Ferrocyanide Assay Determination
The most reliable method of determining ferrocyanide in a cyanide solution is to determine the total iron and calculate to ferrocyanide. Volumetric Method Procedure To 200 to 500 cc solution, depending upon the quality of ferrocyanide thought to be present, add 10 cc HCl and 5 cc HNO3, and evaporate to about 50 cc. Add […]
Measure the Oxygen Content of Cyanide Solutions
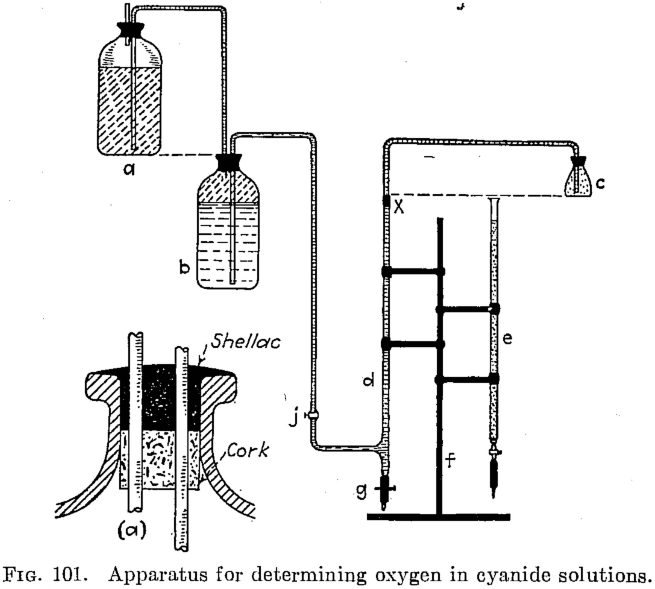
Two methods for determining the oxygen content of cyanide solutions are offered as being simple and accurate. White’s method is a colorimetric one, depending on the degree of coloration imparted to a solution of pyrogallic acid in the presence of caustic soda. Weinig and Bowen’s method, a modification of that of Schutzenberger, depends on the reducing […]
Free Lime CaO Determination Protective Alkalinity
It is important to know the free, or available, CaO in burnt or hydrated limes, especially for the laboratory determination of lime consumption in cyanide tests. The so called sugar method is a convenient one and is widely used. It is based on the solubility of the CaO present in sugar solution. The carbonates and […]
Thiocyanate Assay Determination
Determination of Thiocyanate by Colorimetric To a 100- cc Nessler tube add 50 cc water and 5 cc (more if necessary) of the cyanide solution to be tested, then add 2 cc HCl and 10 cc of 5 per cent solution of ferric chloride, FeCl3 Mix, and dilute to the 100-cc mark with water. If Prussian […]
Determination of Total Cyanide
Total cyanide is a term used to indicate, in terms of NaCN (or KCN), all the cyanogen existing in the form of simple cyanides, hydrocyanic acid, and the double cyanide of zinc. Procedure. Measure 25 cc of clear cyanide solution, add 10 cc of caustic soda-potassium iodide solution, and titrate with standard AgNO3 solution to […]
Handling Waste Cyanide Solution
Tailings pulp carrying traces of cyanide and the discard of barren solutions in some cases constitutes a hazard to both humans and animals, and methods have been devised for destroying the contained cyanide. A recent paper “The Treatment of Cyanide Wastes”by Chlorination by J. G. Dobson published in the Sewage Works J., November, 1947, discusses […]
Gold Chlorination Processes & Methods
In Liddell’s Handbook of Nonferrous Metallurgy, Vol. 2, 1945, there is to be found a very complete account of the uses of chlorine as applied to the recovery of gold and silver, in Chlorination Processes & Methods. Introducing the chapter entitled “Chlorine Metallurgical Processes” Liddell says: Chlorine as a metallurgical agent appears to have lost ground […]
Bromocyanide Process
Bromo salts are a mixture of 57 per cent sodium bromide, NaBr, and 43 per cent sodium bromate, NaBrO3, in the form of light-gray, light- yellow, or reddish-brown crystals or powder. The use of bromo salts for treating a telluride concentrate in the Wright- Hargreaves plant at Kirkland Lake is described by J. T. Willey […]
Carbon Cyanidation

Countercurrent carbon cyanidation with simultaneous dissolution of gold by cyanide and its adsorption by carbon offers several advantages over other carbon cyanidation processes as: the rate of dissolving the gold is faster, higher grade gold-bearing carbon is obtained, less carbon per ton of ore treated is required, separate dissolving and absorbing units are not needed, adsorption […]
