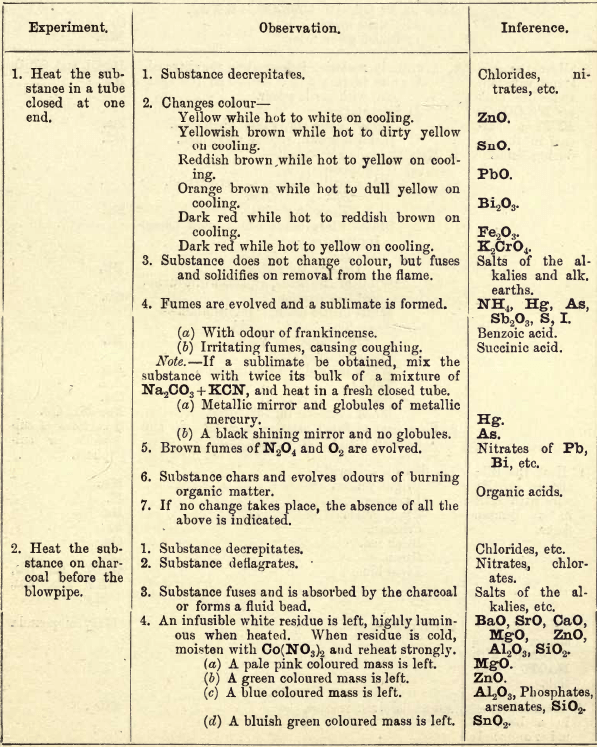
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION FOR ACIDS
Note 1. Do not boil with Na2CO3 unless necessary. If only alkalies are present it is unnecessary. Note 2. If organic acids and Groups I.

Note 1. Do not boil with Na2CO3 unless necessary. If only alkalies are present it is unnecessary. Note 2. If organic acids and Groups I.
Take a few crystals of potassium chlorate (KClO3), place them in a clean dry test-tube, and heat them gently over a small bunsen flame; the salt begins
Our Hydrogen Gas experiment involves taking one or two grams of zinc, put them in a test-tube, and add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid;
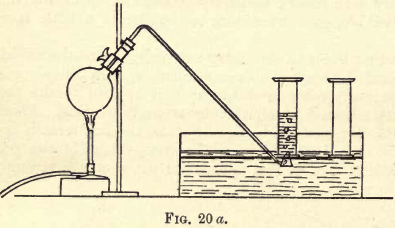
Nitrogen exists in the air, mixed principally with oxygen, so the simplest way to prepare it is to take away the oxygen from the air. Fill
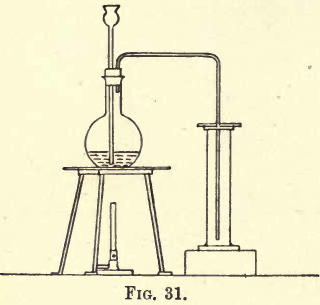
Carbon dioxide is about one and a half times heavier than air, so it can be collected by downward displacement. Fit up a flat-bottomed flask with
Take a glass-stoppered retort with a capacity of about 250 c.c. and a long beak; clean and dry it. Weigh out 25 to 30 grams
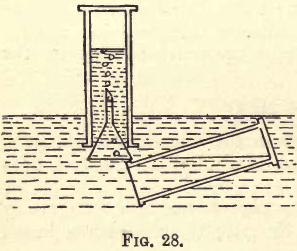
This gas can be prepared from ammonium nitrate, which can be made by neutralising dilute nitric acid with ammonium hydrate. Take some of the nitric
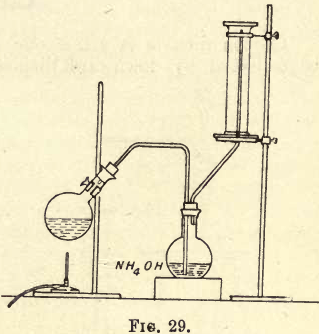
Ammonia Gas is so soluble in water that it cannot be collected as before over water in the pneumatic trough, and as it is lighter than

Take a few crystals of oxalic acid and put them into a dry test-tube, then add a few drops of strong sulphuric acid to them
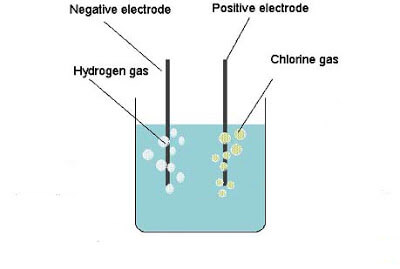
Chlorine is a heavy gas, being about 2½ times heavier than air, so that it can be collected by downward displacement. Weigh out about 30