Cyanide in the Stamp Battery
Use of Cyanide in the Stamp Battery to treat the ore direct from the stamp milling battery instead of first passing it over amalgamated plates. Ore can be crushed with cyanide solution instead of water, and led at once into the filtering tanks. The results are stated to have shown that the coarse gold resisted the attack […]
Zinc Dust Precipitation

The Merrill System or method or Zinc Dust Precipitation was introduced in 1897 at Marysville, Montana; in the plant of the Montana Mining Co., and subsequently at the Homestake Mine in South Dakota, where 130,000 tons of ore are treated per month and 4000 tons of solution precipitated every 24 hours. With very few exceptions this process […]
Agitated Cyanide Gold Leaching Test
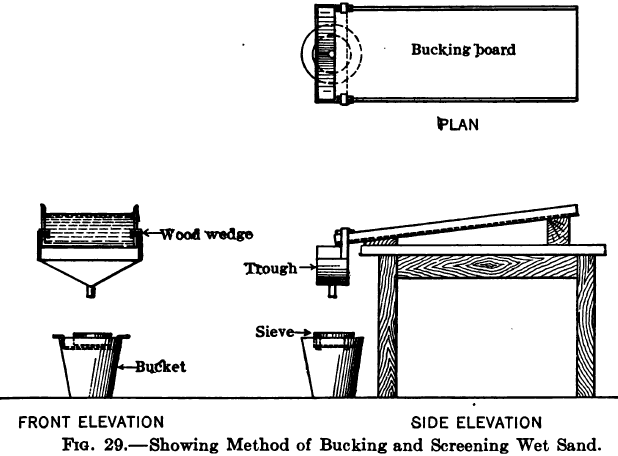
In the old days laboratory tests were usually made by mechanically shaking up in a bottle for a given time a charge of ore and cyanide solution. The most generally convenient device for this purpose is a wheel, to which are attached boxes, each capable of containing a standard acid bottle, and with means for […]
Determine the Proper Grind Size for Gold Ore

Without mineralogy, estimating the optimum Grind Size for Gold Ore Sample is most conveniently made by Laboratory Testing and the agitation leaching method, and it will be necessary to make up 3 or 4 bottle charges in order to have enough ore* for the subsequent screen analysis. Take an average sample of the ore and grind […]
Calculating Cyanide Consumption
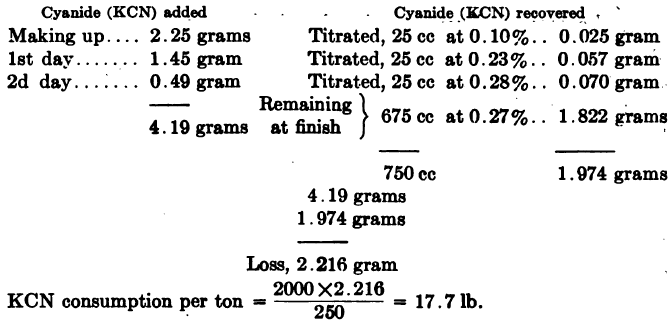
Computing Cyanide Consumption of a laboratory leach test may be done as in the following example: Ore taken, 250 grams. Ratio of solution to ore, 3:1 = 750 cc: 250 grams. Cyanide strength, 0.3% KCN. Or when working on the metric system, Ore taken 200 grams, ratio of solution to ore 3:1 = 600 cc: 200 grams, […]
Gold Precipitation
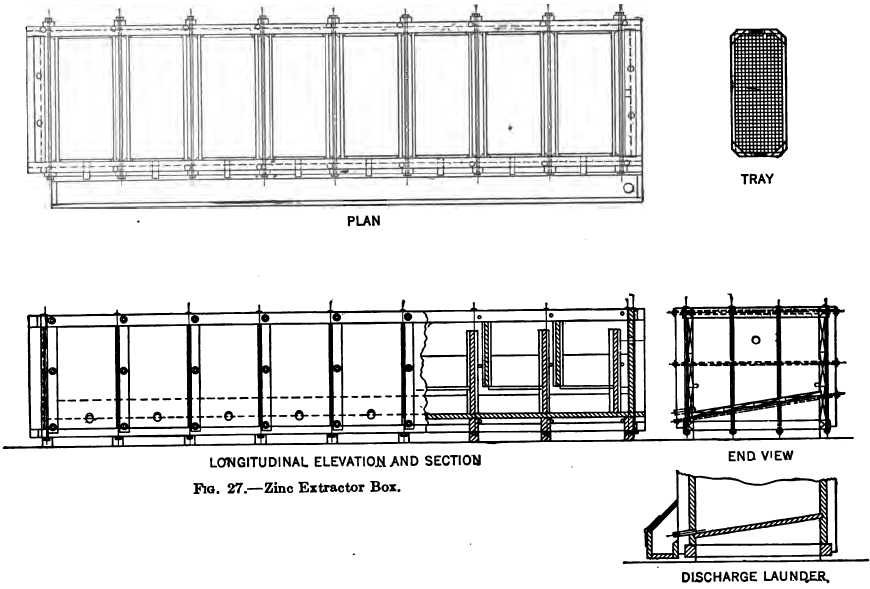
Whatever method of gold precipitation be used it is of great importance that the solution should be absolutely clear and free from suspended matter, and in practice it is almost impossible to obtain solution from slime treatment, either by decantation or by means of the various types of slime filter, that is sufficiently clean to […]
How Arsenic, Antimony Silver Compounds Affects Leaching
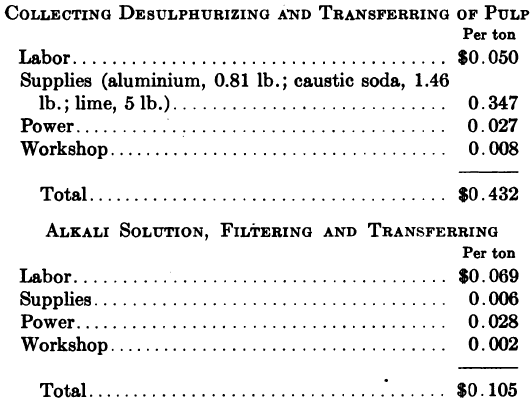
Ores containing silver in Arsenic and Antimony combinations offer considerable difficulties in cyanidation and it has usually been considered that the removal of these compounds by concentration was the only way to deal with them. G. H. Clevenger, however, when working on the ores of the Nipissing Mining Company of Ontario, Canada, found that by […]
Sulphide concentrate leaching

The question as to whether concentration shall be included in the treatment of a given ore will often depend on the possibility or otherwise of recovering the precious metals from the concentrate at the mine. It may be suggested that if the concentrate can be cyanided after being separated from the gangue, why can it not […]
Effect of Manganese on Silver Leaching

In Mexico and elsewhere there are large bodies of valuable silver ore containing manganese which present great, and hitherto insuperable, obstacles to a satisfactory extraction by cyanide. The proportion of the silver that is soluble in cyanide varies greatly and may be as low as 5% only. The mere presence of manganese in the ore […]
How Arsenic Affects Cyanidation Leaching of Gold
The Influence of Arsenic in the Cyanidation of Gold Ores is explained by W. B. Blyth has he is of the opinion that the presence of arsenic in an ore does not necessarily cause that ore to be refractory to cyanide treatment. He thinks the idea arose from the fact that arsenic is so often accompanied by […]
