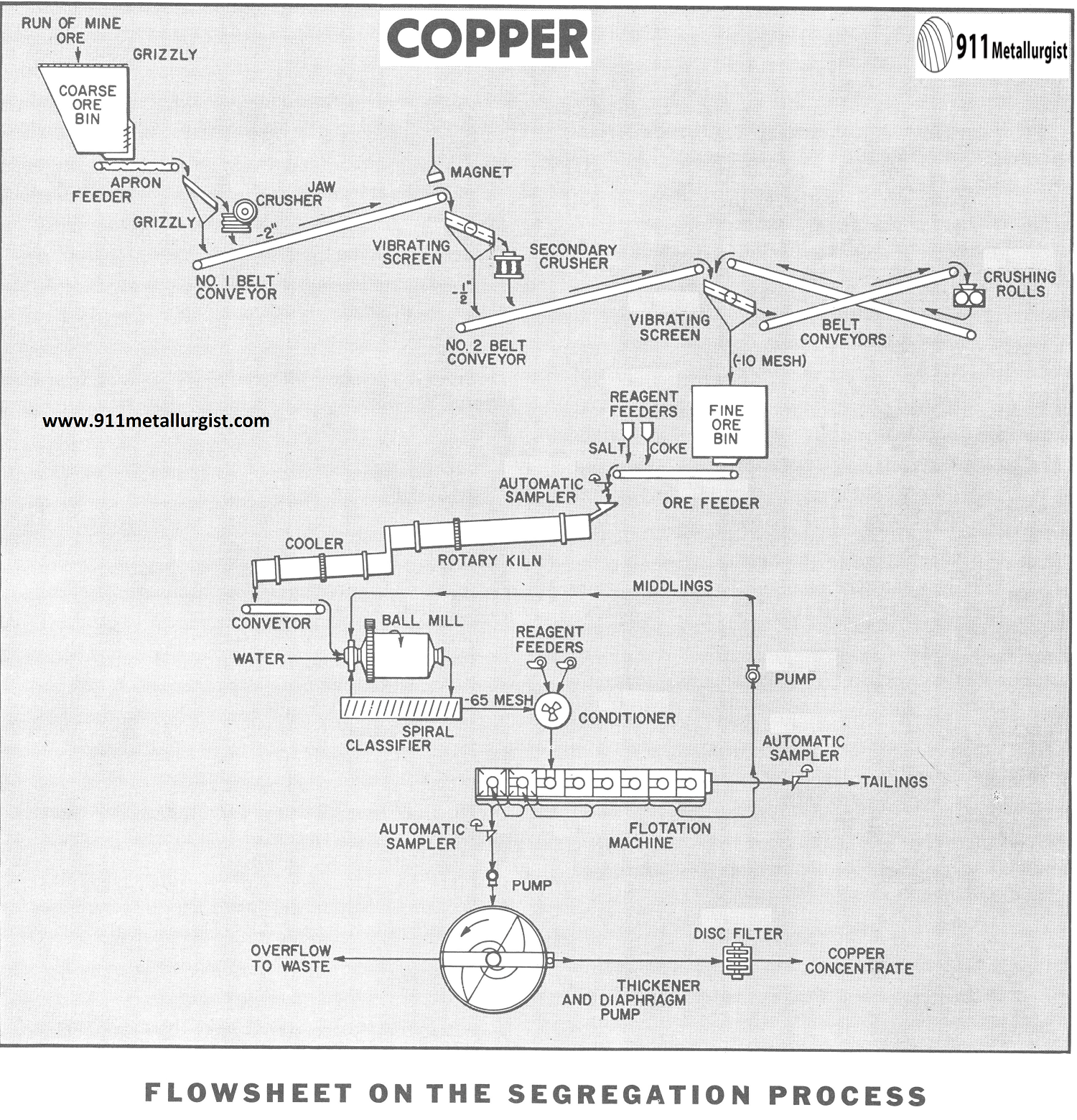
Sulphide copper ores are normally concentrated by flotation while the oxide ores undergo hydrometallurgical treatments. The mixed sulphide-oxide copper ores may be processed by combined methods such as flotation followed by leaching and precipitation of the oxidized portion, or vice-versa. Also a Leach-Precipitation-Float Process (LPF Process) has been successfully applied. However, when oxide or mixed […]
LPF Process Metallurgical Testing
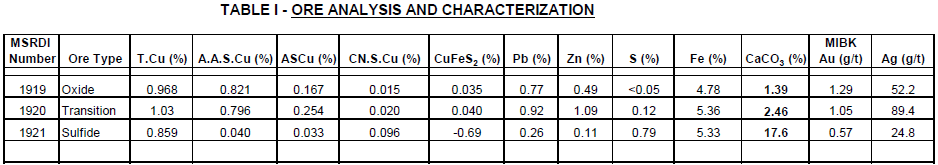
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY A Metallurgical Laboratory had completed preliminary economic studies on various processing options applicable to the Minerals Project in South America, containing oxide, transition and sulfide ore reserves. These included heap leaching with SX-EW; use of Roast-Leach-EW of sulfide concentrates to produce CuSO4 crystals; and potential application of the Leach-Precipitation-Flotation (LPF) option to treat […]
