Milling Methods and Costs
Froth Flotation and its Machines
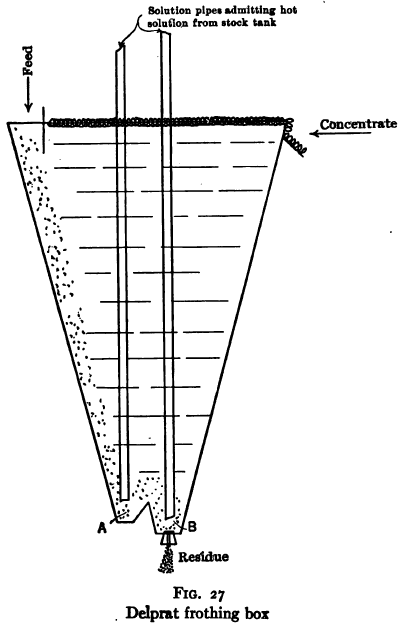
Pulp-body-concentration Processes The Potter and Delprat processes Now combined and known by the name Potter-Delprat process, are described in U. S. patents 735,071, 763,662, 768,035 and 776,145. As at present practiced the dewatered pulp is fed into an apparatus of the type shown in Fig. 27, which is from 10 to 20 ft. deep. Hot sulphuric acid […]
Laboratory Flotation Tests and Plant Results
Translation of laboratory results into terms of plant/mill-scale operations is, in the usual case, less difficult in flotation than in gravity concentration, and in all cases more certain than where chemical reactions such as occur in leaching and precipitation operations are concerned. Any flotation result that can be obtained in a laboratory machine can be obtained […]
Testing Flotation Oils and Frothers
The usual purpose of oil testing in flotation work is to determine that the oil in question is similar in physical properties and therefore probably in its behavior in the flotation cell to a given prior shipment, or in order to set specifications for flotation oil purchase. The following tests will give such information. Color Color is […]
Flotation Process Development in Laboratory
Differential and preferential flotation The pressing problems in differential and preferential flotation of ores are (1) the separation of lead sulphide from zinc sulphide, and (2) the separation of zinc and copper bearing sulphides from sulphides of iron. Methods seeking separation of one sulphide from another by flotation are of two classes, viz.: (1) those in which a difference […]
Metallurgical Testwork for Process Development
Mineralogy & Microscopy Amenability of an ore to flotation is best tested for by a microscopic examination of the ore followed by a few laboratory flotation tests. As stated in Chapter I, most ores containing minerals of metallic, resinous or adamantine luster associated with minerals of earthy, vitreous, or pearly luster, can be divided by froth flotation […]
Flotation Equipment and their Test Procedures
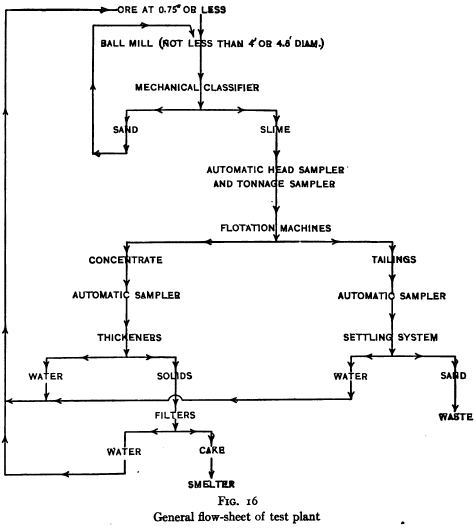
Practice in testing ores for flotation varies, of course, in its detail, from practice in testing work for other purposes, but in this as in other such work certain general principles apply. These principles would seem to be so obvious that they should not need to be enunciated, but the writer has found in going over the results of […]
Laboratory Flotation Equipment & Testing
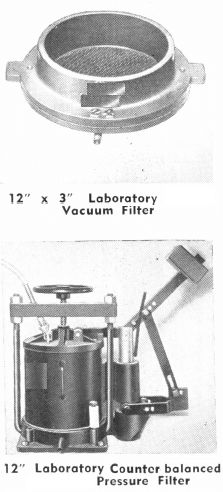
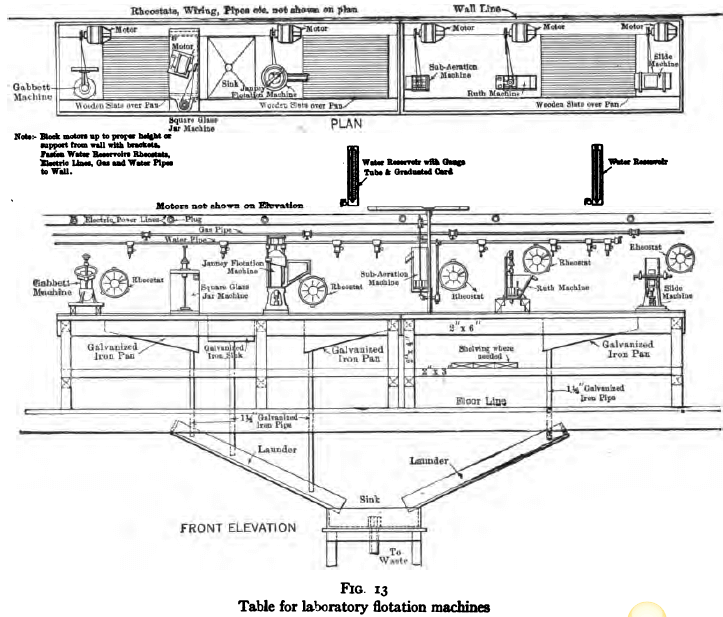
The apparatus listed in the following pages comprises the equipment necessary for complete and thorough testing of flotation processes. Some of it can be omitted where the problems to be studied are of a special character. It is urged, however, that such omission be of the actual flotation machines themselves rather than in the apparatus listed for preliminary […]
Froth Flotation Handbook

What is Flotation Flotation, as the term is applied to ore concentration, means the separation of one of the constituents of an ore from the remainder by causing it to float at or above the surface of a pulp consisting of the finely pulverized ore and water. Minerals that float Minerals that float have a […]
Basic Principles & Variables Affecting Froth Flotation

The basic factors, principles and variables affecting froth flotation are enumerated in condensed form below: Ore. (a) Mineralogical character. (b) Fineness of grinding. (c) Method of grinding. Agents. (a) Principal flotation agent. (“Oil”) α Character. β Quantity. (b) Minor agent. α Character. β Quantity. Water. (a) Quantity with respect to solids, i.e. pulp thickness. (b) […]