Copper Flotation
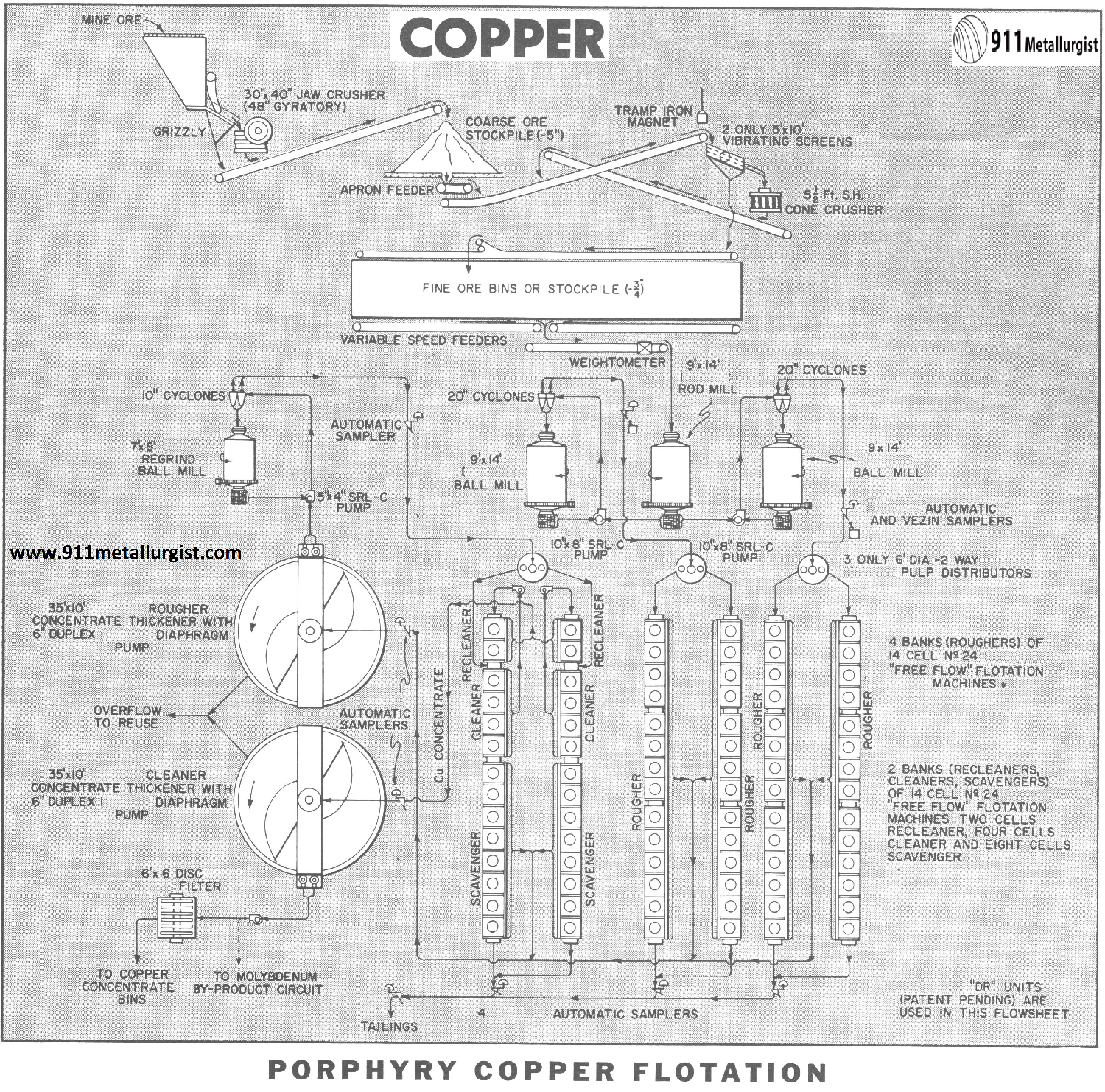
Although basic porphyry copper flotation and metallurgy has remained virtually the same for many years, the processing equipment as well as design of the mills has continually been improved to increase production while reducing operating and maintenance costs. Also, considerable attention is paid to automatic sensing devices and automatic controls in order to assure maximum […]
Copper LPF Leach Precipitation and Flotation Process
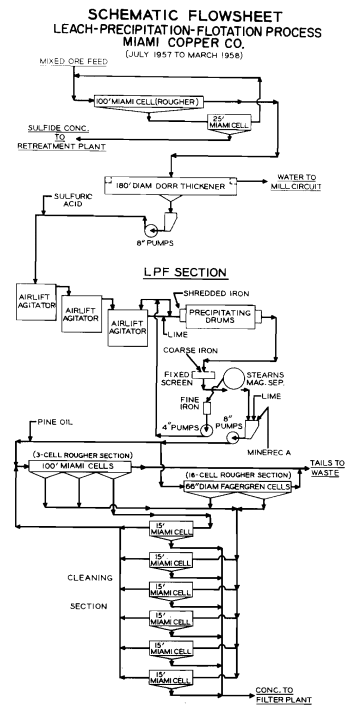
The LPF process is uses for treatment of copper ores in which part or all of the copper occurs in oxidized form presents a problem for recovery. Sulphidization of the oxidized copper minerals using sodium sulphide or sodium sulphydrate is sometimes effective to render the minerals floatable, but generally sulphidization techniques produce low recoveries. Many […]
